1.3.2 Hepatitis Viruses II Flashcards
What do you know about this image?

- Hepatitis B
- Hippo Van: cause of hepatitis
- Hepadnaviridae family
- DNA virus
- Enveloped
- Undergoes intranuclear and cytoplasmic replication
- Partially double stranded DNA
- Reverse transcriptase using RNA-dependent DNA polymerase
- Transmitted via sex and blood products (sex, drugs, and rock & roll)
- Vertical transmission b/t mother and baby during birth, doesn’t cross placenta
- Part of TORCHeS
- 90% of neonatal HBV cases progress to chronic infections
- 10% of HBV progress to chronic HBV infections
- Can lead to polyarteritis nodosa (PAN)
- Rash (purpuric papules)
- Arthralgia (knee pain)
- Chronic kidney disease
- Membranous glomerulopathy
- Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis
- ALT rises during acute infection, then falls when systematic phase is over, ALT > AST
- ALT levels are often normal in neonatal HBV
- HBsAg is 1st serological marker of an active infection
- HBeAg is sign of active viral replication and a sign of high infectivity
- During symptomatic phase, pts will be positive for HBsAg and HBeAg
- Anti- HBc IgM may be only detectable serological marker during window phase of infection
- Presence of Anti-HBe is indicative of low transmissibility
- Presence of Anti-HBs is indicative of recovery from infection or prior immunization
- Immunized patients will have Anti-HBs only
- Can lead to cirrhosis
- Risk factor for HCC
- Hep D only propogates in the presence of Hep B
- Hep D = enveloped RNA virus
- Hep D: circular, single stranded DNA
- Hep D: negative-sense
- Hep D: HBsAg to be infectious
- Coinfection of Hep B and Hep D has better prognosis than Hep B alone
- Superinfection = Contraction of Hep D by a pt with chronic Hep B
- Superinfection associated with a worse prognosis
- Lamivudine is effective against Hep B
- NRTIs are effective against Hep B
- Alpha-interferons are effective against Hep B
- Give at-risk children anti-HB Ig and HepB Vaccine
What are the virions and particles associated with HBV?
Dane particle is the only infective virion

Describe the nucleic material of HBV
Partially double-stranded DNA
What is different about the production of HBeAg and HBcAg?
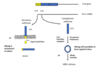
What is the process of HBV replication?
Side note: not listed in objectives specifically but is part of the pathogenesis

What is the typical progression of Acute Hep B in adults?

What is the marker of infectivity? Marker of immunity?
Infectivity: HBsAg
Immunity: anti-HBsAg
Interpret these viral panels
MUST KNOW. THERE ABSOLUTELY WILL BE A TEST ? ON THIS


Interpret this Hep B Virus panel


What HBV pt state?

Asymptomatic carrier
Liver is more or less normal except for the scattered hepatocytes with “ground glass” cytoplasm. The cytobplasm of these cells contain numerous
Which HBV pt state?

Chronic persistent hepatitis
Liver cell destruction. Inflammation is confined to the portal tracts
Which HBV pt state?

Chronic active hepatitis
Mononuclear inflammatory cell infiltrate extends from portal areas and disrupts the limiting plate of hepatocytes which are undergoing necrosis, the so-called “piecemeal” necrosis of CAH
CD8+ T cells present
What are the arrows pointing at?

Councilman Bodies - dying hepatocytes
Define the role of HBV in hepatitis D virus (HDV) disease
HDV replication requires co-infection w/ HBV, which provides HBsAg. Thus, HBV is known as a “helper virus”
What is the difference between co-infection and superinfection with HBV and HDV?

What is the typical progession of HBV-HDV Co-infection (line graph)?

What is the typical progression of HBV-HDV superinfection (line graph)?

What was isolated to developed the HBV vaccine?
Gene for HBsAg

How is the HBV vaccine administered? What % of children and adolescents develop adequate Ab to dosage?
Series of 3 IM doses
95% of children and adolescents develop adequate Ab to recommended series of 3 doses
What are three mechanisms by which HBV infection increase a patient’s risk for HCC?
Inflammation
Integration into host genome
Viral proteins (HBx)

What are some treatment/management options for patients with chronic HBV infecctions?



