Cardiovascular strand: Lecture 12 - Coronary Circulation & Tissue Perfusion Flashcards
When does myocardial perfusion occur?
During diastole
Where does most of the energy that the heart uses come from?
Fat
What is the maximum time a heart can remain active after a person dies?
6-12 hours then muscle dies
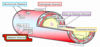
Where are sites of blockages and where are coronary artery bypasses inserted?
saphenous vein is taken from leg (vein graft)
internal mammary artery bypass has been rerouted to the left anterior descending artery (arterial graft)

What is a coronary artery bypass?
Giving blood to heart via a different root, passing the blocking
What does the coronary sinus drain into?
The right atrium
What is the coronary sinus useful for?
resynchronisation pacemaker inserted into left side of heart
Draw two diagrams of an anterior view of coronary arteries and coronary veins

Where does athesclerosis occur?
In the tunica intima (just inside the endothelium) of an artery
What are muscular arteries involved in?
Resistance
How do we calculate pressure?
pressure = flow x resistance
How many RBCs can squeeze through a capillary?
Only one (even has to deform slightly) - single file flow
What is perfusion?
Oxygen, nutrients etc leaving the capillary
Draw and label a diagram of an elastic and musuclar artery

- How are muscle cells in the heart connected?
- What are the structural proteins in the heart that allow the heart to stretch and relax
- intercalated disks
- intercellular collagen network
image is of myocardium capillaries

How does the aorta branch off into smaller arterioles and venules? What is the yellow deposits in the image?
yellow deposits - atherosclerosis (hardening of artery)


Pressure increases during systole
IM - intramyocardium
Draw a graph showing how flow in the coronary arteries is essentially during diastole
A - pressure in aorta
B - flow in LCA
C - flow in RCA
line is less steep i RCA as less blood enters RCA as it is only going to lungs, which requires less than if it were going to heart

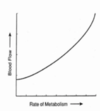
Autoregulation: what is the relationship between blood flow and rate of metabolism?
What substances relax blood vessels (vasodilation)? How can we demonstrate this?
ATP, ADP, AMP, Adenosine, H+, CO2, K+
Place blood pressure cuff on arm - goes red as vessels dilate because theres a build up of waste products causing vasodilation
This is called autoregulation

What happens to coronary arteries if BP drops?
- BP drops
- build up of metabolic substances
- Coronary artery dilates
does the reverse at high BP
What does the green line represent?

Ideal bloodflow
Autoregulation occurs if theres devation from this red line
Heart will adjust resistance on its own to fix flow (local)
How does mean aortic BP, L.Circ coronary flow, cardiac output change during exercise?

Whats your peak heart rate?
200- age