B3 L37: Fractures of the upper limb and their management Flashcards
(127 cards)
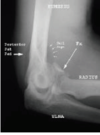
What is the mechanism of injury for clavicle fractures?
Fall onto superolateral aspect shoulder > direct blow to shoulder > FOOSH
What are 4 other injuries which can occur with clavicle fractures (associate EXAM QUESTION
- # scapula
- # ribs – pneumothorax/ haemothorax/ pulmonary contusion
- vascular injuries
- Subclavian artery
- Axillary vessels
- brachial plexus injuries

What is a traction type injury?
head and shoulder go in different directions

What are medial clavicle fractures usually a result of (MOI)?
of high energy blunt trauma such as MVA, MBA, Ped vs car
90% associated with multi trauma

What is the most likely to less likely location that is injured in a clavicle? Why is this the case?
Mid shaft > lateral> medial
- two relatively flat surfaces linked by middle tubular section, area of inherent weakness
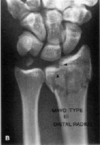
What is the medical management for a medial clavicle fracture?
Medial largely non operative unless posterior displacement that threatens neurovascular structures and skin (risk of injection- complications)
What is the medical management for a middle clavicle fracture?
Middle largely non operative unless significant angulation or shortening
What is the medical management for a lateral clavicle fracture?
Lateral depends on whether conoid segment of coracoclavicular ligament is attached to the medial fragment of the clavicle
What is the medical management for when a ORIF is needed for a clavicle fracture?
ORIF may be indicated if pathological fracture, progressive neurological loss, scapulo- thoracic dissociation, open injury, impending skin disruption
The Position of fracture can affect chance of _____ due to ligamentous structure. Give 2 examples.
healing
- Fracture medial to coracoclavicular ligaments
- Fracture between coraoclavicular ligaments
What are methods of immobilisation for a clavicle fracture?
- Large number of binder applications for fracture immobilisation
- Sling application (eg. figure 8 brace shoulder sling (most common)
What are 2 characteristics of operative treatment for clavicle fractures?
- Plate fixation +/- bone graft preferred method (problems- have screw which loose and burrow to other areas of body (eg. heart))
- Intramedullary nail less rotational control (nail pass down long bone)

What are the 5 important guidelines to follow for clavicle fractures post op?
- 3/52 sling
- gentle active-assist shoulder F and ER in supine (no pendular- due to displacing force of the weight of the arm))
- after 6/52 gentle isometric strengthening with progressive resistance beginning @ 2/12
- light lifting 3/12
- heavy lifting and contact sports restricted until 6/12

What is the mechanism of injury for scapula fractures? List 3 mechanism.
- High energy direct trauma
- Axial loading through fall on outstretched arm
- Dislocation of the shoulder can fracture glenoid
What is the most likely to less likely location that is injured in a scapula?
Body> neck> glenoid > acromion > coracoid
What are 4 signs and symptoms of a scapular fracture?
- Arm held adducted
- local tenderness
- If displaced scap neck or acromial # -> shoulder appears flattened
- deep inspiration - pain from attached muscles
- pec minor - coracoid #
- serratus anterior - body #
- with body #’s - there is deep swelling which is often quite painful -> inhibition RC -> loss of arm elevation - resolves in a few weeks
What are 8 associated injuries in conjunction with scapula fractures?
- pneumothorax
- rib #’s
- pulmonary contusion
- # clavicle
- brachial plexus injury
- arterial injury
- skull #’s and CHI (closed head injuries)
- spinal #’s
What is the complication with an acromial scapula fracture?
decrease subacromial space = pressure on structures that pass through
What is the management of a glenoid fracture (intra-articular), if it is unstable or if the humeral head is unstable?
ORIF and capsular repair
What are the 3 types of acromial fractures?
Type 1
Type 2
Type 3

How is a type 1 acromial fracture classified?
minimally displaced

How is a type 2 acromial fracture classified?
displaced but no reduction in subacromial space

How is a type 3 acromial fracture classified?
displaced with reduction in subacromial space

What are the 2 types of glenoid neck fractures?
- Without associated separation A/C jt or clavicle #
- With above associated injuries