5 - EKG III: Clinical 2 Flashcards
Clinical: Sinus Bradycardia
Is this always pathologic?
Slowing of normal heart rhythm, result of decreased firing at SA Node (pacemaker)
- - -
No, highly trained athletes have elevated vagal tone (parasympathetics)
Can be patholigic with aging, heart disease, medication (B blocker, calccium channel blocker) or metabolic diseas (hypothyroidism)
Diagnose:

Sinus Bradycardia
Normal P
Normal QRS Complex
Normal T
Just HR <60
What is the heart rate in this image?
(peaks x 6 = 24)
Diagnose Image

Ventricular Escape Rythm
No P Wave (no atrial depolarization)
Wide QRS (maybe double peak)
Normal T
Rate 15 - 40
Diagnose Image
Where is conduction originating?

Junctional Escape Rythm
No P Wave
Normal QRS
Normal T Wave
Conduction at AV Node
Rate 40-60
What is the EKG finding for escape rhythms?
How will you differentiate between Junction and Ventricular?
No P Waves Present (atrial depolarization)
Junction - No P, Normal QRS, Normal T
Rate ~ 40-60
Ventricular - No P, Wide QRS (maybe two peaks), Normal T
Rate ~ 15-40
Diagnose Image

First-degree AV Block
Prolonged PR Interval
Normal looking P, QRS, T
1/1 Ratio of P to QRS

Diagnose Image
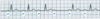
Second-Degree AV Block: Möbitz Type 1 (Wenckebach)
Constant P Wave
PR Interval progressively lengthens, until QRS Blocked–will be missing a QRS in the String
Can be common in Distance runners
P/QRS no 1:1 ratio!

Diagnose Image

Second-Degree AV Block: Möbitz Type II
Consistent PR Interval
QRS Complex will be missing (random drop)
Medical treatment required, pacemaker, syncope
Found lower in His Bundle

Clinical: How do you differentiate AV Block types on ECG Strips?
First-Degree AV Block
Möbitz Type I (Wenckebach)
Möbitz Type II
First-Degree AV Block:
PR Interval > 0.2 Second
Möbitz Type I (Wenckebach)
Progressive Increase in PR Interval, until single QRS Absent
Möbitz Type II
Sudden loss of AV Conduction, Regular PR Intervals (absent QRS)
QRS can be widened in R/L branch block
Requires medical intervention (pacemaker)
Diagnose Image

Third-Degree AV Block “Complete Heart Block”
No relationship between P Waves and QRS Complexes (they will be on two different rhythms)
No progressive lengthening—will be random
Requires medical intervention

Clinical: Supraventricular Arrhythmias
Cause/Treatment
Sinus Tachycardia
SA Node discharge rate > 100 bpm (usually 100-180 bpm)
Cause: Most often Increased Sympathetics/Decreased Parasympathetics (vagal tone)
Treatment: Underlying cause!
Diagnose Image

Sinus Tachycardia
Normal P
Normal QRS
Normal T
HR > 100
What is the HR in the image?
~ 125

Diagnose Image:

Atrial Premature Beats (APB)
Originate from an atrial focus OUTSIDE SA Node
Earlier than expect P Wave, with abnormal shape
QRS Complex Usually Normal
Causes: Smoking, lack of sleep, coffee, alcohol

Clinical: Atrial Flutter
Rapid, Irregular Atrial Activity at rate 180-350 BPM
Will have several high amp P waves, followed by a single QRS complex
May cause palpitations,dyspnea, weakness
Atrial Rate ~ 300
QRS Conduction ~ 150

Diagnose Image

Atrial Flutter
AV Rate ~ 300
Conduction Rate ~ 150
“Sawtooth” Appearance

Clinical: Atrial Fibrillation

Chaotic rhythim with atrial rate 350-600
No P Waves, OR fine, high frequency LOW AMP wavy AV Conduction
Normal QRS-T complex, irregular timing ~ 140-160 bpm

Clinical: Paroxysmal Supreventricular Tachycardias (PSVTs)
What form is most common in adults?
Sudden onset/termination
Atrial rates ~ 140 - 250
Most Common: Atrioventricular Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia (AVNRT)
P Waves not apparent (hidden/retrograde)
Normal QRS Complex

Diagnose Image

Paroxysmal Supraventicular Tachycardia (PSVT)
Atrioventricular Nodal Reentrant Tachcardia (AVNRT)

Clinical: Ventricular Pre-Excitation Syndrome (Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome, WPW)
Ventricles stimulated earlier than normal by conduction over AV Node
Atrial impulses can pass in antergrade direction through AV nose and accessory pathway
Short PR Interval (<0.12 sec)
QRS has slurred upstroke (Delta Wave)
Widened QRS complex

Diagnose Image

Ventricular Pre-excitation Syndrome (Wolf Parkinson White, WPW)
Short PR Interval (<0.12)
Slurred QRS (Delta)
Widened QRS

Clinical: What are patients with WPW Syndrom predisposed to?
Why?
PSVT
Accessory Pathway provides a potential limb of reentrant loop
Clinical:
Orthodromic AVRT (most common)
Antidromic AVRT
Concealed Accessory Pathway
Orthodromic AVRT - most common
Impulse travels anterograde down AV node to ventricles, then retrograde up accessory tract back to atria
No Delta Wave, ventricles depolarize via normal conduction
Antidromic AVRT
Impuls tavels anterograde down accessory pathway, an retrograde up AV Node
Wide QRS, ventricles actived from anterograde conduction via accessory pathways
Concealed Accessory Pathway
Can result in Orthodromic AVRT
ECGs do not result in ventricular pre-excitation
Clinical: Antidromic Atrioventricular Reentrant Tachycardia
What can you not give these patients?
Impulses are conducted anterogradely down accessory tract, and retrogradely up AV Node
RETROGRADE/REVERSED P Waves
WIDE, IRREGULAR QRS Complex
- - -
AV Nodal agens will kill patient!
- Adenosine
- Calcium Channel Blockers
- Beta Blockers
- Digitalis

Diagnose Image:
What should you NOT prescribe these patients?

Antidromic Atrioventricular Reentrant Tachycardia
AV Nodal Agents will kill patient!
- Adenosine
- Calcium Channel Blockers
- Beta Blockers
- Digitalis
Clinical: Ventricular Arrhythmias
Ventricular Premature Beats (VPB)
Ectopic ventricular focus fires action potential
P Wave Generated, not linked to every QRS
Widened QRS, impulse travels cell-to-cell Not His-Purkinje System
T Wave reversed
**Extra beats fired from ventricle**
Diagnose Image

Ventricular Premature Beats (VPB)
Widened QRS
Inverted T
Ectopic beat not related to P Wave

Clinical: Ventricular Tachycardia

Series of three or more VPBs
Wiiiiide QRS Complexes (>0.12)
100 - 200 bpm
If QRS complex are monomorphic, indicates structural abnormality that supports reentry circuit
If QRS complex are polymorphic, (Torsades de Pointes) acute myocardial ischemia / infarction most common causes; abnormalities of ion channels or calcium handling (long-QT syndromes)

Diagnose Image

Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia

Clinical: Ventricular Fibrillation (VF)

Life threatening arrhythmia
No coordinated contractions
No discrete QRS waveforms
Diagnose Image
Treatment?

Ventricular Fibrillation
SHOCK!


