B3 L34 Orthopaedic Inpatient Elective Lower Limb Surgery Flashcards
What are 3 common procedure done for osteoarthritis/rheumatoid arthritis of the hip?
- Primary total hip replacement (THR)
- Revision total hip replacement
- Salvage procedures
What are 4 common procedure done for osteoarthritis and meniscal lesions of the knee?
- Total knee replacement (TKR)
- Uni-compartmental knee replacement (UKR)
- High tibial osteotomy
- Arthroscopy- Washout, meniscal debridement, removal, repair
What is a common procedure done for ligamentous instability of the knee?
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction
What are 2 common procedure done for subluxing/pain patello-femoral joint?
- Lateral Release
- Tibial Tuberosity Transfer
What is common procedure done for toe deformities?
Osteotomy correction for toe deformities (bunion)
What is the goal total hip replacement (THR)?
To attain a durable, painless, functional hip
When was the THR developed? What was the problem with the older version?
- Developed by Charnley in England in the 1950’s
- Original prosthesis metal on metal - poor results due to friction and metal fragments
What is the femoral head made out of (in THR)?
Metal alloy
What is the acetabular cup made out of (in THR)?
Almost frictionless cup
Is there a difference with cement or cementless THR in post-op management?
Same post-op management
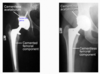
What are the 2 operative approaches of a THR?
- Posterior
- Anterior & Anterior-lateral
What is the most commonly used approach for a THR?
- Most commonly used approach is the posterior operative approach
- However, the anterior and anterior-lateral is becoming more common
What is an advantage of posterior operative approach for a THR?
easier for surgeon
What is a disadvantage of posterior operative approach for a THR?
dislocation a possibility during sitting and excessive hip flexion
What is the dislocation position of posterior operative approach for a THR?
- Flex >90°, adduction past neutral, internal rotation past neutral
- Combined flexion, adduction, internal rotation
What is an advantage of anterior and anterior-lateral operative approach for a THR?
Decreased chance of posterior dislocation as posterior capsule not affected.
What is a disadvantage of anterior and anterior-lateral operative approach for a THR?
more difficult for surgeon
What is the dislocation position of anterior and anterior-lateral operative approach for a THR?
- Forced extension
- Flex or extension with Add and ER
When would use an anterior and anterior-lateral operative approach for a THR instead of the posterior approach?
May be indicated for alcoholics or other patients who may be unable to adhere to routine hip precautions postoperatively.
What are 3 peri-operative complications of a THR?
- Sciatic nerve (posterior approach) damage can lead to short term neuropraxia and subsequent ‘foot drop’. (up to 12 months)
- Poor positioning of acetabular component could increase chance of dislocation.
- Fractured acetabulum; fractured femoral shaft; excessive blood loss.
What are 4 post-operative complication of THR?
- DVT
- Dislocation
- Infection
- Loosening of components
What does a THR dislocation look like? When is the dislocation risk high?
First 3 months (decreases over time)

What is the treatment for a THR dislocation? What position is this in?
Rocket technique- done in the theatre or emergency
Hip and knee flexion (90 degrees) with knee on doctor’s shoulders
What are the 3 goals of a THR in post-operative management?
- Independent mobility w appropriate aid
- Independent with home exercise programme
- Independent mobility on stairs
What are the 5 post-operative presentations of a THR?
- Epidural, PCA, nerve block
- Drips, IDC
- Wound drains
- Abduction wedge, heel wedge
- LL compression device
What are 4 exercises done day 1 of a THR?
- Hip ROM exercises: active/assisted hip flex 90° + abd on powder board.
- Quads exercises inner range.
- Bridging
- Use straight leg raise as LL strength test, but not an strength exercise due to high acetabular pressure.
What are 5 mobility activities done in day 1 of a THR?
- Bed mobility
- Sitting 30min daily. No hip flex > 90°.
- Out of bed on unaffected side
- Uncomplicated surgery > FWB
- Rollator > 4 wheel walker > sticks or crutches
- Walking aid fitting
What is a sitting activity done in day 1 of a THR?
Allowed Day 1-2, 30 minutes initially, dependant on pts symptoms
What are 2 exercises done in day 2 until discharge of a THR?
- Progress ROM & strength functionally (e.g. standing hip/knee flex/ext, abd, mini squats etc.)
- Balance exercises
What are 2 mobility activities done in day 2 until discharge of a THR?
- More WB, rely less on UL.
- Rollator > 4 wheel walker > sticks or crutches > stairs
Advice and education is very important for discharge. What are 8 hip precautions which should be adhered to lifelong (strictly for first 3 months)?
- Avoid combination of dislocating positions
- Do not sit in low chairs
- Do not cross legs
- Do not lie on affected side
- Do not squat down to ground
- Do not bend from hips to pick things up
- No twisting on the affected leg in standing
- No driving first 6/52 until cleared by Drs
Advice and education is very important for discharge. What are 4 considerations for discharge planning?
- Aim for discharge day 3-5
- Occupational Therapy review for ADLs before discharge. Home environment eg bathroom rails, raised toilet seat etc
- Home Exercise Program handout
- Consider Physiotherapy - Home physio or outpatients appointment
What is a revision THR?
- Failed or loose prosthesis is removed and replaced by new prosthesis
- Staged (septic- infection) vs 1 op (aseptic- might only replace one part)
- Remove old hip –> spacer (insert) –> leave spacer –> take spacer out –> new hip added (after infection subsided)
What is an example of a salvage procedure (for THR)? What positions is the arthrodesis?
- Excision arthroplasty - Girdlestone’s
- Arthrodesis - fusion in a position of:
- 15-20 degrees flexion
- neutral abduction and rotation.

