6 - ICH - Variation & Selection Flashcards
(39 cards)
Define:
- Discontinuous variation
- Continuous variation
Discontinuous variation = Phenotypes that have qualitative differences i.e. clear cut groups e.g. blood groups.
- Characteristics are controlled by a single gene
Continuous variation = Phenotypes that have quantitative differences i.e. a wide range of overlapping intermediates e.g. height and mass.
- Characteristics are controlled by at least 2 genes (polygenes)

6 Sources of variation
- Mutations - produces new alleles
- Crossing over in prophase 1 of meiosis
- Independant assortment of homologous pairs of chromosomes in metaphase 1 of meiosis
- Independant assortment of daughter chromatids in metaphase 2 of meiosis
- Random fertilisation to produce different combinations of genomes
- Environmental influences
State 2 processes which act on a natural population of organisms to alter allele frequencies
Give an example of each
Random processes e.g genetic drift
Non-random processes e.g. selection
What is genetic drift?
Where is it likely to occur + why?
Genetic drift = The change in allele frequency that occurs by chance, rather than by natural selection
More likely to occur in island populations as they’re small + isolated from other populations:
- ∴ increases levels of inbreeding
- They form a small sample of the original population ∴ unlikely to be representative of the large population’s gene pool
What is the Founder effect?
Founder effect - Genetic drift:
When this process occurs on a recently isolated small population
- More likely to occur in island populations as they’re small + isolated from other populations:
- ∴ increases levels of inbreeding
- They form a small sample of the original population ∴ unlikely to be representative of the large population’s gene pool
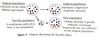
What does natural selection cause? (3)
- Change in allele fequency of a gene in a population
- Arises because individuals have different fertilities
- i.e. individuals with one genotype have more offspring than those of another genotype. Genotype with highest fertility rate = fit
- Increases chance of advantageous adaptive alleles being passed onto the next generation
- Decreases the chance of non-advantageous non-adaptive alleles being passed onto next generation
Summarise Natural selection is 6 points
- Individuals in a population compete for environmental resources e.g. food, space, light…
- There is genetic variation between individuals in a population
- One or more individuals have a competative advantage over the others because they possess a favourable allele of a gene
- These individuals will have more offspring than other without the advantageous allele i.e. they’re fitter
- Fitter individuals pass on their favourable allele onto some of their offspring
- More individuals in the next generation will possess the favourable allele - Increased allele frequency. This is natural selection
What does an individual’s fitness within a population mean?
Their ability to transmit their alleles to the next generation as a result of natural selection
Define selection pressure
Selection pressure = A environmental factor that gives greater chances of survival amd reproduction to some individuals
What is stabalising selection? (5)
Illustrate this concept with an example
Staballising selection occurs when environmental conditions remain the same ∴ characteristics are selected over several generations
- Works against both extremes + reduces the range of possible phenotypes
- Fittest phenotype is in the middle of the range + the closer you are to the middle the more likely to survive + reproduce you are - increased fitness
- After selection, variation around modal value is less
- Allele frequences remain the same
E.g. baby mass

What is directional selection? (6)
Illustrate this concept with an example
Directional selection occurs when environmental conditions change e.g. climate changes giving longer/ colder winters
- Fittest phenotypes are those at one end of the range. Works againsts one extreme
- Selection results in a new modal value
- Allele frequencies change
E.g. House mice and length of hair
- Mice living in cold stores have an advantage if they have long hair rather than short hair
- Over a period of time selection should result in mice with long hair

What are isolating mechanisms? Their purpose?
Can lead to populations with different gene pools from each other. This can result in the evolution of a new species i.e. speciation - formation of a new species from an exisiting one
State 3 forms of isolation
Ecological (geographical) isolation
Seasonal (temporal) isolation
Reproductive isolation
What is allopatric speciation
Populations becoming isolated through a combination of geographical isolation and natural selection
What is ecological (geographical) isolation?
What does it do? (4)
What is it an example of?
Ecological (geographical) isolation = 2 or more populations are seperated from each other by a geographical barrier e.g. mountain range, ocean…
- Habitat conditions differ on either side of the barrier ∴ there’s different selection pressures
- Mutations in the seperated populations are independant of each other
- Both populations evolve to suit their particular habitat by natural selection
- If the populations meet up man generations later, they may have evolved into different species
Is an example of allopatric speciation
What is seasonal (temporal) isolation?
Seasonal (temporal) isolation = 2 populatiions may be unable to breed as they are active at different times of the day or year
What is reproductive isolation?
Give 5 examples
Reproductive isolation = Mechanisms that prevent closely related species interbreeding
E.g.
- Different courtship behaviour
- Mechanical problemts with mating e.g. different sized/ shaped reproductive organs
- Gametes aren’t compatible & can’t fuse e.g. different chromosome number
- Zygote is not viable i.e. it dies
- Hybrid offspring are sterile
Define gene pool
Gene pool = All of the genes and their different alleles in a population. Each individual has a portion of the gene pool in their genome
Define speciation
Speciation = Formation of a new species from an existing one
What does sympatric speciation mean?
Sympatric speciation = Speciation without geographical isolation
What is the biological species concept? (2)
Problems with this definition? (3)
“A group of similar organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offpring”
The group is ∴ reproductively isolated from others.
Problems:
- Not all organisms reproduce sexually
- Some members of a species may look different from others of the same
- Can’t be used for extinct species or fossils
What is the phylogenetic (cladistic / evolutionary) species concept?
- Why is it a better definition than the biological species concept?
- What is the concept based upon?
- What is a clade in relation to species?
“A group of organisms that have similary morphology (shape), physiology (biochemistiry), embryology (stages of development), behaviour and occupy the same ecological niche”
- It’s based on the knowledge that closely related species have more similar DNA base sequences and molecular structures than species that are less closely related
- Definition can be used for all organisms, even if it’s not known whether or not 2 species can interbreed
Clade = Any group of organisms with base sequences that are more similar to each other than any other group
What does the phylogenetic descent of an organism mean?
Phylogenetic descent = The common ancestor of organisms within a clade
What is a monophyletic and paraphyletic group?
Monophyletic group = Single ancestry - used to describe members within a clade
Paraphyletic group = Ignores some of the clades that might have been included e.g. reptiles ignored birrds which are related to reptiles




