(7) [CPA] Upper and Lower Extremity Counterstrain Flashcards
What are the steps for counterstrain?

Where is the tensor fasciae latae?

How do you treat the lateral trochanter (tensor fasciae latae)?

Pt. position = supine or prone
Doc = ipsilateral to TP
Positioning = pt.s knee is ABDUCTED and slightly FLEXED

Where is the liotibial band?

How do you treat the lateral trochanter (IT band)?
Pt position = supine or prone
Doc = ipsilateral to TP
Positioning = pt’s hip/thigh is ABDUCTED and slightly FLEXED until the tenderness is less than or equal to 70% reduction

Where are the lateral hamstring TPs?
Distal aspect of the biceps femoris near attachment to the posterolateral surface of the fibular head

How do you treat lateral hamstring TPs?
Pt position = supine or prone
Doc = ipsilateral to TP
Positioning = pt/s knee is FLEXED and TIBIA is EXTERNALLY ROTATED with slight abduction; compression on the calcaneus is added to plantar flex the ankle

Where are the medial hamstring TPs?

How do you treat medial hamstring TPs?
Pt position = supine or prone
Doc = ipsilateral to TP, grasp lateral ankle/foot to control the lower leg
Positioning = pt.s knee is FLEXED and the tibia is INTERALLY ROTATED with slight ADDUCTION; compression on the calcaneus is added to plantar flex the ankle

What is the quick and dirty medial hamstring treatment?
F IR ADd
Summary slide of all the treatments covered so far:
Latearl trochanter (tensor fasciae latae)
IT band
Lateral hamstring
Medial hamstring

Quick and dirty treatment for:
IT band
f ABD
Quick and dirty treatment for:
Latearl hamstring TP
F ER ABd
Quick and dirty treatment for:
Medial hamstring
F IR ADd
How do you treat lateral meniscus/Lateral (fibular) collateral ligament?
Pt position = supine
Doc = ipsilateral, seated
Positioning = Pts thigh is ABDUCTED so leg is off table, FLEX KNEE 35-40 degrees, tibia is abducted and extrenally or internally rotated until tenderness is reduced by at least 70%

How do you treat the medial meniscus/medial (tibial) collateral ligament?
Pt position = supine
Doc = ipsilateral, seated
Positioning = pts thigh is ABDUCTED so leg is off table, flex knee 35-40 degrees, tibia is adducted and internally rotated until the tenderness is reduced by more than 70%

How do you treat anterior cruciate?
Pt position = supine
Doc = ipsilateral
Positioning = TOWEL/PILLOW under distal femur for fulcrum, apply force to PROXIMAL TIBIA to translate tibia posteriorly on distal femur until tenderness is reduced by 70%

How do you treat posterior cruciate ligament?
Pt position = supine
Doc = ipsilateral
Positioning = TOWEL/PILLOW under proximal tibia for fulcrum, apply force to distal femur to translate femur posteriorly on proximal tibia until the tenderness is reduced by 70%

Where is the popliteus m.?
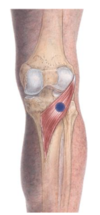
How do you treat the popliteus m.?
Pt position = prone
Doc = ipsilateral
Positioning = pts KNEE FLEXED and TIBIA INTERNALLY ROTATED until the tenderness is reduced by 70% or more

How do you treat extension ankle (gastrocnemius)?
Pt position = prone
Doc = ipsilateral
Positioning = pts KNEE FLEXED and DORSUM OF FOOT on doc’s thigh, add a COMPRESSIVE FORCE through calcaneus until the tenderness is reduced by 70%

Review slide of treatments

Where are the TPs for tibialis anterior?

How do you treat medial ankle (tibialis anterior): inversion TP?
Pt position = LATERAL RECUMBENT with PILLOW UNDER AFFECTED LEG
Positioning= Apply INVERSION force to foot and ankle with slight internal rotation until the tendernes is reduced by at least 70%

How do you treat lateral ankle EVERSION?
Pt position = lateral recumbent w/ PILLOW UNDER AFFECTED LEG
Positioning = Apply EVERSION force to foot and ankle w/ slight EXTERNAL ROTATION until the tenderness is reduced by 70%
Where the flexion calcaneus TP?