What is Birmingham’s Hip Resurfacing?
‘Resurfacing’ the bone with metal surfaces

What does a BHR look like on an x ray?

What is an arthroscopy?
Performed through small portals to allow an irrigation cannula, a fibre optic viewer and light source, and surgical instruments into the joint.
What are the 4 uses of an arthroscopic knee surgery?
- To establish or define accuracy of diagnosis
- Help decision making and planning of surgery
- Observe and record progression of knee joint disorder
- Perform operative procedures
What are the 2 advantages of an arthroscopic knee surgery?
- Rapid recovery
- No hospitalisation and no or limited need for walking aides
What are 4 procedures of arthroscopic knee surgery?
- Menisectomy
- Meniscal repair
- Chondroplasty
- Ligament repair and replacement
What is a menisectomy?
loose fragment excised, flap or oblique tear
How should a menisectomy be managed?
FWB, rapid rehabilitation including ROM ex’s, SLR, IRQ, limit walking to manage swelling
What is a meniscal repair?
only if located in periphery of meniscus as adequate blood supply for healing
How should a meniscal repair be managed?
Mobilised NWB crutches, other rehabilitation as above
What is an advantage of a meniscal repair?
by retaining some meniscal integrity aim for reduction in incidence of degenerative joint changes that commonly occur following a total menisectomy
What is a chondroplasty?
surgery of the cartilage
What is an example of a ligament repair/replacement?
Anterior Cruciate Ligament reconstruction
How should a ligament repair/replacement be managed?
Dr dependent
What are the 3 ways a patella can be realigned?
- Tibial tuberosity transfer
- Lateral release
- Medial plication
What is tibial tuberosity transfer (patella realignment)?
Surgically moving the tibial tuberosity medially
What is lateral release (patella realignment)?
- Used in isolation or as adjunct to other procedures
- Releases tight Lateral Retinaculum and Vastus Lateralis
- May be performed arthroscopically or as open procedure
What is medial plication (patella realignment)?
- ‘Plication’ is the folding in & suturing of tucks
- Tightening of medial structures
What are 4 ways to manage patella realignment surgery?
- Immobilised in extension in Richard’s Splint for 6 weeks
- No active Flexion (interrupted quad attachment), Extension or SLR for up to 6/52
- Only Knee or quads exercise - static quads
- Generally WBAT
What are 2 ways to manage a lateral release without tibual tuberosity transfer?
- Early activation of quads and ROM exercises
- Mobilise FWB and progress exercises as pain and swelling allow
What is the aim of a high tibial osteotomy?
To divide the bone and reposition the fragments to realign the tibia and distribute weight bearing forces more evenly through the knee
What are the 3 advantages of a high tibial osteotomy?
- Does not destroy articular cartilage as tibio-femoral joint not directly operated on
- Can progress later to TKR (delay)
- Reduces OA pain
What are the 3 disadvantages of a high tibial osteotomy?
- Causes considerable discomfort and long period of rehab
- Not a cure for OA but may slow deterioration
- Symptoms may reoccur
When would a high tibial osteotomy be used?
Option to prolonge the need for a knee replacement (to leave as late as possible- has knee replacements only last 20 years- and need revision after that)
What are 8 factors associated with favourable results in a high tibial osteotomy?
- < 65 years of age or ‘long life expectancy’
- Not overweight (risk of failure/recurrence of deformity if overweight)
- 90 degrees flexion
- < 15 degrees flexion contracture
- Higher activity level (HTO instead of TKR)
- Early uni-compartmental OA with corresponding varus or valgus deformity
- Ligamentous stability
- Non- smoker (high rates of complication with smoker)
What are 2 ways the high tibial osteotomy can be done?
To correct a varus deformity
- Closing wedge deformity
- Opening wedge deformity
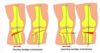
What are 4 activities for post-operative management in a high tibial osteotomy?
- Commence circulo-respiratory exercises day 0
- Commence rehab exercises day 1
- May SLR in Richard’s splint
- If staple fixation - no knee flexion 4-6 weeks
- If plate / screws fixation - may commence gentle knee flexion day 1 or 2
- Mobilise day 1 - NWB with Richard’s splint
- Management can vary dependent on Dr
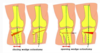
What are 4 features of a total knee replacement (TKR)?
- Femoral component
- Tibial component
- Polyethylene spacer
- Gold standard for treatment of severe OA

What does a TKR look like on an x ray?

