2013 NC State Mock Exam Tangent Questions D Flashcards
- All of the following features are evaluated in the mouse grimace scale EXCEPT?
a. Nose bulge
b. Cheek bulge
c. Ear position
d. Eye bulge
e. Whisker change
d. Eye bulge
Reference: Matsumiya et al. 2012. Using the mouse grimace scale to reevaluate the efficacy of postoperative analgesics in laboratory mice. JAALAS 51(1):42-49
Domain 2; Primary Species – Mouse (Mus musculus)
- You are using an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay to detect IgG antibodies to mouse hepatitis virus in serum. This test is 96% sensitive and 98% specific. The prevalence of mouse hepatitis virus in your colonies is 10%. What is the positive predictive value of your assay?
84%
Reference: Fox JG, Anderson LC, Loew FM, Quimby FW, eds. 2002. Laboratory Animal Medicine, 2nd edition. Academic Press: San Diego, CA. Chapter 10 – Microbiological Quality Control for Laboratory Rodents and Lagomorphs, pp. 385-386.
Domain 3; Primary Species - Mouse (Mus musculus)
- Which of the following species has the longest gestation period?
a. Cavia porcellus
b. Chinchilla laniger
c. Marmota monax
d. Mustela putorius furo
b. Chinchilla laniger - 111 days
* Cavia porcellus* - 68 days
* Marmota monax* - 31-32 days
* Mustela putorius furo* - 41-42 days
1) Harkness JE, Turner PV, VandeWoude S, Wheler CL. 2010. Harkness and Wagner’s Biology and Medicine of Rabbits and Rodents, 5th ed. Wiley-Blackwell: Ames, IA. Chapter 2 – Biology and Husbandry, pp. 56, 64
2) Fox JG, Anderson LC, Loew FM, Quimby FW, eds. 2002. Laboratory Animal Medicine, 2nd edition. Academic Press: San Diego, CA. Chapter 6 – Biology and Diseases of Guinea Pigs, p. 210; Chapter 7 – Biology and Diseases of Other Rodents, p. 286; Chapter 8 – Woodchucks as Laboratory Animals, p. 317; and Chapter 13 – Biology and Diseases of Ferrets, p. 488
3) Suckow MA, Stevens KA, Wilson RP, eds. 2012. The Laboratory Rabbit, Guinea Pig, Hamster, and Other Rodents. Academic Press: San Diego, CA. Chapter 21 – Management, Husbandry, and Colony Health, p. 612; Chapter 40 – Management, Husbandry, and Colony Health, p. 972
Domain 4; Tertiary Species - Other Rodents
- Which of the following is true regarding mouse parvovirus (MPV)?
a. It is an enveloped DNA virus that does not persist in the environment and is easy to inactivate
b. It is a non-enveloped RNA virus that persists in the environment and is difficult to inactivate
c. During the first 2 weeks of infection, transmission via contact or soiled bedding is consistent, with MPV DNA levels detected in the intestine and mesenteric lymph nodes
d. MPV infections are easy to detect because the amount of virus shed is consistently high and transmission is efficient, resulting in consistent seroconversion of sentinel mice
c. During the first 2 weeks of infection, transmission via contact or soiled bedding is consistent, with MPV DNA levels detected in the intestine and mesenteric lymph nodes
1) Compton et al. 2012. Transmission of mouse parvovirus by fomites. JAALAS 51(6):775-780.
2) Compton et al. 2012. Transmission of mouse parvovirus to neonatal mice. JAALAS 51(6):797-802.
3) Percy DH and Barthold SW. 2007. Pathology of Laboratory Rodents and Rabbits, 3rd edition. Blackwell Publishing: Ames, Iowa. Chapter 1 - Mouse, pp. 24-25.
4) Fox JG, Barthold SW, Davisson MT, Newcomer CE, Quimby FW, Smith AL, eds. 2007. The Mouse in Biomedical Research, 2nd edition, Volume 2 – Diseases. Elsevier Academic Press, San Diego, CA. Chapter 4 – Parvoviruses, pp. 94, 100.
5) Fox JG, Anderson LC, Loew FM, Quimby FW, eds. 2002 Laboratory Animal Medicine, 2nd edition. Academic Press: San Diego, CA. Chapter 3 – Biology and Diseases of Mice, pp. 62-63
Domain 1; Primary Species – Mouse (Mus musculus)
- Which of the following statements is FALSE regarding the use of tricaine methane sulfonate for euthanasia of amphibians?
a. Is a conditionally acceptable method of euthanasia that requires a secondary method to confirm death
b. Is acidic and in concentrations ≥ 500 mg/L should be buffered with sodium bicarbonate to obtain a pH of 7.0 – 7.5
c. May be injected into lymph spaces and pleuro-peritoneal cavities
d. Should not be used for euthanasia of animals intended as food
a. Is a conditionally acceptable method of euthanasia that requires a secondary method to confirm death
1) American Veterinary Medical Association. 2007. AVMA Guidelines on Euthanasia (Formerly Report of the AVMA Panel on Euthanasia), pp. 20, 28, 36
(http://www.avma.org/issues/animal_welfare/euthanasia.pdf).
2) Torreilles et al. 2009. Evaluation and refinement of euthanasia methods for Xenopus laevis. JAALAS 48(5):512-516.
Domain 2; Secondary Species – African Clawed Frog (Xenopus spp.) and Tertiary Species – Other Amphibians
- Butorphanol is in which category controlled substance schedules?
** IV**
1) Fish RE, Brown MJ, Danneman PJ, Karas AZ, eds. 2008. Anesthesia and Analgesia in Laboratory Animals, 2nd ed. Academic Press, San Diego, CA. Chapter. 25 – Regulatory Issues, p. 574 (Table 25-1).
2) http://www.deadiversion.usdoj.gov/schedules/index.html
Domain 5
- Which of the following statements best characterizes amyloidosis in hamsters?
a. The incidence in males is approximately 3-fold higher than in females
b. Administration of testosterone to females increases the incidence of disease
c. On histopathologic exam, the most frequently affected organs are the brain, testes, and gastrointestinal tract
d. In the kidneys, amyloid deposition frequently occurs initially in the glomerular tufts
e. In advanced cases, animals commonly enter a hypocoagulable state
d. In the kidneys, amyloid deposition frequently occurs initially in the glomerular tufts
1) Fox JG, Anderson LC, Loew FM, Quimby FW, eds. 2002 Laboratory Animal Medicine, 2nd edition. Academic Press: San Diego, CA. Chapter 5 – Biology and Disease of Hamsters, p. 188.
2) Percy DH and Barthold SW. 2007. Pathology of Laboratory Rodents and Rabbits, 3rd ed. Blackwell Publishing: Ames, Iowa. Chapter 3 – Hamster, pp. 200-202
3) Suckow MA, Stevens KA, Wilson RP, eds. 2012. The Laboratory Rabbit, Guinea Pig, Hamster, and Other Rodents. Academic Press: San Diego, CA. Chapter 33 – Non-Infectious Diseases, pp. 867-869
Domain 1; Secondary Species - Syrian Hamster (Mesocricetus auratus) and Tertiary Species – Other Rodents
- Which of the following statements best describes ketoprofen?
a. Oxicam and is not associated with any toxicity
b. Oxicam and can cause gastrointestinal erosions
c. Proprionic acid derivative and is not associated with any toxicity
d. Proprionic acid derivative and can cause gastrointestinal erosions
d. Proprionic acid derivative and can cause gastrointestinal erosions
1) Fish RE, Brown MJ, Danneman PJ, Karas AZ, eds. 2008. Anesthesia and Analgesia in Laboratory Animals, 2nd ed. Academic Press, San Diego, CA. Chapter 4 – Pharmacology of Analgesics, pp. 106–107
2) Shientag et al. 2012. A therapeutic dose of ketoprofen causes acute gastrointestinal bleeding, erosions, and ulcers in rats. JAALAS 51(6):832-841
Domain 2
- What is the term for when the nuclear genome from one mouse strain is crossed onto the cytoplasm (mitochondrial genome) of another?
Conplastic
1) Fox JG, Anderson LC, Loew FM, Quimby FW, eds. 2002. Laboratory Animal Medicine, 2nd edition. Academic Press: San Diego, CA. Chapter 3 – Biology and Diseases of Mice, p. 37.
