(18.1) Pulmonary Path IV (Singh) Flashcards
(84 cards)
Why do we include the nose, nasopharynx and paranasal sinuses in pulmonary path?
All these structures are lined by respiratory epithelium
They are vulnerable to the same enviornmental factors
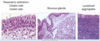
What are the normal histologic features of the nose, nasopharynx and paranasal sinuses?
Respiratory epithelium
Mucous glands
Lymphoid aggregates
What are the common causes of viral rhinitis/sinusitis?
Rhinovirus
Coronavirus
Adenovirus
Echovirus
Symptom of viral rhinitis/sinusitis?
Clear rhinorrhea
What typically causes bacterial rhinitis/sinusitis?
Superimposed infection of streptococcus pneumoniae or haemophilus influenzae
Symptom of bacterial rhinitis/sinusitis?
Thick, purulent nasal secretions
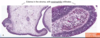
What is a common manifestation of chronic rhinitis/sinusitis?
Inflammatory sinonasal polyps

What are the histologic hallmarks of inflammatory sinonasal polyps?
Edema in the stroma
w/ Eosinophilic infiltrates
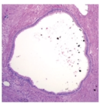
What is an example of a consequence from chronic obstruction of a sinus?
Mucocele
What is a dental consideration with sinusitis?
The pathway of infection to the sinuses!
Normal oral flora may enter the maxillary sinus by tracking along periapical tissues (oral flora)

What are the 4 major sinuses, and where are they located anatomically?
Frontal sinus
Ethmoidal sinus
Maxillary sinus
Sphenoidal sinus

What causes allergic fungal sinusitis?
Occurs as a result of hypersensitivity of fungal organisms (eg aspergillus) that have colonized the sinus tract
What are the histologic features of allergic fungal sinusitis?
Allergic mucin
May see fungal hyphae
+/- mycetoma (fungal ball)
What typically causes acute invasive sinusitis?
Zygomycosis species (mucor)
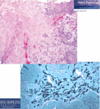
What population does acute invasive sinusitis target?
Diabetic
or
Immunosuppressed

What is the severity of acute invasive sinusitis?
VERY emergent situation
Requires IV antifungal therapy to prevent extension into brain or sepsis
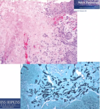
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) typically affects?
Middle aged adults
Where can GPA affect anatomically?
Nasal passages/sinuses
Lungs
Kidney
What is the unique histology associated with GPA?
Granulomatous inflammation/vasculitis
Classic “necrobiotic” necrosis

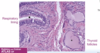
What are the benign tumors of the nose, sinuses and nasopharynx?
Nasopharyngeal angiofibroma
Sinonasal (Schneiderian) papilloma
What are the malignant tumors of the nose, sinuses and nasopharynx?
Olfactory neuroblastoma
NUT midline carcinomas
EBV related malignancies (nasopharyngeal carcinoma and extranodal NK/T cell lympoma)
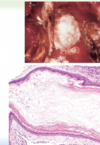
Nasopharyngeal angiofibroma
What is it?
Demographic?
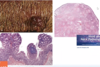
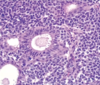
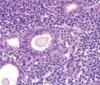
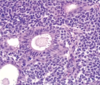
Nasopharyngeal polypoid mass
Young men
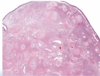
What are the unique histologic features of nasopharyngeal angiofibroma?
Vascular fibrous core lined by benign epithelium
SIMILAR TO spongiosum of erectile tissue
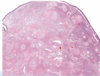
What is the MAJOR association of nasopharyngeal angiofibroma?
Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP)