6 - MZH - Culturing microorganisms & biotech & immobolised enzymes Flashcards
What is a culture?
culture = A population of one type of microorganism that has been grown under controlled conditions in fermentation vessels
Name the 2 types of fermentation that can take place
Batch fermentation
Continuous fermentation
Lable the fermentation vessel


pH
- How is it monitored in a fermentation vessel?
- How does it contribute to an increase in product yield?
- pH is monitored by the pH probe and is kept at optimum level
- Increases yield as enzymes can work efficientlyso rate of reaction is as high as possible

Temperature
- How is it monitored in a fermentation vessel?
- How does it contribute to an increase in product yield?
- Kept at optimum by water jacket that surrounds the vessel
- Increases product yield because enzymes can work efficiently so rate of reaction is kept as high as possible

Oxygen supply
- How is it monitored in a fermentation vessel?
- How does it contribute to an increase in product yield?
- Volume of oxygen is kep at optimum level for respiration by pumping in sterile air when needed
- Increases product yield because microorganisms can always respire to provide energy for growth
Nutrient concentration
- How is it monitored in a fermentation vessel?
- How does it contribute to an increase in product yield?
- Microorganisms are kept in contact with fresh medium by paddles that circulate the medium around the vessel
- Increases product yield because microorganisms can always access the nutrients needed for growth
Contamination
- How is it monitored in a fermentation vessel?
- How does it contribute to an increase in product yield?
- Vessels are sterilised between uses with steam to kill any unwanted organisms and sure the next culture is not contaminated
- Increases prodyct yielf because the microorganisms aren’t competing with other organisms
What is a closed culture?
closed culture = When growth takes place in a vessel that’s isolated from the external environment - extra nutrients are added and waste products are removed
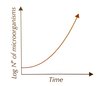
What type of curve does a closed culture, a population of organisms from batch fermentation follow
Standard growth curve

Explain what is going on at the different points of the graph. What type of fermenation does this graph represent?

Batch fermentation:
-
Lag phase
- Pop size increases very slowly as microorganisms need to make enzymes and other molecules before they can reproduce ∴ reproductionr ate is low
-
Exponential (log) phase
- Pop size increases quickly because culture conditions are at their most favourable for reproduction (lots of food + little competition). No’ of microorganisms double at regular intervals
-
Stationary phase
- Pop size hits carrying capacity. Reproductive rate = death rate. microorganisms die because there’s limiting factors e.g. food and waste product build up
-
Decline phase
- Pop size falls as death rate > reproductive rate. Food is scarce and waste products are at a toxic level

Equation for estimating the number of cells in a culture = ?
no’ of cells in population = initial no’ of cells x 2n
where n = number of divisions
What does the graph for continuous fermentation look like?
Why is the graph this shape?
- There’s no stationsary or decline phase because it’s a open culture
- Nutrients are constantly added and waste is constantly removed so it doesn’t build up causing limiting factors
What would happen if you had no medium paddles in a fermentation vessel?
Nutrients woud sink to the bottom ∴ conc wouldn’t be the same throughout the vessel
2 forms that microorganisms can be cultured in
Broth and agar plate
What does downstream processing mean?
Downstream processing = The isolation and purification of the product (this could be the microorganism itself or the product of the microorganism)
What are:
- Primary and secondary metabolites?
- Which type fo fermentation are they used in?
- Give an example of each
Primary metabolites = Produced as a part of normal growth
- Continuous culture
- E.g. Insulin from E.Coli
Secondary metabolites = Only produced during the log phase as it’s not produced as a part of normal growth - when the microorganism gets stressed
- Batch culture
- E.g. Penicillin

What are the shapes of the graphs for batch and coninuous cultures in relation to when the metabolite is produced?

Compare batch culture and continuous culture:
- Aim of the game? + Example
- Nutrients & waste products
- Growth rate
- Ease of maintanence
- What is the result of contamination
- Which one is more efficient and why
Batch culture:
- AIM - Harvest the product during the stationary phase of pop growth, when secondary metabolites are made e.g. penicillin
- Starter pop + nutrients are added at the start only. Product is removed and tank is reset for next batch after a fixed period of time
- Slower growth rate because nutrients diminish + waste accumulates
- Easier to set up & maintain
- Contamination causes loss of one batch only
- Less efficient - periods of no production when disinfecting & resetting bioreactor
Continuous culture:
- AIM - Maintain pop growth at log phase so there’s a continuous production of primary metabolite e.g. insulin by E.Coli
- Nutrients are continuously supplied and products + wastes continuously removed
- Higher growth rate - nutrients added + waste removed to eliminate limiting factors
- Difficult to set up + challenging to maintain optimum conditions
- Contamination causes loss a lot of product
- More efficient - continuously producing product

How do you ensure asceptic conditions when culturing microorganisms in the lab? (5)
- Regularly disinfect work surfaces
- Worknear bunsen flame - hot air rises taking any microorganisms w/ it
- Sterilise a wire inoculation loop using the bunsen flame
- If you’re using a broth, briefly pass the neck of the container through bunsen flame just after opened + just ebfore closing
- Minimise time agar plate is open + only open it at an angle
Steps to making a bacterial broth (5)
- Add bacteria from a starter culture / suspension from another source to a sterile nutrient medium
- Stopper the flask to prevent contamination
- Incubate at appropriate temp
- Shake reguarly to aerate if required
- Broth can now be used as a starter culture for bioreactor or other expeirments
Steps to making a streak plate on agar (5)
- Heat a wire loop in a bunsen flame to sterilise it
- Take sample from bacteria source. Lift lid of petri deish at an angle (and as little as possible). Swipe the surface of the agar with the loop lightly. Rotate the plate and repeat steaks
- Replace the lip + seal w/ tape but leave gaps to maintain aerobic conditions
- Incubate at appropriate temperature
- Aim with a streak plate is to spread out the bacteria on the loop so that by the end of the streak there are colonies derives from individual cells

How is a streak plate an example of serial dilution?
Aim with a streak plate is to spread out the bacteria on the loop so that by the end of the streak there are colonies derives from individual cell
What are immobolised enzymes?
Immobolised enzymes = Enzymes that are attached to an isoluble material so they can’t become mixed with the product
4 main types of immobolised enzymes
Adorption
Entrapment in a silica gel matrix
Encapsulation in jelly-like alginate beads, which act as a semi permeable membrane
Covalent bonding to cellulose or collagen fibres

Advantges & disadvantages:
Immobolised enzymes (3 of each)
Advantages:
-
Columns can be washed + reused
- Reduces costs of running it on a industrial scale
- Product isn’t mixed w/ enzymes so no money is needed to be spent on seperating them
-
Immoboised enzymes are more stable than free enzymes
- They’re less likely to denature
Disadvantges:
- Extra equipment is required - expensive
- Immobolised enzymes are more expensive to buy than free enzymes. Coupled w/ equipement costs it’s not always the most economical option
- Immobolisation of enzymes can sometimes lead to a reduction in the enzyme activity because they can’t freely mx w/ theur substrate



