11. Gut as an Immune Organ Flashcards
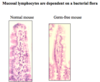
Villi give the intestine a huge SA. Describe 2 diseases that affect the villi.
Where are CD4 and CD8 cells fround in the GI tract, and what do they do?
What type of cells does HIV kill?

Norovirus: villi shink and disappear so can’t absorb food. Coeliac disease: T cell immune reponses made to gluten, and villi disappear
CD4: T helper, live in lamina propria, involved in coeliac disease, activated by antigen presenting cells
CD8: cytotoxic, in epithelium/close to, kill viral infected epithelial cells
CD4 T cells -> patients get gut and lung infections from low grade pathogens
Label A-D of the ileum. What are the clear cells?

A: Epithelium
B: Core of villus full of lymphocytes
C: Lymph node
D: Gut lumen
Clear cells = goblet cells
What is Cryptosporidium?
What are Peyer’s patches?
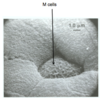
What are M cells?
Protozoan parasite, lives on surface of epithelial cells and causes them to secrete H2O. T cell immune system deals with low grade infections.
Lymph nodes of the gut - organised lymphoid follicles. Imp part of GALT. Mainly in distal jujenum and ileum.
Phagocyte-specialised epithelial cell: takes antigens from lumem and presents to T cells below (transports gut antigens across epithelium into body).
How does cholera infect the GI system?
Waterbourne disease. Sits on microvilli and secretes cholera toxin which enters epithelial cell and causes secretion of H2O, Na+, K+, Cl−, and HCO3− into the lumen of the small intestine and rapid dehydration.
What is the micrograph showing?
What does the arrow indicate?

Peyer’s patch from normal highly-activated individual.
Arrow = germal centre (B cells dividing)
What is gut-specific homing?
What vitamin is important in this process and why?
Gut-specific homing is the mechanism by which activated T cells and antibody-secreting cells (ASCs) are targeted to both inflamed and non-inflamed regions of the gut in order to provide an effective immune response. Relies on interaction between integrin α4β7 and the addressin MadCAM-1 on the surfaces of the appropriate cells
Vit A - imprints cells to home to gut mucosa from Peyer’s patches. Vit A turned to retinoic acid (by retinal dehydrogenase) = signalling molecule, switch on genes: CCR9 receptor and α4β7 integrin on T cell.

How do gut homing cells know to home to the gut?
Describe IgA and IgM. What can they form?
How is IgA transported across the epithelium?
Why are people with an IgA deficiency (common) usually symptomless?
Epithelial cells make CCL25 (ligand for CCR9) and endothelial cells in gut express MadCAM (the ligand for α4β7)
IgA: dimer in mucous secretions. IgM: pentamer in plasma. Both can form multimers, initiated by J chain. Too big to diffuse into gut so need transporters.
By polymeric Ig receptor made by epithelial cell. It binds J chain of IgA, taken in, transcytosed across cell, and J chain cleaved off at end when it’s passed out into gland lumen.
IgM has J chain and is taken up too, so get compensatory IgM responses.

What are the isotypes of IgA?
Describe how IgA makes you immune to cholera.
Two isotypes: A1 and A2 (mucosal plasma cells, has resistance to IgA1 proteases from some bacteria= most recent evolved isotype!)
IgA binds molecules of pathogenic viri/bacteria together to keep them out of the mucus = agglutination. Swept away by peristalsis.
What happens to gut-specific homing during breastfeeding?
Do newborns have IgA?
What does Peyer’s patch immune activation depend on?
Some B cells which leave Peyer’s patch move to the breast and make IgA - they know to go there because MadCAM expression and secretory component in polymeric Ig expressed on mammary epithelial cells -> protect baby.
No, only IgG (transferred over placenta). Breast feed to transfer IgA and protect from antigens.
Flora

What is the immune system in the gut essentially driven by?
Where are gut T and B cells activated?
What actively transports IgA across the epithelium?
Commensal bacteria living in the gut - mucosal lymphocytes depend on bacterial flora
In Peyer’s patches (PP). Then they migrate to mucosa.
Poly Ig receptor made by epithelial cell