2) Fox JG, Barthold SW, Davisson MT, Newcomer CE, Quimby FW, Smith AL, eds. 2007. The Mouse in Biomedical Research, 2nd edition, Volume 1 – History, Wild Mice, and Genetics. Academic Press: San Diego, CA. Chapter 4 – Breeding Systems: Considerations, Genetic Fundamentals, Genetic Background and Strain Types pp. 66-71; Chapter 5 – Mouse Strain and Genetic Nomenclature: An Abbreviated Guide, pp. 5 – Mouse Strain and Genetic Nomenclature: An Abbreviated Guide, pp. 81, 87-88.
3) International Committee on Standardized Genetic Nomenclature for Mice and Rat Genome and Nomenclature Committee. Guidelines for Nomenclature of Mouse and Rat Strains. October 2011.
http://www.informatics.jax.org/mgihome/nomen/strains.shtml#conplastic
Domain 3; Primary Species – Mouse (Mus musculus)
- Diets formulated for the mini- and microbreeds generally are formulated how, compared to other types of commercially available swine diets?
Lower energy, higher fiber and lower protein
1) Fox JG, Anderson LC, Loew FM, Quimby FW, eds. 2002. Laboratory Animal Medicine, 2nd edition. Academic Press: San Diego, CA. Chapter 15 – Biology and Diseases of Swine, p. 620.
2) Swindle, MM. 2007. Swine in the Laboratory Surgery, Anesthesia, Imagine, and Experimental Techniques. CRC press, Boca Raton. Chapter 1, p. 7.
Domain 4; Primary Species – Pig (Sus scrofa)
- According to the Animal Welfare Act and its regulations, the ambient temperature in the sheltered part of the facility for dogs must not fall below 45ºF or must not rise above 85ºF for more than ______ consecutive hours?
4
Reference: Animal Welfare Act, 9 CRF Part 3 – Standards, Subpart A – Specifications for the Humane Handling, Care, Treatment, and Transportation of Dogs and Cats, §3.3 (a) Sheltered housing facilities.
Domain 5; Primary Species – Dog (Canis familiaris)
- Which of the following is a normal finding in a ferret?
a. Decreased hematocrit
b. High reticulocyte count
c. Increased platelet count
d. Low reticulocyte count
b. High reticulocyte count
1) Fox JG, Anderson LC, Loew FM, Quimby FW, eds. 2002. Laboratory Animal Medicine, 2nd edition. Academic Press: San Diego, CA. Chapter 13 – Biology and Disease of Ferrets, p. 486
2) Quesenberry, KE, Carpenter, JW, eds. 2012. Ferrets, Rabbits, and Rodents Clinical Medicine and Surgery, 3rd edition. Saunders: St. Louis, MO. Chapter 1 - Basic Approach to Veterinary Care, p. 19
Domain 1; Secondary Species - Ferret (Mustela putorius furo)
- Which strain(s) of mice is the most frequent source of embryonic stem cells from which most gene-targeted mice are derived?
129
1) Fox JG, Anderson LC, Loew FM, Quimby FW, eds. 2002. Laboratory Animal Medicine, 2nd edition. Academic Press: San Diego, CA. Chapter 28 - Transgenic and Knockout Mice, pp: 1130-1131.
2) Percy DH and Barthold SW. 2007. Pathology of Laboratory Rodents and Rabbits, 3rd ed. Blackwell Publishing: Ames, Iowa. Chapter 1 - Mouse, pp. 5-6.
Domain 3; Primary Species - Mouse (Mus musculus)
- Which type(s) biological safety cabinet is/are designed to be used with toxic chemicals and has air exhausted directly out the building with no air recirculated through the cabinet?
Class II Type B2
1) U. S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and National Institutes of Health. 2007. Biosafety in Microbiological and Biomedical Laboratories. 5th ed. U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, D. C. Appendix A – Biological Safety Cabinets, pp. 292-297.
(http://www.cdc.gov/biosafety/publications/bmbl5/BMBL5_appendixA.pdf).
2) Fox JG, Anderson LC, Loew FM, Quimby FW, eds. 2002. Laboratory Animal Medicine, 2nd edition. Academic Press: San Diego, CA. Chapter 24 – Control of Biohazards, pgs. 1050-1051.
Domain 4
- According to the Animal Welfare Act and its regulations, the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee can have no more than how many members from the same administrative unit of the facility (Departmental level)?
3
1) Animal Welfare Act, 9 CFR Part 2 – Regulations, Subpart C – Research Facilities, §2.31(b)(4) Institutional animal care and use committee (IACUC). (1-1-01 Edition, p. 21).
2) Applied Research Ethics National Association (ARENA) and Office of Laboratory Animal Welfare (OLAW). 2002. Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee Guidebook. 2nd Edition. OLAW, Bethesda, MD. Section A.2. Authority, Composition and Functions, p. 14.
3) Fox JG, Anderson LC, Loew FM, Quimby FW, eds. 2002. Laboratory Animal Medicine, 2nd edition. Academic Press, San Diego, CA. Chapter 2 – Laws, Regulations, and Policies Affecting the Use of Laboratory Animals, p. 21
Domain 5
- Based on a survey of over 4650 different knockout mouse lines, which of the following is likely the most common underlying pathogenic mechanism responsible for the development of congenital hydrocephalus in mice?
a. Disruption in normal neuronal migration
b. Dysfunction of motile cilia
c. Impaired cerebrospinal fluid absorption in the subarachnoid space
d. Overproduction of cerebrospinal fluid at the choroid plexus
b. Dysfunction of motile cilia
Reference: Vogel et al. 2012. Congenital hydrocephalus in genetically engineered mice. Vet Pathol 49(1):166-181.
Domain 1; Primary Species - Mouse (Mus musculus)
- Which one of the following analgesics can provide the longest duration of analgesic effect in dogs?
a. Morphine intramuscular
b. Buprenorphine intramuscular
c. Oxymorphone intramuscular
d. Butorphanol intramuscular
e. Fentanyl transdermal patch
e. Fentanyl transdermal patch
1) Fish RE, Brown MJ, Danneman PJ, Karas AZ, eds. 2008. Anesthesia and Analgesia in Laboratory Animals, 2nd ed. Academic Press, San Diego, CA. Chapter 13 - Anesthesia and Analgesia in Dogs and Cats, p. 378.
2) Fox JG, Anderson LC, Loew FM, Quimby FW, eds. Laboratory Animal Medicine 2nd edition. Academic Press: SanDiego, CA. Chapter 22 – Preanesthesia, Anesthesia, Analgesia and Euthanasia, pp. 978-979.
Domain 2; Primary Species – Dog (Canis familiaris)
- Excessive noise appears to have which of the following effects on mice and growing chickens?
a. Decreased reproductive efficiency in mice, but no effect on growing chickens
b. No effect on reproductive efficiency in mice but increased morbidity and mortality in growing chickens
c. Decreased reproductive efficiency in mice and increased morbidity and mortality in growing chickens
d. No effect on either mice or growing chickens
c. Decreased reproductive efficiency in mice and increased morbidity and mortality in growing chickens
1) Rasmussen et al. 2009. Construction noise decreases reproductive efficiency in mice. JAALAS 48(4):363-370.
2) Pavek et al. 2010. Operation of an air filtration device results in morbidity and mortality in growing chickens (Gallus gallus domesticus). JAALAS 49(5):578–582.
Domain 4; Primary Species - Mouse (Mus musculus) and Tertiary Species – Chicken (Gallus domesticus)
- All of the following are used by AAALAC, International as primary standards to evaluate animal care and use programs EXCEPT?
a. Guide for the Care and Use of Agricultural Animals in Research and Teaching (FASS 2010)
b. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, 8th edition
c. Guide for the Care and Use of Mammals in Neuroscience and Behavioral Research (ILAR 2003)
d. European Convention for the Protection of Vertebrate Animals Used for Experimental and Other Scientific Purposes, Council of Europe (ETS 123)
c. Guide for the Care and Use of Mammals in Neuroscience and Behavioral Research (ILAR 2003)
References: http://www.aaalac.org/about/guidelines.cfm
Domain 5
- What is the most likely cause of 1 mm-white mucoid nodules observed on the skin and gills of zebrafish?
a. Atypical mycobacterium
b. Ichthyophthirius multifilis
c. Piscinoodinium pillulare
