4.2 Lower Leg Flashcards













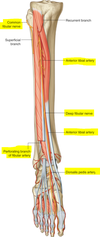




What are the compartments of the calf?
-
Lateral Calf/Sural Compartment
- Action: Eversion of the foot (tilting to left and right)
- Innervation: Superficial peroneal nerve
- Muscles: Peroneus Longus, Peroneus Brevis
-
Posterior Calf/Sural Component
- Action: Plantarflexion of ankle joint, and flexion of toes
- Innervation: Tibial nerve
-
Muscles:
- Superficial Muscles: Gastrocnemius, Soleus, Plantaris
- Deep Muscles: Tibialis Posterior, Flexor Digitorum Longus, Flexor Hallicus Longus
-
Anterior Calf/Sural Component
- Action: Dorsiflexion of ankle joint, and extension of toe joints
- Innervation: Deep peroneal nerve
- Muscles: Tibialis Anterior, Extensor Hallicus Longus, and Extensor Digitorum Longus
What muscles and cutaneous regions are innervated by the superficial peroneal nerve? What is the main movement it causes?
Muscles: Lateral calf muscles (Peroneus Longus, and Peroneus Brevis)
Movement: Foot Eversion
Cutaneous: Lateral lower leg, and medial dorsum of foot excluding the web between the first and second phalanx
What muscles and cutaneous regions are innervated by the tibial nerve? What is the main movement it causes?
Muscles: Posterior calf muscles (Gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris, tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum longus, and flexor hallicus longus)
Movements: Plantarflexion of ankle, and flexion of toes
Cutaneous: Posterior medial calf and plantar surface of foot
What muscles and cutaneous regions are innervated by the Deep Peroneal Nerve? What is the main movement it causes?
Muscles: Anterior calf muscles (Tibialis Anterior, Extensor Hallicus Longus, and Extensor Digitorum Longus)
Movements: Dorsiflexion of ankle, and extension of toe joints
Cutaneous: Web between first and second phalanxes
What do all superficial muscles of the posterior calf have in common? List the muscles.
Gastrocnemius, Soleus, and Plantaris
All superficial posterior calf muscles attach to calcaneal/achilles tendon which crosses the posterior talocrural (back of ankle)
All cause plantarflexion (Gastrocnemius and plantaris cause knee flexion, but soleus does not)
All innervated by tibial nerve
All superficial to the tibial nerve, posterior tibial artery, and 2 posterior tibial veins
What do all deep muscles of the posterior calf have in common? List the muscles.
Tibialis Posterior, Flexor Digitorum Longus, and Flexor Hallucis
All deep muscles of the posterior calf travel under the flexor retinaculum / through the tarsal tunnel along the medial malleolus
All innervated by the tibial nerve
All cause flexion of one part of the foot (Tibialis Posterior causes Plantarflexion, Flexor Digitorum Longus flexes toes 2-5, and flexor hallucis longus flexes the big toe)
What is the flexor retinaculum? What is the position of structures related to it?
-
Flexor Retinaculum- A band of connective tissue holding tendons of the foot flexors in place
- Holds (from medial to lateral): Tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum longus, posterior tibial artery and posterior tibial veins, tibial nerve, and flexor hallucis longus
Relative to the tibia, where are the tibialis anterior and extesor digitorum longus
- Tibialis Anterior is anterior and directly lateral
- Then extensor digitorum longus is lateral to tibialis anterior
Where is the end of the extensor hallucis longus? What does it do and what is it innervated by?
Dorsal surface of big toe’s distal phalange
Causes dorsiflexion (crosses ant talocrural joint) and extends big toe (dorsally/superiorly crosses interphalangeal of big toe)
Deep peroneal nerve
Where is the end of the extensor digitorum longus? What does it do and what is it innervated by?
Dorsal surface of toes 2-5’s distal and middle phalanges
Dorsiflexion (crosses ant talocrural joint), and extends toes 2-5 (dorsally/superiorly crosses proximal and distal interphalangeal joints of phalanxes II-V)
Where is the end of the peroneus longus / fibularis longus? What does it do, what muscle group is it in, and what is it innervated by?
Goes around lateral malleolus of fibula, then across plantar/inferior of foot, then to plantar side of medial cuneiform and metatarsal I
Eversion of Foot (Crosses lateral talocrural)
Lateral calf
Superficial Peroneal Nerve
Where is the end of the peroneus brevis/ fibularis brevis? What does it do, what muscle group is it in, and what is it innervated by?
Medial cuneiform and to metatarsal I
Eversion of Foot (Crosses lateral talocrural)
Lateral calf
Superficial Peroneal Nerve


