12. Heart failure Flashcards
Left sided heart failure is due to
hypertension
Right sided failure is due to
chronic lung disease
Biventricular failure
LV HF = pulmonary congestion = RSHF
Clinical features of heart failure
Hypotension
Oedema
tiredness and dizziness
Cold peripheries
Atrial fibrillation
Reduced urine flow
Mechanism of Left sided heart failure - systolic dysfunction
impaired contractility + pressure overload → left ventricular systolic dysfunction→ Left sided heart failure

Left Sided Heart Failure due to Systolic Dysfunction causes an
↑ESV
↑EDV
downwards, rightwards shift in graph
Mechanism of Left sided heart failure - diastolic dysfunction
reduced V wall comp + Obstruction of LV filling → LV diastolic dysfunction → LSHF

Cardiac Failure - Diastolic dysfunction
↓ EDV
↓ SV
upwards shift in graph
Compensatory mechanisms in heart failure

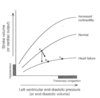
a. Cardiac performance increases as a function of pre-load
b. ↓ V contractility = ↑ EDV = so fall in SV is less
c. ↑ LV filling = pulmonary congestion
In Heart Failure a reduced Stroke Volume and hence Cardiac Output activates:
- Sympathetic reflexes
- ADH release
- Renin angiotensin system
Drugs used to treat
heart failure
- Diuretics
- Positive inotropes
- Vasodilators
- Beta adrenoceptor antagonists

a. ↓ SV, ↑LVEDP = pulmonary congestion
b. Diuretics reduce pc but do not increase SV
b’. Excessive diuresis = ↓SV = hypotension
Inotropic therapy (c) and arteriolar dilation (d) ↑ SV = ↑ V emptying = ↓LVEDP
e. represents the potential of combining vasodilator and inotropic therapy
Treatment of Heart Failure - Vasodilators
act on the venous side = ↓pre-load, ↓ risk of p.c
act on the arterial side = ↓after-load, ↑SV
Venodilator
nitrates
mixed vasodilators
nitroprusside
alpha-adrenergic blockers
ace inhibitors
alpha2-central agonists
arteriolar dilators
hydralazine
minoxidil
CCBs
Inotropes
Stimulate cardiac b1 receptors
Short 1/2 life
IV infusion via central line
Risk of arrhythmias
May increase myocardial oxygen demand
K+ losing diuretics
1) Loop diuretics
2) Thiazide diuretics
K+ sparing diuretics
1) Aldosterone antagonists
2) Aldosterone independent
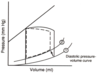
Left Sided Heart Failure due to Systolic Dysfunction change in graph
a downward and rightward shift in the relationship (from 1 to 2)

Left Sided Heart Failure due to Diastolic dysfunction change in graph
curve is shifted up (1 to 2)
Heart failure can be indicated on an echocardiogram by an ejection fraction less than…
45%
Furosemide
Loop diuretic
Bumetanide
Loop diuretic
Bendroflumethiazide
Thiazide diuretics
Spironolactone
Aldosterone antagonist
Eplerenone
Aldosterone antagonist
Amiloride
Aldosterone independent