d. Saprolegnia spp.
b. Ichthyophthirius multifilis
1) Fox JG, Anderson LC, Loew FM, Quimby FW, eds. 2002. Laboratory Animal Medicine, 2nd edition. Academic Press: San Diego, CA. Chapter 19 – Biology and Management of the Zebrafish, pp. 876-881.
2) http://zebrafish.org/zirc/health/diseaseManual.php#Ich%20(White%20Spot%20Disease)
3) http://zebrafish.org/zirc/health/diseaseManual.php#Mycobacteriosis (Fish TB)
4) http://zebrafish.org/zirc/health/diseaseManual.php#Velvet Disease (Piscinoodinium pillulare)
5) Fox JG, Anderson LC, Loew FM, Quimby FW, eds. 2002. Laboratory Animal Medicine, 2nd edition. Academic Press: San Diego, CA. Chapter 20 – Biology and Health of Laboratory Fishes, pp. 899-902, 905-907.
Domain 1; Secondary Species – Zebrafish (Danio rerio)
- Which of the following pharmaceuticals is a controlled substance schedule IV drug?
a. Buprenorphine
b. Diazepam
c. Ketamine
d. Gabapentin
b. Diazepam
1) Fish RE, Brown MJ, Danneman PJ, Karas AZ, eds. 2008. Anesthesia and Analgesia in Laboratory Animals, 2nd ed. Academic Press, San Diego, CA. 25 – Regulatory Issues, p. 574 (Table 25-1).
2) http://www.deadiversion.usdoj.gov/schedules/index.html
Domain 2
- When the drug N-nitroso-N-ethylurea (ENU) is injected into male mice, what changes are created in the germ cells?
**Point mutations **
1) Fox JG, Barthold SW, Davisson MT, Newcomer CE, Quimby FW, Smith AL, eds. 2007. The Mouse in Biomedical Research, 2nd edition, Volume 1 – History, Wild Mice, and Genetics. Academic Press: San Diego, CA. Chapter 12 – Chemical Mutagenesis in Mice, p. 232.
2) Fox JG, Anderson LC, Loew FM, Quimby FW, eds. 2002. Laboratory Animal Medicine, 2nd edition. Academic Press: San Diego, CA. Chapter 30 – Animal Models in Biomedical Research, p. 1190.
Domain 3; Primary Species –Mouse (Mus musculus)
- According to the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory, all of the following are considered a category of ‘life support system’ relative to the housing and management of aquatic animals EXCEPT?
a. Aerated
b. Flow-through
c. Recirculating
d. Static
a. Aerated
1) Mason and Matthews. 2012. Aquatic environment, housing, and management in the eighth edition of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals: additional considerations and recommendations. JAALAS 51(3):329-332.
2) National Research Council. 2011. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, 8th ed. National Academies Press, Washington D.C. Chapter 3 – Environment, Housing, and Management, p. 79.
Domain 4
- Which of the following husbandry practices regarding feeding and watering of nonhuman primates WOULD NOT be compliant with the Animal Welfare Act and its regulations?
a. Nonhuman primates must be fed at least once each day
b. If water is not continuously available, it must be offered at least once daily for at least 1 hour each time
c. Water receptacles must be sanitized at least once every 2 weeks
d. Diet for nonhuman primates must be appropriate for the species, size, age, and condition of the animal
e. Food receptacles must be a readily accessible to all nonhuman primates being fed
b. If water is not continuously available, it must be offered at least once daily for at least 1 hour each time.
Reference: Animal Welfare Act, 9 CRF Part 3 – Standards, Subpart D – Specifications for the Humane Handling, Care, Treatment, and Transportation of Nonhuman Primates. §3.82 Feeding and §3.83 Watering. (1-1-05 Edition, p. 97)
Domains 4 and 5
- The case definition of simian type D retrovirus-induced simian AIDS includes generalized lymphadenopathy and/or splenomegaly accompanied by all of the following clinical and lab findings EXCEPT?
a. Bone marrow hyperplasia
b. Noma
c. Opportunistic infections
d. Retroperitoneal fibromatosis
e. Vaginal papillomas
e. Vaginal papillomas
Reference: Fox JG, Anderson LC, Loew FM, Quimby FW, eds. 2002. Laboratory Animal Medicine, 2nd edition. Academic Press: San Diego, CA. Chapter 16 - Nonhuman Primates, p. 756 (Table LV)
Domain 1; Primary Species - Macaques (Macaca spp.)
- Which of the following statements describing allergens in laboratory animals is TRUE?
a. Allergens can be commonly found in dander, hair, saliva, urine and feces of laboratory animals
b. A major mouse allergen with 2 isoforms (Mus d 1A and Mus d 1B) is predominantly found in the urine
c. The major rat allergen is produced in the sebaceous glands of the skin
d. Allergic reactions to laboratory animal allergens are examples of classic immunoglobulin G-mediated reactions
e. Airborne concentrations are related to the number of mice present in the sampling area and the degree of work activity
e. Airborne concentrations are related to the number of mice present in the sampling area and the degree of work activity
1) Committee on Occupational Safety and Health in Research Animal Facilities, Institute of Laboratory Animal Resources, Commission on Life Sciences, National Research Council. 1997. Occupational Health and Safety in the Care and Use of Research Animals. National Academy Press, DC. Chapter 4 – Allergens, pp. 53-56.
2) Glueck et al. 2012. Exposure of laboratory animal care workers to airborne mouse and rat allergens. JAALAS 51(5):554-560.
Domain 4
- According to the current Guide for Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, what is the recommended dry-bulb temperature range for mice and rats?
20-26°C
References: National Research Council. 2011. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, 8th ed. National Academies Press, Washington D.C. Chapter 3 - Environment, Housing and Management, p. 44.
Domain 5; Primary Species – Mouse (Mus musculus) and Rat (Rattus norvegicus)
- Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding the immune system effects of mouse hepatitis virus infection in immune competent mice?
a. Decreases interferon production
b. Increases the proliferative response of lymphocytes to mitogens
c. Induce thymic involution and apoptosis
d. Suppresses polyclonal immunoglobulin production
c. Induce thymic involution and apoptosis
1) Fox JG, Anderson LC, Loew FM, Quimby FW, eds. 2002. Laboratory Animal Medicine, 2nd edition. Academic Press: San Diego, CA. Chapter 29 – Factors That May Influence Animal Research, p. 1159.
2) Fox JG, Barthold SW, Davisson MT, Newcomer CE, Quimby FW, Smith AL, eds. 2007. The Mouse in Biomedical Research, 2nd edition, Volume 2 – Diseases. Academic Press: San Diego, CA. Chapter 6 – Mouse Hepatitis Virus, pp. 154-157
3) Percy DH and Barthold SW. 2007. Pathology of Laboratory Rodents and Rabbits, 3rd ed. Blackwell Publishing: Ames, Iowa. Chapter 1 – Mouse, pp. 31-36
Domain 1; Primary Species– Mouse (Mus musculus)
- Pentobarbital is classified under which of the following controlled substances schedules?
** II**
1) Fish RE, Brown MJ, Danneman PJ, Karas AZ, eds. 2008. Anesthesia and Analgesia in Laboratory Animals, 2nd ed. Academic Press, San Diego, CA. 25 – Regulatory Issues, p. 574 (Table 25-1).
2) http://www.deadiversion.usdoj.gov/schedules/index.html
Domain 2
- Certified and natural ingredient diets should be stored at _____ and purified and chemically defined diets should be stored at ______.
< 21ºC (70ºF); < 4ºC (39ºF)
1) Fox JG, Anderson LC, Loew FM, Quimby FW, eds. 2002. Laboratory Animal Medicine, 2nd edition. Academic Press: San Diego, CA. Chapter 21 - Design and Management of Animal Facilities, p. 916.
2) Institute for Laboratory Animal Research. 2011. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals Academies Press: Washington, D.C. Chapter 3 - Environment, Housing and Management, p. 66.
