2009 International Coalition Flashcards
- In addition to social housing, which of the following forms of enrichment provide the best opportunities for species typical behavior in this animal?

a. gum feeders
b. swimming pool
c. insect feeders
d. a and c
e. none of the above
Answer: d. a and c
References:
1) Vignes S, Newman JD, and Roberts LR. 1999. Mealworm feeders as environmental enrichment for common marmosets. Cont Topics 40(3) pp. 26-29
2) Roberts LR, Roytburd LA, and Newman JD. Puzzle feeders and gum feeders as environmental enrichment for common marmosets. Cont Topics 38(5) pp. 27-31
Domain 4; Secondary species – Common marmoset (Callithrix jacchus)
- Which of the following is an “Unacceptable” method of euthanasia for neonatal mice?
a. carbon dioxide asphyxiation
b. hypothermia
c. inhalant anesthesia
d. decapitation
e. cervical dislocation
Answer: b. hypothermia
References:
1) 2007 AVMA Guidelines on Euthanasia (Formerly Report of the AVMA Panel on Euthanasia). http://www.avma.org/issues/animal_welfare/euthanasia.pdf
2) Report of the ACLAM Task Force on Rodent Euthanasia. http://www.aclam.org/print/report_rodent_euth.pdf
Domain 2; Primary species – mouse (Mus musculus)
- The condition depicted in this slide may be seen in mice infected with all of the following agents, EXCEPT:
a. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
b. Mouse hepatitis virus
c. Citrobacter rodentium
d. Escherichia coli
e. Helicobacter spp
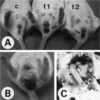
Answer: a. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
References:
1) Harkness JE and Wagner JE. The Biology and Medicine of Rabbits and Rodents, 4th Ed. Wilkins and Wilkins, Media, PA, 1995. Pg 163
2) Percy DH, Barthold SW. Pathology of Laboratory Rodents and Rabbits, 3rd Ed. Blackwell Publishing, Ames, IA, 2007. Pg 55
Domain 1 Primary species – mouse (Mus musculus)
- Which of the following ACLAM recommendations for CO2 euthanasia of rats is FALSE?
a. Minimize changes in the animal’s environment.
b. Euthanasia chambers should be large enough for the animal to turn around and perform normal postural movements.
c. Excess gas must escape and should not pressurize the euthanasia chamber.
d. Carbon dioxide delivery should be predictable, controllable, and add to air by dilution.
e. Carbon dioxide filling rate should be balanced to render then animal unconscious and minimize aversive experiences.
Answer: d. Carbon dioxide delivery should be predictable, controllable, and add to air by
dilution.
References: http://www.aclam.org
: McIntyre, A. et. al. 2007. Automated Mouse Euthanasia in an Individually
Ventilated Caging System: System Development and Assessment. JAALAS 46
(2): 65-73.
Domain 2; Primary species – rat (Rattus norvegicus)
- What does the date on a bag of feed indicate? What is the recommended shelf life of guinea pig chow?
a. Milling date and 90 days
b. Best by date and 180 days
c. Nutrient production date and 180 days
d. Expiration date and 180 days
Answer: a. Milling date and 90 days
Reference:
1) Harkness, E.J., et al. Diet, nutrition, and feeding behavior. In Laboratory Animal Medicine (Fox, G.J. et al, eds.), pgs. 208-209. Academic Press, New York.
2) Institute of Laboratory Animal Resources, Commission on Life Sciences, National Research Council. 1996. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. National Academy Press: Washington, D.C. Chapter 2 – Animal Environment, Housing and Management, p. 39
Domain 4; Secondary species – Guinea pig (Cavia porcellus)
- What schedule is ketamine and which agency regulates the use of these substances?
a. III; Drug Controller Agency
b. III; Drug Enforcement Administration
c. II; Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee
d. III; Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee
e. II; Drug Enforcement Administration
Answer: b. III; Drug Enforcement Administration
References: http://www.usdoj.gov/dea/index.htm
: http://www.deadiversion.usdoj.gov/drugs_concern/ketamine/ketamine.htm
: http://www.usdoj.gov/dea/pubs/csa.html
Domain 5
- (2 slides) The first slide depicts the clinical signs associated with the pathogen depicted in the second slide. Which of the following is TRUE regarding this pathogen?
a. This is a walking mite that induces an intense pruritus
b. The mites are rarely seen on histologic section and skin scrapings
c. The condition is zoonotic
d. The mites move frequently between the animal and the environment
e. Ivermectin has been shown to be ineffective in treating the condition

