Acid/base Flashcards
(12 cards)
describe the effects of respiration on pH
- HYPOventilation results in: RESPIRATORY ACIDOSIS
–> Increased pCO2 which results in Increased H2CO3 and increase H+
–> DECREASED pH
- HYPERventilation results in: RESPIRATORY ALKALOSIS
–> Decreased pCO2 which results in decrease H2CO3 and decreased H+ conc
–> INCREASED pH

respiratory and metabolic effect changes in what?
- Respiratory imbalances –> changes in pCO2
- Metabolic imbalances –> changes in HCO3-
describe compensation of acid-base imbalances
- with compensated acid-base imbalances:
–> ratio of HCO3- to dissolved CO2 can be normal or close to normal, but ABSOLUTE VALUES of dissolved CO2 and HCO3- both may be abnormal
–> body maintains the ratio of HCO3-/CO2

describe graphically the effects of Hypoventilation and hyperventilation on the bicarbonate buffer system
Respiratory acidosis = line A –> D (Hypoventilation)
Respiratory alkalosis = line A –> E (Hyperventilation)
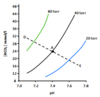
describe respiratory acidosis
- HYPOventilation –> increased pCO2
- point on normal buffer slope below pH 7.4

Describe respiratory alkalosis
- HYPERventilation –> decreased pCO2
- point on normal buffer slope above pH 7.4

describe metabolic acidosis
- loss of HCO3-
- point on 40 torr isobar below pH 7.4

describe Metabolic alkalosis
- increase in HCO3- concentration
- Point on 40 torr isobar above pH 7.4

describe the compensation of metabolic acidosis
- the body compensates through INCREASED VENTILATION –> pCO2 is DECREASED and the pH INCREASES
- renal compensation also involved: secretion of acid urine and increased HCO3-
- Point B moves to Point C
describe compensation of respiratory acidosis
- Respiratory acidosis
–> hypoventilation causes an increase in pCO2 that drives an increase in H+ and bicarbonate from dissociation of resulting H2CO3 (point A to B)
- compensates via kidney
–> kidneys act ot increase plasma HCO3- conc (point B to C)
- renal conc is slow and takes days

describe respiratory alkalosis compensation
- respiratory alkalosis
–> hyperventilation causes a decrease in pCO2 resulting in increased pH (less dissolved CO2, so less H2CO3) (point A to B)
- compensation via kidneys
–> kidneys excret HCO3- resulting in pH returns to a value closer to normal (Point B to C)

describe compensation for metabolic alkalosis
- Metabolic alkalosis
–> bicarbonate is increased (A to B)
- conpensation via HYPOVENTILATION
–> point B moves to point C
–> kidney can compensate through secretion of HCO3-