Domain 4
- IgE levels are suggested for routine biosecurity screening for which of the following etiological agents in mice?
a. Mouse hepatitis virus
b. Myobia musculi
c. Helicobacter hepaticus
d. Trichophyton mentagrophytes
b. Myobia musculi
1) Percy DH and Barthold SW. 2007. Pathology of Laboratory Rodents and Rabbits, 3rd ed. Blackwell Publishing: Ames, Iowa. Chapter 1 – Mouse, pp. 31-36, 58-61, 82, 85-86
2) Roble et al. 2012. Total IgE as a serodiagnostic marker to aid murine fur mite detection. JAALAS 51(2):199-208.
Domain 1; Primary Species – Mouse (Mus musculus)
- Which of the following is TRUE regarding helicobacter in mice?
a. Helicobacteriosis in adult immunocompetent mice can readily causes clinical disease
b. Liver enzymes in A/J mice are elevated with Helicobacter rodentium infection
c. Helicobacters can persist in the gastrointestinal tract, particularly the ileum and stomach.
d. Helicobacter hepaticus infections provoke a strong Th2 pro-inflammatory response
e. Histopathologic exam of the liver should include silver stains to identify spiral or curved organisms
e. Histopathologic examination of the liver should include stains such as GMS to identify spiral or curved organisms
1) Fox JG, Anderson LC, Loew FM, Quimby FW, eds. 2002. Laboratory Animal Medicine, 2nd edition. Academic Press: San Diego, CA. Chapter 3 – Biology and Diseases of Mice p. 88-90
2) Percy DH and Barthold SW. 2007. Pathology of Laboratory Rodents and Rabbits, 3rd ed. Blackwell Publishing: Ames, Iowa. Chapter 1 – Mice, pp. 58-61
3) Fox JG, Barthold SW, Davisson MT, Newcomer CE, Quimby FW, Smith AL, eds. 2007. The Mouse in Biomedical Research, 2nd edition, Volume 2 – Diseases. Academic Press: San Diego, CA. Chapter 17 – Helicobacter Infections in Mice, pp. 410-415, 419, 428
Domain 1; Primary Species – Mouse (Mus musculus)
- Which of the following animal identification techniques requires the use of anesthesia in mice greater than 2 weeks of age?
a. Ear tags
b. Ear notch
c. Toe clipping
d. Tattoo
e. Microchipping
c. Toe clipping
1) Fox JG, Anderson LC, Loew FM, Quimby FW, eds. 2002. Laboratory Animal Medicine, 2nd edition. Academic Press: San Diego, CA. Chapter 23 – Techniques of Experimentation, pp. 1006-1008.
2) Institute for Laboratory Animal Resources. 2011. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. National Academy Press, Washington, D.C. Chapter 3 – Environment, Housing, and Management, p.75.
Domain 4; Primary Species – Mouse (Mus musculus)
- Which organization is dedicated to enhancing the quality of management and care of laboratory animals throughout the world?
Laboratory Animal Management Association
1) http://www.lama-online.org/about/mission/
2) http://www.aalas.org/resources/branches-affil.aspx
Domain 6
- What is the clinical triad of the Horner syndrome?
**Ipsilateral eyelid ptosis, pupil miosis and facial anhydrosis **
References: Ding et al. 2012. Horner syndrome after carotid sheath surgery in a pig: anatomic study of cervical sympathetic chain. Comp Med 61(5):453-456.
Domain 1
- What does the acronym HVAC stand for?
Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning
1) Fox JG, Anderson LC, Loew FM, Quimby FW, eds. 2002. Laboratory Animal Medicine, 2nd edition. Academic Press: San Diego, CA. Chapter 21 – Design and Management of Animal Facilities, p. 919.
2) Hessler JR, Lehner NDM, eds. 2009. Planning and Designing Research Animal Facilities. Academic Press, San Diego, CA. Chapter 34 – Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning (HVAC): Special Considerations, pp. 461-462
3) http://www.epa.gov/iaq/schooldesign/hvac.html
Domain 4
- All of the following methods are recommended for routine pest control in laboratory animal environments EXCEPT?
a. Seal all potential entry points (cracks, etc)
b. Use of organic pesticides
c. Eliminate hiding or nesting places
d. Enforce a zero-tolerance policy on the consumption of food within the animal facility
b. Use of organic pesticides
1) Fox JG, Anderson LC, Loew FM, Quimby FW, eds. 2002. Laboratory Animal Medicine, 2nd edition. Academic Press: San Diego, CA. Chapter 21 – Design and Management of Animal Facilities, pp. 929-930.
2) National Research Council. 2011. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, 8th ed. National Academies Press, Washington D.C. Chapter 3 – Environment, Housing, and Management, p 74.
Domain 4
- Signs characteristic of Salmonella septicemia in swine include which of the following clinical signs?
a. Arthritis
b. Chronic wasting
c. Cough, dyspnea, cyanosis of the ears
d. Hemorrhagic diarrhea with rectal strictures
c. Cough, dyspnea, cyanosis of the ears
1) Fox JG, Anderson LC, Loew FM, Quimby FW, eds. 2002. Laboratory Animal Medicine, 2nd edition. Academic Press: San Diego, CA. Chapter 15 – Biology and Diseases of Swine, p. 630.
2) Zimmerman J, Karriker L, Ramirez A, Schwartz K, Stevenson G, eds. 2012. Diseases of Swine, 10th ed. Wiley-Blackwell: Ames, IO. Section IV – Bacterial Diseases, p. 826.
Domain 1; Primary Species – Pig (Sus scrofa)
- The presence of which agents leads to increased algal growth in aquatic systems?
Nitrogen and phosphorus
1) Institute for Laboratory Animal Resources. 2011. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. National Academy Press, Washington, D.C. Chapter 3 – Environment, Housing, and Management, p. 86.
2) Fox JG, Anderson LC, Loew FM, Quimby FW, eds. 2002. Laboratory Animal Medicine, 2nd edition. Academic Press: San Diego, CA. Chapter 19 – Biology and Management of the Zebrafish, p. 869
Domain 4
- Dubbing refers to which of the following standard agricultural practices?
a. Beak trimming of birds
b. Partial removal of the comb of chickens
c. Removal of supernumerary teats of cattle
d. Tail-docking in lambs
b. Partial removal of the comb of chickens
Reference: Committees to Revise the Guide for the Care and Use of Agricultural Animals in Agricultural Research and Teaching. 2010. GUIDE For the Care and Use of Agricultural Animals in Research and Teaching. 3rd Edition. Federation of Animal Science Societies, Savoy, IL. Chapter 7 – Dairy Cattle, p. 80; Chapter 9 – Poultry, pp. 117, 119; Chapter 10 – Sheep and Goats, p. 135 (http://www.fass.org/docs/agguide3rd/Ag_Guide_3rd_ed.pdf)
Domain 4; Tertiary Species – Chicken (Gallus domestica)
- What is the etiological agent of thromboembolic meningoencephalitis in cattle?
**Haemophilus somnus **
1) http://www.merckvetmanual.com/mvm/index.jsp?cfile=htm/bc/55500.htm
2) Fox JG, Anderson LC, Loew FM, Quimby FW, eds. 2002. Laboratory Animal Medicine, 2nd edition. Academic Press: San Diego, CA. Chapter 14 – Biology and Diseases of Ruminants: Sheep, Goats, and Cattle, pp. 548-551.
Domain 1; Tertiary Species – Other Livestock Species Including Cattle and Horses
- Which of the following is utilized as a model for diabetes mellitus?
a. Cricetus cricetus
b. Cricetulus griseus
c. Mesocricetus auratus
d. Phodopus sungorus
b. Cricetulus griseus
1) Fox JG, Anderson LC, Loew FM, Quimby FW, eds. 2002. Laboratory Animal Medicine, 2nd edition. Academic Press: San Diego, CA. Chapter 5 - Biology and Diseases of Hamsters, pp. 188-190, 192, 195-197.
2) Suckow MA, Stevens KA, Wilson RP, eds. 2012. The Laboratory Rabbit, Guinea Pig, Hamster, and Other Rodents. Academic Press: San Diego, CA. Chapter 35 – The Chinese or Striped-Back Hamster, p. 912; Chapter 36 – The European Hamster, p. 929; Chapter 37 – Other Hamsters, pp. 937-938.
Domain 3; Tertiary Species – Other Rodents
What does the equipment depicted below measure?

Rotational behavior
1) http://www.harvardapparatus.com/hapdfs/HAI_DOCCAT_3/BH1_18.pdf
2) http://www.panlab.com/panlabWeb/Hardware/ROTAMETER/ROTAMETER.pdf
Domain 3
For which rat strain is this spontaneous lesion the most common?

Fisher 344 (Interstitial cell tumor 78% incidence)
1) Fox JG, Anderson LC, Loew FM, Quimby FW, eds. 2002. Laboratory Animal Medicine, 2nd edition. Academic Press: San Diego, CA. Chapter 4 – p154
2) Percy DH and Barthold SW, eds. 2007. Pathology of Laboratory Rodents and Rabbits, 3rd edition. Blackwell Publishing: Ames, IA. Chapter 2 – p174
Domain 1; Primary species – Rat (Rattus norvegicus)
The pictured device utilizes a luciferase/luciferin reaction to detect what as an indicator of environmental contamination?

ATP
1) Pharmacal website: http://www.pharmacal.com/charm.htm
2) Ecolab website: http://www.ecolab.com/Europe/downloads/novalum.pdf
Domain 4, T1, K3
You performed a necropsy on rat and found the following finding depicted in the picture below. What is the most likely signalment of this rat?

An old male SD rat fed with high-protein diet.
1) Percy DH and Barthold SW. 2007. Pathology of Laboratory Rodents and Rabbits, 3rd edition. Blackwell Publishing: Ames, Iowa. Chapter 2 – Rat, p. 161.
2) Fox JG, Anderson LC, Loew FM, Quimby FW, eds. 2002. Laboratory Animal Medicine, 2nd edition. Academic Press: San Diego, CA. Chapter 6 – Biology and Diseases of Rats, p. 157.
Domain 1; Primary Species – Rat (Rattus norvegicus)
(Note: Picture shows pale kidneys with finely-pitted surface consistent with chronic progressive nephropathy.)
The depicted clinical presentation may be seen in mice infected with all of the following agents, except:
a. Syphacia spp
b. Mouse hepatitis virus
c. Citrobacter rodentium
d. E coli
e. Mouse norovirus
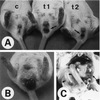
e) Mouse norovirus
MNV-1 is nonpathogenic in all or nearly all mouse strains except is lethal in all STAT1 deficient mice.
1) Harkness JE, Turner PV, VandeWoude S, Wheler CL. 2010. Harkness and Wagner’s Biology and Medicine of Rabbits and Rodents, 5th ed. Wiley-Blackwell: Ames, IA.
2) Percy DH, Barthold SW. Pathology of Laboratory Rodents and Rabbits, 3rd Ed. Blackwell Publishing, Ames, IA, 2007. Pg 44-55
Domain 1; Primary species – Mouse (Mus musculus)
In the following photomicrograph, what are the pathologic features of this mouse disease?

