5 - EKG II: Clinical (Kim) Flashcards
****What is a stardard strip for a 12 lead EKG?
What is a rhythm strip?
VERIFY W/DR KIM VIA EMAIL
10 second
What is the count off method?
Start at peak of 1st QRS complex
Each dark line is the following:
300-150-100-75-60-50
2nd peak falls between those numbers
Would not work very well for an irregular heart beat
How would you measure heart rate using markers on an EKG?
What method is the most accurate to measure a heart rate?
Count QRS complexes in the 6-sec, multiply by 10
Markers are often 3-sec intervals
Count the QRS peaks on the strip, multiply by 6
What should you look for to indicate normal SA Rhythm?
Every P Wave is followed by QRS Wave
Every QRS Wave is preceded by a P Wave
The P Wave is upright in Leads: I, II, III
How do you quickly asses the Mean QRS Axis?
Lead I: + or -
Positive: -90 to +90
Lead II: + or -
Positive: -30 tp +150
Overlap gives -30 to +90 normal range
Predominantly UPRIGHT QRS in Leads I and II
Clinical: EKG Presentation of Right Ventricular Hypertrophy?
V1 / V2: Large R Wave
Right Axis Deviation
Clinical: EKG Presentation of Left Ventricular Hypertrophy?
V5, V6, I, aVL: Taller than normal R Waves
V1, V2: Deep S Waves
Clinical: Right Bundle Branch Block (RBBB)

Normal right ventricle depolarization interrupted
Contraction is spread from Right Ventricle via cell-to-cell, no bundle of His–QRS Widened, Late Current in direction of right ventricle
V1 will have RSR’ Wave (Rabbit Ears), V6 S Wave
Clinical: Left Bundle Branch Block
Widened QRS
Notched R in V6
No R, prominent S in V1
Downward directed QRS in V1

Fascicular Blocks (hemiblocks)
Left Anterior Fascicle
Left Posterior Fascicle
Blockage of divisions after the bundles
LAF - Anterior, Superior, Lateral LV
LPF - Posterior, Inferior, Medial LV
Do not widen QRS
LAFB most common, Left Axis Deviation of Mean QRS Axis
LPFB - Right Axis Deviation
Left Axis Deviation
Right Axis Deviation
Left Axis: I (+) , II (-), aVF (-)
Right Axis: I (-), aVF (+)
Clinical: Pathologic Q Waves in Myocardial Infarction?
Irreversible necrosis of heart can be marked by formation of pathologic Q waves
More prominant that regular, will form in leads overlying infarcted tissue
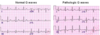
What would be the leads with pathologic Q waves in the following areas?
Inferior
Septal
Anterior
Lateral
Posterior*
Inferior: II, III, aVf
Septal: V1, V2
Anterior: V3, V4
Lateral, V5, B6, I, aVL
Posterior: V1, V2 (tall R, not Q)
Posterior due to no leads on back, will NOT be RAD (RVH causes RAD, Post. MI does NOT)
Clinical: Transient Myocardial Ischemia
Abnormality of ST Segment and T waves–related to coronary artery disease
ST Segment Depression and T Wave flattening/inversion
Clinical: Acute ST Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction (Acute STEMI)
ST Elevation, Tombstoning of T Waves
T Wave inversion, decreased R wave

Lead Locations:
Inferior Leads
High Lateral Leads
Low Lateral Leads
Septal Leads
Anterior Leads
Inferior Leads: II, III, aVF
High Lateral Leads: I, aVL
Low Lateral Leads: V5, V6
Septal Leads: V1, V2
Anterior Leads: V3, V4
What is meant by currents of injury?
Possible cause for deviation of the ST segment as result of injur
A voltage gradient exists between normal and ischemic zones, leading to current flow between these regions
Clinical: Acute Non-ST Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction (non-STEMI)
Cause: Usually acute partially occlusive coronary thrombus; result in ST segment depression and/or T Wave inversion (rather than elevation)

What condition can cause the following:
- ST ‘scooped’ Depression/Mild PR Prolongation
- Tall “peaked” T Waves (Castle)
- Flattened P, Wide QRS
- ST Depression, Flat T, U Wave
- Shortened QT Inerval
- Prolonged QT Inerval
- Digoxin Therapy
- Hyperkalemia (high potassium)
- Severe Hyperkalemeia
- Hypokalemia (low potassium)
- Hypercalcemia
- Hypocalcemia


