ANS , Endocrine System And Glucose Homeostasis Flashcards
What part(s) of the brain is/are associated with the ANS?
Pons
Medulla
(Lower centres of thinking, primitive/intrinsic responses)
What nerve controls the majority of the organs?
Vagus nerve
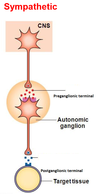

What neurotransmitter is used in parasympathetic postganglionic terminals as opposed to norepinephrine (noradrenaline) in the sympathetic nervous system?
Acetycholine
Acetylcholine is used as a neurotransmitter in both the SNS and PNS in preganglionic terminals, what receptor does it act on?
Nicotinic receptors
What is the receptor for ACh (from the postganglonic parasympathetic terminal) in the target tissue?
Muscarinic receptors
What receptors are on the target tissue for the SNS?
Adrenergic receptors
What neurons stimulates the release of adrenaline from the adrenal gland?
Sympathetic preganglionic
What is the effect of α1 and ß1 receptors on their target tissue?
Stimulation
α1 - blood vessels of smooth muscle
ß1 - heart
What neurotransmitter/endocrine acts on α receptors most strongly?
Norepineprhine/noradrenaline
What kind of receptors are most common of α and ß?
α
What receptor responds to both noradrenaline and adrenaline equally?
ß1 receptors
What receptor responds most strongly to adrenaline?
ß2 receptors
What division of the ANS contains adrenergic receptors?
Sympathetic
What target tissue do α2 and ß2 receptors inhibit?
α2 - gut and pancreas
ß2 - blood vessels of heart, liver, skeletal muscle and bronchiole smooth muscle
What controls a generalised sympathetic response?
Hypothalamus
What is different between an exocrine and an endocrine?
An exocrine is released into a duct then lumen of an organ
An endocrine is released into the blood
What are characteristics of a steroid hormone?
Insoluble
Long half-life
Diffuses or binds to cell membrane, nucleus or cytoplasmic receptor
Slow response
What are characteristics of protein hormones?
Soluble
Short half-life
Binds to receptor on cell membrane
Rapid response
The catabolic state takes ___ components and converts it to ____
Cellular
Energy
Insulin is secreted pancreatic ___ cells
Beta
____ spikes before a meal and insulin spikes after
Glucagon
Excess glucose undergoes ___ to form glycogen or is passed as urine
in ___
Glycogenesis
Diabetics
Fats are first broken down into ____ ___ acids and ____ and some is converted into fat stores by ___
Free fatty
Glycerol
Lipogenesis


