B3 L35: Pelvic & Acetabular Fractures Flashcards
What are 5 functions of the pelvis?
- provide stability
- allow us to walk
- support in sitting
- large stable base of support (BOS)
- provide protection for all pelvic and abdominal structures (intestine, colon)

Is there a large or small amount of movement (nutation or counter-nutation) of the pelvis (sacroiliac joint)? What is the degree of movement?
Small amount of movement
2-3 degrees

Where is the pelvis mostly reinforced? Why?
Reinforced by ligaments, muscles POSTERIORLY
This is because this is where most force goes through (when WB)

What are the 3 parts of the bone that make up the coxa? Which part takes most the the weight during sitting?
- Ischium
- Pubis
- Ilium
What happens when there is a fracture of the pelvis? Be specific (2).
- Loss of stability
- Vertical instability (do not WB, flex/ext is fine) Rotational instability
What is the Young-Burgess system for pelvic fractures?
Classification system based on direction of force
What are the 4 classifications of a pelvis fracture in the Young-Burgess system?
- AP compression (APC)
- Lateral compression (LC)
- Vertical shear (VS)
- Combination
What are 2 features that AP compression (Young-Burgess system) fracture classified by?
- pubic diastases
- vertical #’s of pubic rami
What is the AP compression (Young-Burgess system) fracture caused by? Give 2 examples.
Caused by frontal collision (A-P force)
- Car vs pedestrian
- MB vs pole
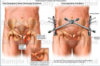
What happens in an AP compression (Young-Burgess system) fracture? Where are 3 features of seperation/fracture?
- Hemipelvis bones seperated (due to direction)
- separation at pubic symphysis (PS), SIJ
- fracture through pubic rami
What are the 3 severity classifications (Young-Burgess system) of an AP compression pelvis fracture?
- APC 1
- APC 2
- APC 3
What are 3 characteristics of an APC 1 (pelvis fracture) based on the Young-Burgess system?
- Less than 2.5 cm of pubic diastases either at the symphysis or through vertically oriented rami fractures
- SI joints and posterior ligaments remain intact
- Stability is maintained (still have both vertical and rotational stability and no much restrictions)

How should an APC 1 (pelvis fracture) based on the Young-Burgess system be managed?
Conservatively

What are 4 characteristics of an APC 2 (pelvis fracture) based on the Young-Burgess system?
- Pubic diastases exceeds 2.5 cm
- Divergent SIJ widening
- Posterior ligaments disrupted except post SI ligament
- Rotationally unstable (which can cause further separation), vertically stable

What are 3 characteristics of an APC 3 (pelvis fracture) based on the Young-Burgess system?
- Uniform SIJ widening (>2.5cm)
- Complete posterior ligament disruption
- Vertically and rotationally unstable

In an AP compression pelvic fracture, what is the pubic diastasis in an APC 1,2 and 3?
APC 1: <2.5cm
APC 2: >2.5cm
APC 3: >2.5cm
In an AP compression pelvic fracture, are the posterior ligaments intact or disrupted in an APC 1,2 and 3?
APC 1: Intact
APC 2: Disrupted
APC 3: Disrupted
In an AP compression pelvic fracture, are the SIJ ligaments intact or disrupted in an APC 1,2 and 3?
APC 1: Intact
APC 2: Intact
APC 3: Disrupted
In an AP compression pelvic fracture, is the fracture stable in an APC 1,2 and 3? Be specific with vertical and rotational stability.
APC 1: Yes
APC 2: vertical- yes; rotational- no
APC 3: vertical- no; rotational- no
What are 2 features that lateral compression (Young-Burgess system) fracture classified by?
- horizontal pubic rami #’s
- locked symphasis
What is the AP compression (Young-Burgess system) fracture caused by? Give 2 examples.
Side on road accident or fall from height onto side
What are the 3 severity classifications (Young-Burgess system) of a lateral compression pelvis fracture?
- LC 1
- LC 2
- LC 3
What are 4 characteristics of a LC 1 (pelvis fracture) based on the Young-Burgess system?
- Ipsilateral anterior sacral impaction
- Ipsilateral horizontal pubic rami # (compressive force on SIJ = no contralateral effect)
- Posterior ligaments
- Pelvis stable

What are 4 characteristics of a LC 2 (pelvis fracture) based on the Young-Burgess system?
- Ipsilateral anterior sacral impaction
- Ipsilateral horizontal pubic rami fracture
- Ipsilateral fracture of iliac wing
- Pelvis rotationally unstable (flex/ext is not fine), vertically stable (WB is fine)