(17.1) Pulmonary Pathology III (Singh) Flashcards
What is THE most significant risk factor for aquiring lung cancer?
Tobacco use in terms of duration and intensity
What is a “pack-year”?
(packs smoked per day) x (years of use)
ex: 1 pack a day for 35 years = 35 pack years
2 packs a day for 30 years = 60 pack years
What are other risk factors for aquiring lung cancer?
Radiation
Uranium
Asbestos
Radon
What genetic factors can mitigate carcinogen exposure?
P450 polymorphisms
Genes responsible for DNA repair
What are the major classifications of lung tumors?
“Small cell” vs. “Non-small cell”
What is the origin of squamous-cell carcinoma?
Coming from the respiratory epithelium
Arises from metaplastic adaptive phenomenon

What is the origin of small-cell carcinoma?
Neuroendecrine cells

What is the origin of adenocarcinoma?
Type II pneumocytes

Describe the 4 steps in the progression of pulmonary adenocarcinoma
Normal –> AAH –> AIS –> Adenocarcinoma

Atypical adenomatous hyperplasia (AAH)
Size?
Describe appearance:
Less than or equal to 5mm
Dysplastic pneumocytes present along alveoli with some interstitial fibrosis

Adenocarcinoma in Situ (AIS)
Size?
Describe appearance:
<3cm
Dysplastic pneumocytes confluently growing along alveoli

What is the most common form of lung cancer?
Pulmonary adenocarcinoma

How can you tell histologically that a lung biopsy has pulmonary adenocarcinoma?
Histology shows malignant GLANDS invading the lung tissue

What is the pathology?

Mucinous adenocarcinoma

Why is mucinous adenocarcinoma frequently misdiagnosed?
CAN MIMIC PNEUMONIA on CXR
What is the progression of squamous carcinoma?
Normal bronchial epithelium –> Squamous metaplasia –> Squamous carcinoma in situ –> Invasive squamous carcinoma

Demographic of squamous carcinoma?
Men
Smokers
Where in the lungs does squamous carcinoma occur?
Centrally
What are these?

KERATIN PEARLS
Diagnostic for squamous carcinoma

What does an orange cytoplasm represent in cytology?
Orange cytoplasm = keratin
That means wer are dealing with squamous carcinoma

What is the pathology?
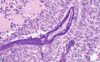
Small cell *neuroendocrine* carcinoma

What is one of the newer methods physicians use for “typing” tumors?
Molecular testing
Has implications for how you can treat them
Squamous carcinoma is correlated with….
Hypercalcemia
PTH-related peptide
What is small cell carcinoma correlated with?
SIADH (Syndrome of inappropriate ADH secretion)
Cushing’s syndrome (secretion of ACTH)













