Audiology Flashcards

R Masked air conduction threshold

Right no response

R masked bone conduction threshold

R Air Conduction Threshold
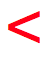
R bone conduction threshold

L air conduction threshold

L bone conduction threshold

L masked bone conduction threshold

L no response

L masked air conduction theshold
A) What type of hearing loss is this?
B) How do you know?
C) Etiology and site of lesion?
D) What phonemes are effected?
E) How and why?

A) Sensorineural hearing loss
B) You know bc bone and air conduction thresholds are similar
C) Etiology: Occurs when there is damage to the hair cells. Site of lesion: cochlea or 8th cranial nerve
D)
A) What type of hearing loss is this?
B) How do you know?
C) Etiology and site of lesion?
D) What phonemes are effected?
E) How and why?

A) Mixed
B) It looks like a sensorineural hearing loss in that both thresholds are about the same, but there is a notch at 4000 Hz - the hallmark of noise-induced hearing loss
C) Etiology: Prolonged exposure to loud sounds. Site of lesion is in the cochlea.
D)
E)
A) What type of hearing loss is this?
B) How do you know?
C) Etiology and site of lesion?
D) What phonemes are effected?
E) How and why?

A) This is conductive hearing loss
B) You can tell bc there is a gap between thresholds. Air conduction will necessarily be lower than bone conduction. This is why it is important to memorize the symbols and what they mean. Remember this by analyzing the name of the loss: *conductive*.
C) Etiology: Damage to the outer or middle ear resulting in inefficiency xferring sound. E.g.: Otitis media.
D) Mild to moderate hearing loss affecting the right ear. Will have difficulty hearing sounds: /b, d, n, a, l, r, o/
What is the range for:
a) mild hearing loss:
b) moderate hearing loss:
c) Moderate-severe hearing loss:
d) severe hearing loss:
e) profound hearing loss:
What does dBh mean?
a) mild hearing loss: 26-40 dBh
b) moderate hearing loss: 41-55 dBh
c) Moderate-severe hearing loss: 56-70 dBh
d) severe hearing loss: 71-90 dBh
e) profound hearing loss: 91+ dBh
dBh indicates that the person heard the target frequency ≥ 50% of the time
A) What frequencies will a person with sensorineural hearing loss have difficulty hearing most?
B) What frequencies will a person with conductive hearing loss have difficulty hearing most?
A) High frequencies
B) This will depend on how severe their loss is because a person with conductive hearing loss will have difficulty receiving all sounds do to structural/mechanical anomalies. They may have difficulty hearing all sounds.