What are 5 complications of a TKR?
- Fracture
- DVT
- Infection
- Loosening of components
- Ongoing knee pain
What are 5 goals of a TKR for post-operative management?
- Knee Flexion >/= 90 degrees
- Knee extension 0 degrees
- SLR
- Independence with HEP
- Independent mobility on stairs
What are 3 post-operative presentations of a TKR?
- Epidural, PCA, local infiltrates, pain busters, regional nerve blocks
- Drips, IDC
- Wound drains
What are 4 exercises that are done on day 1 as post-operative management for a TKR?
- Commence Circulo-Respiratory exercises Day 0
- Commence quads exercises Day 1
- Active/assisted knee flexion – aiming for 90 degrees
- Inner Range Quads (IRQ), Straight Leg Raise (SLR)

What are 4 mobility activities that are done on day 1 as post-operative management for a TKR?
- Routine uncomplicated TKR will be FWB
- Day 1 – aim to mobilise
- Out of bed on un-affected side
- Rollator initially progressing to 4ww, 2 x SPS as able
What is a sitting activity that are done on day 1 as post-operative management for a TKR?
Allowed Day 1-2, 30 minutes initially, dependant on pts symptoms
What are 4 activities that need to be done on day 2 until discharge as post-operative management for a TKR?
- Swelling management (very important) POLICE
- Don’t SOOB for too long
- Elevation and compression with ice, polar pack, cryo-cuff
- Continue quads rehab – aim for SLR with minimal lag
- Graded knee flexion aiming for 90 (Don’t do too much if swelling a problem!)
- eg. 90° flexion D1 while drain in, 70° D2, 80° D3, 90° D4
- Gait re-education with appropriate aid
- Progress rollator to 4ww to sticks/crutches

What are 4 criteria for discharge for a TKR?
- Independent mobility including stairs with appropriate aid
- Knee flexion >80 degrees
- SLR with minimal quadriceps ‘lag’ (<5 degrees)
- Independent H.E.P.
What are 3 considerations for discharge (D/C) planning for a TKR?
- Aim for DC within 3-5 days
- Provision of HEP
- Follow-up physiotherapy
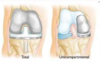
What is a compartmental knee replacement? Compare to a TKR.
Procedure similar to TKR, however only one compartment is replaced.

What are 3 characteristics of a compartment knee replacement?
- Other compartment must be healthy.
- Rehabilitation can be quicker than TKR
- Aim up to 120° flexion

What is an indicator for a ACL reconstruction?
Significant functional disability due to instability

What are 3 options for intra-articular reconstructions?
- Synthetic Grafts (LARS)
- Allografts (Cadaver)
- Autografts (Hamstrings, patella tendon)
What are synthetic grafts?
- There is great appeal for using synthetic grafts to replace a torn ACL
- Several synthetic ligaments have come and gone but none have met the qualifications needed for a lasting ACL substitute
- Examples have included Dacron, carbon fibre and Gortex grafts
What is a LARS (synthetic grafts)?
- Quicker return to function, sport
- Currently the AOA recommends against the use of LARS due to poor outcomes and high failure rates
What are 3 advantages of allografts?
- No donor site pathology
- Shorter op
- Eventually fully replaced by new tissue
What are 2 disadvantages of allografts?
- Graft rejection
- Allograft ruptures - especially using grafts from older donors (>30-35 yrs a risk factor)
What are 2 examples of when autografts are used?
- Patella Tendon
- Bone-Patella Tendon
- Hamstring
- Gracillis, Semitendinosis Graft

What is an advantage of a hamstring (auto)graft?
Good graft strength and no anterior knee pain
What is an disadvantage of a hamstring (auto)graft?
Evidence of elastic creep in graft due to poorly-aligned collagen fibres. This may produce a slightly lax graft
What are 3 advantage of a patellar tendon (auto)graft?
- Strong
- Biological
- Eventually replaced by new tissue
What are 2 disadvantage of a patellar tendon (auto)graft?
- Anterior knee pain
- Donor site pathology
What is the procedure for a toe deformity surgery?
Example of Osteotomy of 1st Metatarsus Valgus

What is the management for toe deformity surgery?
- Patient mobilised with surgical shoe (HWB)
- Walking aid not essential but may require a stick or crutches depending on balance and pain
What is a mobility activity done in day 0 until discharge of a THR?
Mobilise on the day of surgery as soon as motor & sensory functions return. Will reduce length of stay and complications.
What is an exercise done day 0 of a THR?
Circulatory-respiratory exercises