Answer: c. The condition is zoonotic
References:
1) Fox J, Anderson L, Lowe F, Quimby F. Laboratory Animal Medicine, 2nd edition. American College of Laboratory Animal Medicine. Academic Press, 2002. Pg 425
2) http://www.avma.org/animal_health/brochures/external_parasites/external_parasites_brochure.pdf
Domain 1; Primary species – dog (Canis familiaris)
- The object depicted is used to determine:
a. effectiveness of cage sanitation
b. air flow velocity
c. water pressure in pressure reducing stations
d. cage rack ball bearing torque
e. fiber optic transmission efficiency

Answer: a. effectiveness of cage sanitation
References:
1) Wardrip CL, Artwohl JE, Oswald J, Bennett BT. 2000. Verification of bacterial killing effects of cage wash time and temperature combinations using standard penicylinder methods. Contemp Top Lab Anim Sci.39(4):9-12.
2) Ednie, D.L.; Wilson, R.P.; Lang, C.M. (1998). Comparison of two sanitation monitoring methods in an animal research facility. Contemporary Topics in Laboratory Animal Science 37(6): 71-74.
Domain 4
- All of the following are true regarding hamsters with this lesion EXCEPT:
a. More common in females
b. Associated with atrial thrombosis
c. Most commonly occurs after 15 months of age
d. Steiner silver stain is ideal stain to verify diagnosis
e. Testosterone administration will reduce incidence of disease in females
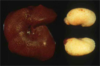
Answer: d. Steiner silver stain is ideal stain to verify diagnosis References: Percy, D. and Barthold, S. 2007. Pathology of Laboratory Rodents and Rabbits 3rd ed. Blackwell Publishing. Chapter 3, pages 200-202
: Fox, J., Anderson, L., Lowe, F., and Quimby, F. 2002. Laboratory Animal
Medicine, 2nd ed. Academic Press, San Diego, CA, Chapter 5, p. 188.
Domain 1; Secondary species – Syrian hamster (Mesocricetus auratus)
- What is the most likely morphologic diagnosis depicted in this slide, as recently described in a Rhesus macaque?
a. Ascariasis
b. Gongylonemiasis
c. Schistosomiasis
d. Hydatidosis
e. Myiasis

Answer: a. Ascariasis
References:
1) Bennett BT, Abee CR, Henrickson R, eds. 1998. Nonhuman Primates in Biomedical Research: Diseases. Academic Press, San Diego, CA. Chapter 3 – Parasitic Diseases, p. 136-169
2) Gonzalo AS, Maximova OA, StClaire MC, Montali RJ, Ward JM, Cheng LI, Elkins WR, Kazacos KR. 2008. Visceral and Neural Larva Migrans in Rhesus Macaques. JAALAS 47(4):64-67.
Domain 1; Primary species – Rhesus macaque (Macaca mulatta)
- Which type of learning is illustrated in these pictures?
a. auditory learning
b. visual learning
c. tactile / kinesthetic learning
d. realistic learning
e. model learning

Answer: c. tactile / kinesthetic learning
Reference: Stevens, C. and Dey, N. 2007. A Program for Simulated Rodent Surgical Training.
Lab Animal 36 (9): 25-31.
Domain 6
- Which of the following agents does NOT directly induce this condition in swine?
a. Cytomegalovirus
b. Pasteurella multocida
c. Haemophilus parasuis
d. Bordetella bronchiseptica
e. All of the above directly induce this condition

Answer: a. Cytomegalovirus
References:
1) Fox J, Anderson L, Lowe F, Quimby F. Laboratory Animal Medicine, 2nd edition. American College of Laboratory Animal Medicine. Academic Press, 2002. Pg 635
2) BE Straw, JJ Zimmerman, S D’Allaire, DJ Taylor. Diseases of Swine. Blackwell Publishing, 2006. Pg 152
Domain 1; Primary species – Swine (Sus scrofa)
- The animal depicted in the slide above is a model for which human infectious organism?
a. Mycobacterium leprae
b. Yersinia pestis
c. Marburg virus
d. Plasmodium falciparum

Answer: a. Mycobacterium leprae
References:
1) Job CK. 2003. Nine-banded armadillo and leprosy research. Indian J Pathol Microbiol 46(4): p. 541-550.
2) http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/UW082
Domain 3; Tertiary species
- What is the purpose of the object depicted?
a. Pacemaker
b. Holter monitoring
c. Mucus impedance
d. MRI
e. Identification

Answer: e. Identification
References:
1) http://www.avidid.com/
2) http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Microchip_implant_(animal)
Domain 4
- This non-human primate arrived at your facility 30 days ago, and is currently being quarantined. An intradermal old mammalian tuberculin test was grade 0 at 6 days post-arrival, then again two weeks later. A final TB test was performed, and the results are shown below. Based on this photograph, what is the best clinical course of action?
a. Release the monkey from quarantine, as he is grade 0 again.
b. Repeat the intradermal TB test in 7 days, using the opposite eyelid, as this is a grade 4 reaction. Extend the quarantine period and include an alternative secondary test.
c. Repeat the intradermal TB test in 7 days, using the same eyelid, as this is a grade 4 reaction. Extend the quarantine period and include an alternative secondary test.
d. This is a grade 5 reaction; the animal should be euthanized.
e. Use an alternative TB test in 14 days, and take chest radiographs while the animal is sedated.

Answer: b. Repeat the intradermal TB test in 7 days, using the opposite eyelid, as this is a grade 4 reaction. Extend the quarantine period and include an alternative secondary test.
References:
1) Fox JG, Anderson LC, Loew FM, Quimby FW. Laboratory Animal Medicine 2nd Edition. 2002. Boston: Academic Press. Chapter 16. p 724-25, 738-40.
2) Lyashchenko KP, et al. PrimaTB STAT-PAK Assay, a Novel, Rapid Lateral-Flow Test for Tuberculosis in Nonhuman Primates. Clinical and Vaccine Immunology. 2007. 14(9): 1158-1164.
Domain 1; Primary species – Rhesus macaque (Macaca mulatta)
- What is this purpose of the instrument depicted in this slide?
a. Cesium irradiating of mice
b. Body fat analysis of mice
c. Radiography of mice
d. Ultrasound of mice

Answer: c. Radiography of mice
References:
1) http://www.faxitron.com/products/lx60.html
2) Li, M et al “Osteopenia and impaired fracture healing in aged EP4 receptor knockout mice” Bone 37(1): 46-54, 2005
Domain 3
- What is the correct genus and species of this unusual rodent used as an emerging model of infectious disease research?
a. Octodon degu
b. Cynomys ludovicianus
c. Sigmodon hispidus
d. Meriones unguiculatus
e. Pachyuromys duprasi

Answer: e, Pachyuromys duprasi (fat-tailed jird)
Reference: 1) Felt SA et al, Biology, breeding, husbandry and diseases of the captive Egyptian fat-tailed jird (Pachyuromys duprasi natronensis). Lab Animal (NY), 2008, 37(6):256-61. (cover photo)
2) Felt SA et al, An Effective Venipuncture Technique and Normal
Serum Biochemistry Parameters of the Captive Fat-Tailed Jird (Pachyuromys duprasi), JAALAS, 2009, 48(1)
Domain 3; Tertiary species - fat-tailed jird
- Which of the following environmental conditions has been reported to contribute to this condition?
a. low humidity
b. high humidity
c. high ambient temperature
d. low ambient temperature
e. none of the above

Answer: b. high humidity
References:
1) http://www.peteducation.com/article.cfm?c=18+1799&aid=2463
2) Donnelly TM and Quimby FW. 2002. Biology and diseases of other rodents. In Laboratory Animal Medicine 2nd ed. (Fox, Anderson, Loew, and Quimby eds.). p. 276-277. Academic Press, San Diego
Domain 4; Secondary species – gerbil (Meriones unguiculatus)
- Inanimate models like the ______ rat can help augment animal biomethodolgy training and help reduce animal usage
a. Little
b. Koken
c. Lokie
d. Boswell
e. Always

Answer: b, Koken
Reference: 1) SL Conarello et al, Training Strategies for Research Investigators and Technicians, ILAR J, 2007, 48(2):120-130
2) http://www.kokenmpc.co.jp/english/products/life_simulation_models/animal_experiment/lm-046a/index.html
Domain 6; Primary species – rat (Rattus norvegicus)
- Which of the following statements best characterizes the biosafety cabinet depicted in the image:
a. Product protection; a minimum of 75 lfpm face velocity; suitable for work with radionuclides
b. Product protection; a minimum of 100 lfpm face velocity; not suitable for work with volatile toxic chemicals
c. Operator and product protection; 100% recirculated air; suitable for work with radionuclides
d. Operator and product protection; 70% recirculated air; a minimum of 75lfpm face velocity
e. Operator protection without product protection; 70% recirculated air; not suitable for work with toxic volatile chemicals

Answer: d. Operator and product protection; 70% recirculated air; a minimum of 75 lfpm face velocity
References:
1) Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and National Institutes of Health. 2007. Biosafety in Microbiological and Biomedical Laboratories, 5th edition. U. S. Government Printing Office: Washington, D.C. Appendix A, Section III Biological Safety Cabinets.
2) Fox JG, Anderson LC, Loew FM, Quimby FW, eds. 2002. Laboratory Animal Medicine, 2nd edition. Academic Press, San Diego, CA. Chapter 24 – Control of Biohazards, p. 1050
Domain 5