How do you treat flexion calcaneus (quadratus plantae)?
Pt: Supine or prone
Doc : Ipsilateral to TP
Positioning : pts knee is FLEXED, dorsum of foot on doc’s thigh, marked FLEXION while translating calcaneus toward the forefoot until the tenderness is reduced by at least 70%
Where is the navicular?

Where is the supraspinatus m.?

How do you treat the supraspinatous m. TP?
Pt position = supine
Doc = ipsilateral to TP
Positioning = pt.s arm is FLEXED 45 degrees, ABDUCTED 45 degrees, and ER until the tenderness is reduced by at least 70%

Where is the infraspinatus m.?

How do you treat the infraspinatous m. TP?
Pt position = supine
Doc = Ipsilaterl to TP
Positioning = pts arm is FLEXED 90-120 degrees and ABDUCTED

How do you treat the lower infraspinatus m. TP?
F Abd ER
Pt position = Lateral recumbent (TP up)
Doc = in front or behind pt
Positioning = pts arm is FLEXED 135-150 degrees, ABDUCTED, and ER to fine tune

Where is levator scapulae m.?

How do you treat levator scapulae?
IR Abd traction
pt position= prone, head rotated away
doc= ipsilateral to TP
Positioning = INTERNAL ROTATION of pts shoulder, add mild-mod TRACTION w/ minimal abduction

Where are the rhomboid m.s?

How do you treat rhomboid minor/major?
E Add
pt position= seated/prone
Doc = either side
Positioning = pts shoulder is EXTENDED ADDUCTED by pulling elbow POSTERIOR/MEDIAL

Where is the subscapularis m.?

How do you treat subscapularis TP?
E IR
Pt position = supine
Doc= seated ipsilateral
Positioning = pts shoulder is EXTENDED and INTERNALLY ROTATED, traction can help

Where is the long head of the biceps brachii?

How do you treat biceps brachii (long head)?
F ABd IR
Pt position = supine
Doc = ipsilateral
Positioning = Elbow and shoulder are FLEXED, arm is minimally abducted and internally rotated
Where is the short head of biceps brachii?

How do you treat the short head of biceps brachii?
Pt position = supine
Doc = ipsilateral
Positioning = elbow and shoulder FLEXED and arm is minimally abducted and internally rotated

Where is pectoralis minor m.?

How do you treat pectoralis minor m.?
Pt position = supine
Doc = ipsilateral
Positioning = pts arm accross chest, shoulder/scapula pulled ANTERIOR, INFERIOR and MEDIAL to shorten fibers

Where is the radial head/lateral (supinator)?

How do you treat the radial head?
Pt position = supine
Doc = ipsilateral
Positioning = pts elbow in FULL EXTENSION, forearm markedly SUPINATED

Where is the pronator teres m. TP?

How do you treat medial epicondyle (pronator teres)?
F PRO Add
Pt position = supine
Doc = ipsilateral
Positioning = pts elbow is FLEXED, marked PRONATION, forearm slightly ADducted

Where is the extensor carpi radialis?
Dorsal wrist

How do you treat dorsal wrist?
Pt position = seated or supine
Doc = ipsilateral
Positioning = pts wrist passively extended and ABducted

Where is extensor carpi ulnaris?
Dorsal wrist

How do you treat extensor carpi ulnaris?
Pt position = supine or seated
Doc = ipsilateral
Positioning = Pts writs passivley EXTENDED and ADDucted

Where is flexor carpi radialis?

How do you treat flexor carpi radialis?
Pt positon= supine or seated
Doc = ipsilateral
Positioning = pts wrist passively FLEXED and ABducted

Where is flexor carpi ulnaris?

How do you treat flexor carpi ulnaris?
Pt position = supine or seated
Doc = ipsilateral
Positioning = pts wrist passively FLEXED and ADDUCTED

Where is abductor pollicis brevis?

How do you treat abductor pollicis brevis?
Pt position = supine or seated
Doc = ipsilateral
Positioning = pts wrist passively FLEXED, THUMB is ABUCTED



