Cell types with pictures (and boom goes the dynamite) Flashcards
Name the function of this cell inicated by the arrow

Function: FIBROBLAST
Key cellular player in repair
Produces interstitial ground substance and fibers
(extracellular matrix)
HOW TO ID: Spindle shaped fibroblasts in a case of nodular fasciitis
Cytoplasm: generally tapered ends, usually sharply pointed,
sometimes bifurcated, sometimes resembling a swallow tail
(Note the fibroblast with bifurcated cytoplasm [blue arrow])
Name this cell (tissue has been associated with radiation)

fibroblast
Two adjacent fibroblasts with prominent
nucleoli in repair response to radiation injury
Name the cell and its function

NEUTROPHILS:
- Polymorphonuclear leukocytes
- First responder phagocytes
- Neutrophils = acute inflammation
- Short-lived (1-2 days)
- Normally 40-70% of the leukocytes measured in the blood
HOW TO ID: Granulocytes with neutral granules (neither blue or red on smear)
variably shaped nuclei, segmented into 2 to 5 lobes
Name the cell

neutrophil (in peripheral blood)
Name the cell and function

Band (immature adolescent
neutrophil)
immature (adolescent) neutrophils,
with partially segmented nuclei
normally <5% of blood leukocytes
Name the cells in this slide

Blood smear:
1-4 = neutrophils
(note the variety of nuclear morphology)
A & B = bands (immature neutrophils)
What are the chronic inflammation players?
Macrophages
Lymphocytes
Plasma cells
Eosinophils
Mast cells
Multinucleated giant cells
Name the cell and its function

MACROPHAGES:
- Phagocytes derived from blood monocytes, who live only a day in blood, but live a long time if recruited to become tissue macrophages
Macrophages = chronic inflammation
HOW TO ID:
Large cells with oval nuclei that may be flattened or even indented on one side, but never segmented, and abundant, variably colored cytoplasm with small subtle granules and vacuoles
Name this cell and function

MONOCYTE
(BLOOD PRECURSOR OF MACROPHAGE)
Name the cell and function

LYMPHOCYTES:
Two types:
T (thymus-derived) lymphocytes
carry out cell-mediated immunity
B (bone marrow-derived) lymphocytes
carry out humeral immunity
HOW TO ID: Usually small cells with small round
dense nuclei and scant cytoplasm
Name the cell

LYMPHOCYTE
in peripheral blood smear
Name the cell and function

PLASMA CELLS:
Derived from activated B cells
Produce large amounts of single-
specificity antibody
HOW TO ID:
- Nuclear chromatin clumped around periphery (“clockface”)
- Prominent perinuclear Golgi apparatus (“hof”)
- Plasma cells with clockface clumps of nuclear chromatin and perinuclear hof (Golgi apparatus)
name the cell and function

Plasma cell
(arrow)
eccentric nucleus
peri- nuclear clearing (“hof”)
Name the cell and function

EOSINOPHILS:
Prominent in many allergic and parasitic diseases
Granulocytes with granules with major basic protein (toxic to parasites, but also host cells)
HOW TO ID: Granules avidly take up red eosin dye
Nuclei frequently have 2 lobes
Eosinophil with typical bi-lobed nucleus
Name the cell and function

EOSINOPHIL in peripheral blood
Name the cell and function

MAST CELLS:
Bone-marrow-derived cells around
blood vessels, nerves and skin
Granules loaded with histamine,
chemotactic factors, proteases, etc.
HOW TO ID:
Granules avidly take up hematoxylin
(blue dye) and other basophilic dyes
Name the cell and function

Mast cell in bone marrow (arrow)
[Giemsa stain]
Name the cell and function

Basophil:
Blood counterpart to mast cell
Name the cell and function

Multinucleated giant cell (arrow)
- Foreign body type (with nuclei
arranged haphazardly) - Langhans type (with nuclei
arranged peripherally)
associated with immune granulomas
What is this an example of? How does it form?

GRANULOMA = AN AGGREGATE
OF ACTIVATED MACROPHAGES
a distinctive form of chronic inflammation associated with autoimmune and infectious diseases such as sarcoidosis
and tuberculosis
THIS SLIDE => Foreign body type granuloma in the wall of the stomach at a gastrostomy feeding tube site
Foreign body: persistent material too large or undigestible for clearance (e.g. suture, talc)
Immune: persistent antigen induces cell-mediated immune reaction (e.g. tuberculosis)
Name the cell
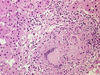
Langhans type multinucleated giant cell
with peripheral nuclei arranged in a horseshoe (semicircle) in a case of tuberculosis
What is this?

1-3: bits of stuff in the foreign body
type granuloma = candidates for
the material eliciting the reaction
What kind of cell is the arrow
pointing at?

What is the most numerous cell type in this picture?




