Anatomical Terminology (Pt. 3) Flashcards
Viscera
The body’s internal organs
Cranial Cavity
- Dorsal cavity
- Lies inside skull and contains the brian
- Brain is protected by membrane sac called the meninges.
Spinal Cavity
- Dorsal Cavity
- Formed by canal through vertebrae
- Contains the spinal cord
- Spinal cord is protected by the meninges
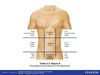
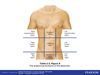
Thoracic Cavity
- Superior of two ventral cavities
- Found enclosed by ribs and separated from abdominopelvic cavity by diaphragm muscle
- Contains organs such as the lungs, heart, esophagus, trachea, aorta, thymus gland.
Into how many regions can the thoracic cavity be divided?
It can be subdivided into one central and two side regions:
- Mediastinum
- Pleural Cavities
Mediastinum
- Central Region
- Contains the heart, trachae, esophagus, aorta, and thymus gland.
- Heart is encased in the pericardial sac.
Pleural Cavities
- Side regions
- Each contains a lung
- Sac protecting lungs is called the pleura
Abdominopelvic Cavity
- Inferior of two ventral cavities
- Large cavity generally subdivided into abdominal and pelvic cavities
- However, no clear structure indicating where one cavity stops and the other begins
- Organs of the abdominopelvic cavity are protected by membrane covering called the peritoneum.
Abdominal Cavity
Houses the stomach, liver, gallbladder, spleen, pancreas and portions of colon and intestine.
Pelvic Cavity
- Contains the urinary bladder, ureters, urethra, and portions of colon and instestine in both genders
- In females also contains the uterus ovaries, fallopian tubes, and vagina
- In males also contains the prostate gland, seminal vesicles, bulbourethral gland, and portion of the vas deferens
What is unique about the anatomical positioning of the kidneys?
The only major abdominopelvic organs that lie outside of the peritoneum are the kidneys. These organs lie along either side of the vertebral column just under the lower ribs. Because they lie behind the peritoneum, their position is called retroperitoneal (retro- = behind).
Clinical vs. Anatomical Divisions (Abdominopelvic)
- If using clinical, then it is divided into four regions.
- If using anatomical, then it is divided into nine regions.
Clinical Divisions

Anatomical Divisions

Right Upper Quadrant
*

Right Lower Quadrant

Left Upper Quadrant

Left Lower Quadrant

Right Hypochondriac
Right lateral side of upper row under lower ribs that are connected to the sternum by cartilage.

Epigastric
Middle area of upper row overlying stomach

Left Hypochondriac
Left lateral side of upper row

Right Lumbar
Right lateral side of middle row near waist

Umbilical
Middle area of middle row containing navel (also called umbilicus)

Left Lumbar
Left lateral side of upper row