Marked epidermal hyperplasia (acanthosis)
Orthokeratotic hyperkeratosis
Corynebacterium bovis
Which of the pictured quality assurance systems is more applicable to be used in tunnel and rack washers?

A (monitors temperature only)
Reference: http://www.pharmacal.com/TriTempTape.htm
Domain 4
Pathologic changes are consistent with what pathogen in rats?

Coronavirus - both Parker’s rat coronavirus (RCV-P) and sialoacryoadenitis virus (RCV-SDA) can cause these lesions.
Infection with either cannot be differentiated by comparison of clinical signs or lesions. The antigenic differences between them are significant enough to allow cross-infection with either virus. Can be asymptomatic. There are two distinct types of clinical disease: 1) endemic in breeding colonies where preweanling show transient conjunctivitis; 2) sudden onset in naive postweanling to adults with cervical swelling from inflammation and edema of submaxillary salivary glands, nasal/ocular discharge, porphyrin stain, photophobia, corneal opacities and ulceration.
The lesion depicted in the following slide has a higher prevalence in SD and Wistar rats.

Auricular chondritis associated lesions
1) Percy DH and Barthold SW. 2007. Pathology of Laboratory Rodents and Rabbits, 3rd edition. Blackwell Publishing: Ames, Iowa.. pp. 167
2) Kitagaki M, Hirota M. Auricular chondritis caused by metal ear tagging in C57BL/6 mice. Vet Pathol. 2007 Jul;44(4):458-66. PubMed PMID: 17606507.
Domain 1; Primary species – Rat (Rattus norvegicus)
What strain of mouse is this most likely to be?

129
Neoplasms of the mouse male reproductive tract are relatively rare, except in GEMs. Teratomas of the testis are frequent in 129/Sv-ter+ (129S4/SvJae and other lines derived from Stevens), with up to 10% affected by 3 weeks of age, and up to 94% of older ter+/+ with 75% bilateral involvement.
1) Fox JG, Davisson MT, Quimby FW, Barthold SW, Newcomer CE, Smith AL. 2007. The Mouse in Biomedical Research 2nd edition. Academic Press: San Diego, CA. Volume II, Chapter 24 – p615
2) Percy DH and Barthold SW, eds. 2007. Pathology of Laboratory Rodents and Rabbits, 3rd edition. Blackwell Publishing: Ames, IA. Chapter 1 – p121
Domain 1 – Primary (Mouse)
What is the strain and its main use in research?

Brattleboro; diabetes insipidus
1) Fox, J.G. et. Al. (Eds.) (2002). Laboratory Animal Medicine (2nd ed.). Elsevier: San Diego, CA. (p. 122).
2) Baker, H.J. et. Al. (Eds.). (1980). The Laboratory Rat: Volume II, Research Applications. Academic Press, Inc.: New York, NY. (p. 171).
Domain 3; Primary species – Rat (Rattus norvegicus)
What is the purpose of this device?

Providing automatic water to laboratory animals
http://www.edstrom.com/product/solutions/animal-watering/products/automated-animal-watering/
Domain 4
The following image depicts a frequently used surgical model in rodents to study which condition in humans?

Sepsis
1) Cotroneo TM, Hugunin KM, Shuster KA, Hwang HJ, Kakaraparthi BN, Nemzek-Hamlin JA. 2012. Effects of buprenorphine on a cecal ligation and puncture model in C57BL/6 mice. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 51(3):357-65.
2) http://www.nature.com/nprot/journal/v4/n1/fig_tab/nprot.2008.214_F1.html
Domain 3
What are the two pieces of equipment, pictured below, which are included in most automatic watering systems?

Pressure-reducing station and chlorine injection station
1) Fox JG, Anderson LC, Loew FM, Quimby FW, eds. 2002. Laboratory Animal Medicine, 2nd edition. Academic Press: San Diego, CA. Chapter 21 – Design and Management of Animal Facilities, p. 936.
2) National Research Council (U.S.). 2011. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. Washington, D.C.: National Academies Press. Chapter 3- Environment, Housing and Management, p. 67-68.
Domain 4 – Animal Care
What rat stock/strain is the condition depicted in the picture below most likely seen (may not be the pictured strain?

SHR or Sprague-Dawley; also occurs in rats with late-stage chronic nephropathy
Picture: thickened, dilated, tortuous, hemorrhagic, and inflamed mesenteric arteries consistent with polyarteritis nodosa.
1) Percy DH and Barthold SW. 2007. Pathology of Laboratory Rodents and Rabbits, 3rd edition. Blackwell Publishing: Ames, Iowa. Chapter 2 – Rat, p. 164.
2) Suckow MA, Weisbroth SH, Franklin CL, eds. 2006. The Laboratory Rat. Academic Press: San Diego, CA. Chapter 15 – Metabolic, Traumatic, and Miscellaneous Diseases, p. 517-519.
Domain 1;Primary Species – Rat (Rattus norvegicus)
This slide depicts the contents of pan liner from a female rabbit. All of the following are possible differentials EXCEPT:
a. urolithiasis
b. endometrial venous aneurysms
c. ovarian teratoma
d. pyelonephritis
e. uterine adenocarcinoma

c) ovarian teratoma
1) Fox J, Anderson L, Lowe F, Quimby F. Laboratory Animal Medicine, 2nd edition. American College of Laboratory Animal Medicine. Academic Press, 2002. Pg 358.
2) Percy DH, Barthold SW. Pathology of Laboratory Rodents and Rabbits, 3rd Ed. Blackwell Publishing, Ames, IA, 2007, pg 254.
Domain 1, primary species – rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculi)
Which of the following is not commonly associated with the condition pictured?
a. Obesity
b. Mycoplasma infection
c. Trauma
d. Wire bottom caging
e. Poor sanitation

b. Mycoplasma infection
Staph. aureus is most frequnt isolate from these lesions.
1) Percy DH and Barthold SW. 2007. Pathology of Laboratory Rodents and Rabbits, 3rd ed. Blackwell Publishing: Ames, Iowa. Chapter 6 – Rabbit, pg 299
2) Hrapkiewicz K, Medina L, 2010. Clinical Laboratory Animal Medicine – An Introduction, 3rd edition. Blackwell Publishing, Ames, Iowa. Chapter 10 – Rabbits, pg 236.
The prevalence of this parasite, identified in a blood smear, was recently evaluated in non-human primates from Louisiana. What is the genus and species?

Trypanosoma cruzi
1) Dorn, PL, et al. 2012. “Low prevalence of Chagas Parasite infection in a nonhuman primate colony in Louisiana.” JAALAS 51 (4), pp443-447.
2) Fox JG, Anderson LC, Loew FM, Quimby FW, eds. 2002. Laboratory Animal Medicine, 2nd edition. Ch. 16. Nonhuman Primates, p. 761.
Domain 1; Primary species – Macaques (Macaca spp.)
The following is a traditional breeding scheme in producing what type of mice?

Congenic
1) Armstrong NJ, Brodnicki TC, Speed TP. 2006. Mind the gap: analysis of marker-assisted breeding strategies for inbred mouse strains. Mamm Genome 17(4):273-87.
2) Fox JG, Anderson LC, Loew FM, Quimby FW, eds. 2002. Laboratory Animal Medicine, 2nd edition. Academic Press: San Diego, CA. Chapter 3 – Biology and Diseases of Mice, p. 37.
Domain 4; Primary Species – Mouse (Mus musculus)
The following figure from a recent publication depicts which imaging technique?

