B3 L40: Vascular Surgery Flashcards
What is peripheral vascular disease (PVD)?
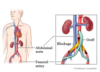
Obstruction of the large arteries that supply blood to the peripheries (outside of the heart and brain). PVD ranges from asymptomatic disease through to limb threatening reduced blood supply.
What is the prevalence of PVD of people over the age of 55?
10-25% of people
Does the risk of PVD increase/decrease with age? Or is it unaffected?
Increases with age
PVD is more prevalent is ___(men/women).
Men
70-80% of people with PVD are _____.
asymptomatic- this means it is highly underdiagnosed
About half of patients with PVD have symptomatic ____ or _____ vascular disease. This means it doesn’t happen in isolation
coronary; cerebral
What are the 11 causes of PVD?
- Atherosclerosis
- Thromboembolism
- Aneurysm
- Inflammatory processes
- Smoking
- Diabetes Mellitus
- Dyslipidemia (high cholesterol)
- Hypertension
- Obesity
- Stroke/CV disease
- Family history of vascular disease
What is atherosclerosis?
Thickening of the artery wall as a result of the accumulation of calcium and fatty materials (cholesterol)
What does the thickening of the artery wall in atherosclerosis lead to?
Leads to reduced elasticity of the artery walls – allows less blood to travel through and increases blood pressure
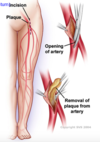
What happens when plaque is deposited in the artery in atherosclerosis?
Plaque deposits can expand and cause blockage of the artery or lead to a thrombus formation, or can break away as an embolus and occlude smaller downstream branches
What is an aneurysm?
Localised blood filled balloon-like bulge (weakness) in the wall of a blood vessel (leading to a possible rupture) – Can be the starting point for a thrombus
What is the problem with an aneurysm?
Can lead to a possible rupture
How do inflammatory processes cause PVD?
leading to stenosis through swelling of the arterial wall
Why is smoking such a high risk factor and cause of PVD?
Smoking causes changes in and damage to the endothelial lining of blood vessels (which are permanent and irreversible), which leads to atherosclerosis
Is smoking a high risk factor/cause for PVD?
Over 80% of patients with PVD are current or exsmokers
Smoking results in earlier onset of symptoms and the severity of PVD _____ (increases/decreases) with the number of cigarettes smoked and number of _____.
increases; years
Why is Diabetes Mellitus a risk factor/cause of PVD?
2-4 times increased risk of PVD by causing endothelial and smooth muscle cell dysfunction (damage) in peripheral arteries
______ account for up to 70% of non-traumatic amputations performed
Diabetics
A known diabetic who smokes runs an approximately 30% risk of ______ within 5 years
amputation
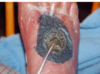
What does diabetes cause (neurally)?
Peripheral neuropathy
What a characteristic of peripheral neuropathy?
lack of sensation to feet
(eg. won’t feel injuries –> infection and lack of healing –> possible amputation)
What is Dyslipidemia?
high cholesterol levels
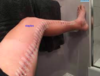
What do people have with chronic PVD?
long standing symptoms
What is claudication?
pain with walking -not getting enough blood to muscles that help with walking