B3 L38 Orthopaedics Inpatients- Common Surgeries of the Upper Limb Flashcards
Inpatient Physiotherapy management of four shoulder surgeries commonly seen on the Orthopaedic Ward. What are they?
- Subacromial Decompression (SAD)
- Rotator Cuff repair
- Shoulder Reconstruction
- Shoulder Arthroplasty
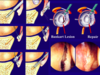
What is a subacromial decompression?
Indicated for Impingement of Rotator Cuff non responsive to conservative Mx

What does a subacromial impingement look like?
Image

What are 2 ways that the subacromial decompression (SAD) can be perfomed?
- arthroscopically
- open (predominantly A/S)
What are 4 things that the subacromial decompression surgery involve?
Clearing of subacromial arch:
- removal of bursa
- coracoacromial ligament,
- reshaping undersurface of the acromion (Acromioplasty)
- Possible- Excision of the lateral 1/3 of the clavicle
What are 3 things that the subacromial decompression surgery does not involve? What does that mean for the patient?
- Disruption or repair of muscle
- Disruption or repair of tendon
- Disruption to the joint
Therefore the patient can commence immediate active movement of the affected shoulder within limits of pain
What is the Post Operative Presentation of a subacromial decompression?
Arm supported in sling for comfort only (removed as soon as able)
Why can the sling be removed as soon as possible post a subacromial decompression?
not protecting any structures (no physiological reason) can impact other surrounding structures eg. sling causes kyphotic spine
What are the 4 procedures to follow the Post Operative management of a subacromial decompression?
- Post operative Respiratory check if required (Circulatory care not a priority as patient will be mobile)
- Day 0-1 may commence - Neck, Scapular (LTs), Elbow, Wrist and Hand movements
- IF there is no muscle, tendon or joint disruption (only a SAD) – may commence active assisted shoulder ROM exercises on Day 1 and progress as tolerated. Exercises are then progressed as pain allows
- Education ++ re sling use, ice for pain relief (+/- No abduction 3-6 weeks depending on Drs orders)
What is the position of the arm that the patient cannot be in for 3-6 weeks post subacromial decompression?
+/- No abduction 3-6 weeks depending on Drs orders
What are the types of slings?

What are 4 characteristics of rotator cuff tears?
- Usually the Supraspinatus Tendon
- Single substantial trauma or micro-trauma over time
- The Supraspinatus tendon can rupture traumatically with associated symptoms or spontaneously without causing acute symptoms.
- With increasing age more people will have torn cuff muscles with or without pain.

A rotator cuff repair Can be performed ______ or ______.
arthroscopically; open
How is rotator cuff repair done? (procedure) How does this affect the patient post op?
- Surgeon will initially perform an arthroscopy of the shoulder to examine the structures involved – can then be converted to open procedure if required
- Disruption or repair of muscle with deltoid split
- Disruption or repair of tendon of rotator cuff
- Therefore the patient cannot commence immediate active movement of the affected shoulder

What is the goal of the rotator cuff repair?
reattach good quality tendon to the bone from which it is torn (good re-attachment point)
If RC is repairable, a ______ or ______ is fashioned in the normal attachment site.________ draw the edge of the tendon securely into the groove to which it is to heal
groove; trough; Sutures
What is the Post Operative Presentation of a rotator cuff repair?
- Arm supported in sling and binder
- Some surgeons use an abduction wedge or abduction brace to maintain abduction whilst the repaired tendon heals (less common over last three to four years) to take the tendon off stretch

What are the 5 procedures to follow the Post Operative management of a rotator cuff repair?
- Post operative Respiratory check if required (Circulatory care not a priority as patient will be mobile)
- Sling on at all times except for exercises usually for 6 weeks (protect structures- remain in abduction)
- Day 1 may commence - Neck, Scapular (LTs), Elbow, Wrist and Hand movements, as well as gentle pendular exercises (gentle pendular exercises are usually classified as passive exercises)
- NO active movements or increasing of shoulder ROM (structures are at risk with contraction) for 6 weeks post op. Patient is usually reviewed by the surgeon at that stage and referred for outpatient physiotherapy to progress the rehabilitation
- Pain relief including ice important in post op management
When are 2 cases where anterior stabilisation (shoulder reconstruction) is needed?
acute dislocation recurrent instability
Over 95% of shoulder dislocations are _______ Dislocation but may also have_______, _______ or ______ dislocations
Anterior; Posterior; Inferior; Multidirectional
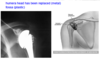
What is the mechanism of injury with an acute shoulder dislocation?
a fall on the outstretched hand.
- Ninety to ninety-five per cent of dislocations are anterior with the head of the humerus being driven forward and externally rotated. The capsule of the joint is usually torn and the glenoid labrum may be avulsed
What is the mechanism of injury with recurrent shoulder instability?
Recurrent instability may result from recurrent dislocations or from repeated activities that stress and subsequently stretch the capsule
What are 4 characteristics of Anteroinferior Glenohumeral Ligament in an anterior stabilisation procedure?
- Originates as a portion of fibrous glenoid labrum anteroinferiorly
- primary restraint to anterior and anteroinferior instability
- avulsion of this complex from the antero inferior glenoid labrum results in a bankart lesion (85% of anterior dislocations)
- IGHL must fail for anterior dislocation to occur as primary restraint to anterior and anteroinferior instability
What is the natural history for Young patients to have re-dislocations?
When the patient’s proximal humeral growth plate is open, there is up to 100% rate of re-dislocation
In young adults, the rate of re-dislocation ranges from 55 to 95%