11. Enzymes Flashcards
What is an enzyme? Explain in a wider sense
Enzymes - biological catalysts made from protein
Can work both alone and in groups (attached to a scaffolding protein)
Structure is essential to function, only tiny amount of am a are the catalytic site but all other am a are important
Active site = binding site + catalytic site
Enzymes are essential to metabolic pathways
Enzymes are very specific - speed up only particular reactions - heat speeds up all the reactions in the system
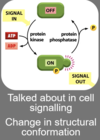
In catalysis enzyme changes its conformation
Enzymes not only catalyse the reactions but also hold together the unstable intermediate for them to react and form products
Enzymes are re-usable
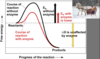
Explain activation E
Heat can be used as activation E

Explain the role of catalysts in a reaction
Enzymes can only speed up reactions that would happen anyways - cannot change an endergonic reaction to exergonic - even catalysed reactions need an E input to procede (but much lower)
What is the enzyme catalysed recation equation?
Enzymes not only catalyse the reactions but also hold otgether the unstable intermediate for it to react and from products

What are the mechanisms by which enzymes can lower Ea?

How does the reaction rate graph change when a catalyst is introduced?
Uncatalysed - directionally proportional relationship between [substrate] and velocity
Catalysed - velocity increases but plateus after a certain point - not enough substrate
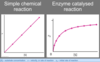
Explain the enzyme catalysed reaction rate graph? What are Vmax and Km?
Vmax and Km are for a certain environments (pressure, temperature, pH)
Vmax - where plateau (in this graph plateau hasn’t been reached)

For what can Vmax and Km be used?
For comparing different enzymes in the same conditions

How can enzyme activity be regulated?
Rate can be increased / decreased
Regulation can done by:
- cofactors (not proteins - organic/inorganic)
- phosphorylation
- allosteric sites (activation and inhibition)
- inhibitors (competitive / non-competitive)
- temperature
- pH
Explain cofactors in regulating enzyme activity
Cofactors usually essential nutrients - are not produced by the body - must be consumed with food
- organic / inorganic
- prosthetic / cosubstrates

Explain phosphorylation in regulating enzyme activity
Phosphorylation can activate enzymes - attaching phosphate group - changing conformation into active
How can pH and temperature regulate enzyme activity?
Denaturation
Optimal temperature / pH

Explain how can inhibitors regulate enzyme activity
- competitive - binds to the active site - shares homology with substrate - to resume the work of enzyme - add more enzyme (treatment for sarin leakages)
- non-competitive - change conformation of enzyme - some reduce efficacy (not completely destroy the efficiency) - some reactions still happen - to overcome the inhibitor
- if inhibitor produced by the organism: stop its production / induce degradation
- reversible inhibitor -
- irreversible inhibitor - CO, CN - toxic usually - important to keep non bound enzymes in organism able to work

Explain allosteric enzyme activators and inhibitors
Allosteric molecules can be activators or inhibitors - usually for enzymes with multiple active sites - allosteric bind to their own active site on the enzyme, not substrates’

What is cooperative binding?
Cooperative binding - substrate binds to one of the active sites and locks the enzyme into an active conformation - ex: O2 and haemoglobin - increases efficacy