In vivo bioluminescent imaging (BLI), a sensitive and reliable technique using the luciferase reaction for studying gene expression
1) Semprini S, Saunter CD, Ludwig M, Girkin JM, Mullins JJ. 2012. Use of Fiber Optic Technology to Measure the Effects of Anesthesia on Luciferase Reaction Kinetics. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 51(6):820-24.
2) Fox JG, Anderson LC, Loew FM, Quimby FW, eds. 2002. Laboratory Animal Medicine, 2nd edition. Academic Press: San Diego, CA. p.1033.
Domain 3
B6.BKS(D)-Leprdb/J
The strain of mouse shown above has

a spontaneous mutation in the Leptin receptor gene
1) William T. Cefalu. 2006. Animal Models of Type 2 Diabetes: Clinical Presentation and Pathophysiological Relevance to the Human Condition ILAR Journal 47(3):90
2) http://jaxmice.jax.org/strain/000697.html
3) Czupryn A, Zhou YD, Chen X, McNay D, Anderson MP, Flier JS, Macklis JD. 2011. Transplanted hypothalamic neurons restore leptin signaling and ameliorate obesity in db/db mice. Science. 334(6059):1133-7.
Domain 3; Primary species – mouse (mus musculus)
What is the correct genus and species of this lizard?

Anolis carolinensis
1) Fox JG, Anderson LC, Loew FM, Quimby FW, eds. 2002. Laboratory Animal Medicine, 2nd edition. Academic Press, San Diego, CA. Ch 18. Biology and Diseases of Reptiles, p. 829
2) Ascher JM, Bates W, Ng J, Messing S, Wyatt J. Assessment of xylazine for euthanasia of anoles (Anolis carolinensis and Anolis distichus). J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2012 Jan;51(1):83-7.
Domain 3; Tertiary species – Anoles (Anolis carolinensis)
What is the genus name of the animal shown below, and what does the normal diet consist of in the wild?
a. Peromyscus; seeds, invertebrates
b. Onychomys; grasshoppers, beetles, scorpions, other rodents
c. Dipodomys; seeds, plant material, larvae
d. Oryzomys; rodents, small birds, insects
e. Mystromys; seeds, plant material, invertebrates

b. Onychomys; grasshoppers, beetles, scorpions, other rodents
O. torridus and O. leucogaster are commonly studied. They are aggressive predators.
1) Fox JG, Anderson LC, Loew FM, Quimby FW, eds. 2002. Laboratory Animal Medicine, 2nd edition. Academic Press: San Diego, CA. Chapter 7 – Biology and Diseases of Other Rodents, p. 264
2) Sarko DK, Leitch DB, Girard I, Sikes RS, Catania KC. Organization of somatosensory cortex in the Northern grasshopper mouse (Onychomys leucogaster), a predatory rodent. J Comp Neurol. 2011; 519(1):64-74.
Domain 4; Tertiary Species – Other Rodents
Genus and species and use in research?

Heterocephalus glaber
- Model of social cooperation
- Model of reproductive suppression
- Model of somatosenosory processing
- Model of pain insensitivity
- Model of cutaneous Substance P Calcitonin Gene Related Peptide
- Model of delayed puberty and prolonged hypogonadism
- Model of bone elongation
- Model of aging - they are the longest lived rodent known, living approximately 30 years in captivity
The following is a kidney section from a guinea pig. What causes the histopathologic feature below?

Coccidia (Klossiella cobayae)
1) Percy DH and Barthold SW. 2007. Pathology of Laboratory Rodents and Rabbits, 3rd edition. Blackwell Publishing: Ames, Iowa. Chapter 5 – Guinea Pig, p. 236.
2) Fox JG, Anderson LC, Loew FM, Quimby FW, eds. 2002. Laboratory Animal Medicine, 2nd edition. Academic Press: San Diego, CA. Chapter 6 – Biology and Diseases of Guinea Pigs, p. 224.
3) Baker DG, ed. 2007. Flynn’s Parasites of Laboratory Animals, 2nd edition. Blackwell Publishing: Ames, Iowa. Chapter 14 – Parasites of Guinea Pigs, p. 432.
Domain 1; Secondary Species – Guinea pig (Cavia porcellus)
The histology image in (A) depicts normal jejunum in a rat. The histology image in (B) resulted after the administration of what substance?
a. Buprenorphine
b. Ketamine
c. Ketoprofen
d. Isoflurane
e. Halothane

c. Ketoprofen
1) Shientag L, Wheeler SM, Garlick DS, Maranda LS. 2012. A Therapeutic Dose of Ketoprofen Causes Acute Gastrointestinal Bleeding, Erosions, and Ulcers in Rats. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 51(6):832-41.
2) Flecknell P, Waterman-Pearson A, eds. 2000. Pain Management in Animals. WB Saunders, London. P.36.
Domain 2; Primary Species – Rat (Rattus norvegicus)
This image represents what technique, which was recently validated as useful in laboratory mice?

Blood collection from the jugular vein of an awake mouse
Reference: Shirasaki, Y, Y Ito, M Kikuchi, Y Imamura, T Hayashi. 2012. Validation Studies on Blood Collection from the Jugular Vein of Conscious Mice. JAALAS. 51(3): 345-51.
Domain 3; Primary Species – Mouse (Mus musculus)
What is the following imaging technique and in conjunction with 18F-labeled fluoro-2-D-deoxyglucose can be used for measuring what?

Positron Emission Tomography–Computed Tomography; Metabolic Activity
1) Kim JI, Ah Lee Y, Won LJ, Min Jeong S, Woo Chung H, Soo Han J. 2012. Use of 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography–Computed Tomography in a Miniature Pig (Sus scrofa domestica) with Pneumonia. Comp Med 62:203-208
2) Lee YA, Kim JI, Lee JW, Cho YJ, Lee BH, Chung HW, Park K, Han JS. 2012. Effects of Various Anesthetic Protocols on 18F-Flurodeoxyglucose Uptake into the Brains and Hearts of Normal Miniature Pigs (Sus scrofa domestica). J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci 51:246 – 252
Domain 3;
The equipment pictured is used for what purpose?

Bedding disposal
1) Fox JG, Anderson LC, Loew FM, Quimby FW, eds. 2002. Laboratory Animal Medicine, 2nd edition. Academic Press: San Diego, CA. Chapter 21 – Design and Management of Animal Facilities, p. 933.
2) National Research Council (U.S.). 2011. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. Washington, D.C.: National Academies Press. Chapter 2- Animal Care and Use Program, p. 19-20.
Domain 4; Animal Care
What is this, what does it measure, and how is that response mediated?

Tail Flick Assay
Measures reflexive, spinally-mediated response to noxious stimuli.
What is this, what does it meaure, and how is the response mediated?

Hot plate test
Measures supra-spinally mediated response to noxious stimuli.


