5 - MZH - Homeostasis 5 - Excretion and the Liver Flashcards
(24 cards)
Define:
Excretion
Metabolic waste
Detoxification
Excretion = The removal of metabolic waste from the body
Metabolic waste = A substance that is produced in excess by the metabolic processes in cells
Detoxification = Breakdown of toxins into less harmful products
why is it important to remove metabolic wastes?
Because if they build up they can inhibit enzyme activity or become toxic
4 examples of extretory waste that we’ve already met?
- CO2 from the lungs in respiration
- Nitrogen containing substances e.g. Ureafrom kidneys
- Bile pigments removed from blood by liver and found in faeces
- Combination of water, salts, urea, uric acid and ammonia excreted in sweat from skin
Where is the liver found in the body?
It’s the biggest organ in the body and lies in the abdomen just below the diaphram

Function of:
Hepatic artery
Hepatic vein
Hepatic portal vein
Hepatic artery = Delivers oxygenated blood from the aorta
Hepatic vein = Drains blood from the liver and delivers it back to the inferior vena cava
Hepatic portal vein = Delivers blood from the small intestines and is rich in absorbed nutrients
Fill in the blanks for the strucutre of the liver
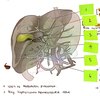

Draw a more simple diagram of this and explain the parts of the liver


What is the purpose of the bile duct?
The bile duct drains bile from the liver, this is stored in the gall bladder before being entied into the duodenum
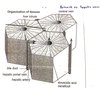
What type of cells is the livermade from?
It’s made primarity from hepatocytes which are packed together into columns called lobules
Properties of hepatocytes/ liver cells (3)
- Relatively unspecialised - therefore you can have a partial liver transplant
- Cubodial in shape with many microvilli on their cell surface membrane to max SA
- Cytoplasm is very dense - contains specific organelles needed to carry out a range of functions
Functions of the liver (5)
- Regulates - levels of glucose, amino acids & lipids
- Synthesises - Cholesterol, bile, plasma proteins (blood clotting proteins) and fetal RBCs
- Stores - Vitamins A,D and B12 and iron and glycogen
- Removes - Hormones from the blood and ages RBCs
- Detoxifies - e.g. H2O2, alcohol, drugs and ammonia
Describe the structure of a lobule

- Each lobule blood from the hepatic artery and hepatic portal vein mix and pass through channels called sinusoids between hepatocytes and empty into the branch of the heaptic vein.
- Hepatocytes have many mitochondria to provide ATP for all the energy requiring processes in the cells.
- The plasma membranes of the hepatocytes and lining of sinusoids have microvilli to increase SA for uptake of substances from the blood.
- Kupfer cells are specialised cells in the lining of the sinusoid and are phagocytic. They digest debris and bacteris to help defend against disease. Also break down old RBCs.
- In between the liver cells are channels called canaliculi. Tehy collect bile as it is formed in the hepatocytes and carry it towards the bile duct.

What is bile made up of?
Bilirubin and biliverdin
How does the liver breandown surplus amino acids?
- It first undergoes deamination to remove an amine group
- The Ammonia produced then gets fed into the ornithine cycle and the keto acid left over is respired

Define deamination
Deamination = The removal of nitrogen-containing amino groups from surplus amino acids to form ammonia and organic acids
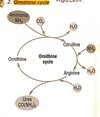
Fill in the blanks for the ornithine cycle

Write the general equation for the break down of surplus amino acids in the liver

Why do you need to breakdown ammonia to form urea?
Ammonia is very soluble and very toxic and can’t be excreted directly by mammals. You’d require too much water to do so.
To eliminate this ammonia is fed into the ornithine cycle, combines with CO2 to prduce urea.
A summarised simple equation of the formation fo urea = ?
Why urea? How is it removed from the body?
Urea is both less toxic and less soluble than ammonia.
The liver releases urea into the blood and it is removed from the blood as it passes through the kidneys.

Complete the table and give examples of animals that fall into each category of ammonia, urea and uric acid


Example of a substance detoxified by the liver?
Alcohol (ethanol)
Equation for the detoxification of alcohol (ethanol)?

The downside of detoxification fo ethanol?
How does it cause a fatty liver?

It inhibits the metabolism of fatty acids, so these are converted in to facts and stored in te liver cells.
Excess fats in the liver cells causes damage leading to cirrhosis (fatty degeneration of the liver) when liver cells no longer break down toxins and other vital liver functions cannot occur.
Apart from alcohol name 2 other substances that are detoxified by the liver
- Drugs - e.g. antibiotics and paracetamol
- Hormones - which themselves are not toxic but if they remain in the blood too long there effects could well continue long after they are needed. Breaking them down limits their effects


