Cardiovascular system: Lecture 3 - Development of the Cardiovascular System 1 Flashcards
When does the formation of the heart begin?
week 3
What day is the first heart contraction?
Day 22
What are the 3 layers that the heart is composed of?
(from inner to outer)
- Endocardium - derived from the heart tube
- Myocardium - derived from the viscerla mesoderm overlying the heart tube
- Epicardium - this is the visceral layer of the pericardium and is also derived from the visceral mesoderm

What does the myocardium go onto form?
Muscular cells that allow contraction of the heart
What is vasculogenesis?
Making new vessels from scratch
Explain how vasculogenesis works?
- the endoderm induces some cells of the overall visceral mesoderm to differentiate into angioblasts
- angioblasts differentiate into endothelial cells and form endocardial tubes
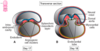
When does embryonic folding begin?
Day 17/18
What do endocardial tubes form when they fuse during lateral folding?
The primitive heart tube

What does the myocardium secrete and why is this important?
The myocardium secretes cardiac jelly which is important in cardiac looping and septation of the heart
How is the developing heart tube brought into the thorax?
Craniocaudaul folding

What does th endocardium and myocardium go on to form?
The internal endothelial lining of the heart and muscular wall respectively
What is the cardiac jelly?
gelatinous connective tissue separating the myocardium and heart tube endocardium
What occurs in the caudaul region during week 4 of embryobic development?
3 paired veins drain into the tubular heart via the right and left horn of the sinus venosus: heart is already beating at this point
(blue branches in image)

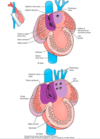
With differential growth of the heart tube, which 5 dilations become apparent?
Truncus arteriosus
Conus arteriosus
Ventricle
Atrium
Sinus venosus
These develop into the adult structures of the heart

Which direction does blood flow through the heart tube?
Bottom to top (caudal to cranial) - from sinous venosus to truncus arteriosus
What happens during day 23?
The heart tube starts to fold in preparation for dividing into 4 chambers
Explain the sequence of events in looping of the heart
- Straight heart tube
- C-shaped loop
- S-shaped loop
Bulbus cordis moves caudally, ventrally and to the right
Primitive ventricle is displaced before moving back to midline
Primitive atrium displaces cranially and dorsally

When does the sinus venosus degenerate?
In week 5
What happens to the remnants of the sinus venosus?
It remains as part of the wall of the right atrium (right horn) and contributes to the venous drainage (left horn) of the heart
What does the left horn of the atrium go on to form?
The left horn forms the oblique vein of the left atrium and coronary sinus

What does the right horn form?
the smooth-walled part of the right atrium – sinus venarum
How can the part of the right atrial wall formed from the right horn be distinguished from the rest of the right atrial wall (the majority)?
As the rest appears rough - trabeculated and was derived from the primitive atrium
What is the crista terminalis?
The clear border between the trabeculated part of the right atrium and the sinus vernarum
Annotate this image (Name the rough parts and the smooth parts)