Zoonoses II Flashcards
(57 cards)
What organism causes Cat Scratch Disease?
Bartonella henselae
T/F Cat scratch disease is a serious, life threatening disease in all humans
FALSE Self limiting disease in immunocompetent hosts (no abx needed)
Lesions from B. henselae demonstrate _____ spread, and will cause a _____
Demonstrate lymphatic spread Will cause a regional lymphadenopathy
What is the manifestation of Cat Scratch disease (B. henselae) characterized by sepsis in immunocompromised patients?
Bacillary Angiomatosis
Lesions of Bacillary Angiomatosis from B. henselae resemble _____, and must be distinguished by biopsy.
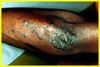
Kaposi Sarcoma
What sequelae of Cat Scratch disease (B. henselae) is characterized by the presence cystic, blood filled lesions in the liver and spleen parenchyma of immunocompromised patients? What are some other symptoms of this sequelae?

Hepatic or Splenic Peliosis
Other sx: Target organ enlargement, weight loss, nausea, fever, and elevated liver enzymes and alkaline phosphate.
How is Cat Scratch disease (B. henselae) diagnosed?
Serology and physical findings
The organism is hard to culture
How is bacillary angiomatosis and peliosis caused by B. henselae infection of immunocompromised patients treated?
Erythromycin/Doxycycline
B. henselae appears as a gram _____, slightly curved _____
B. henselae appears as a gram NEGATIVE, slightly curved ROD
The disease caused by Ehrlichia chaffeensis, Ehrlichia ewingii and Anaplasma phagocytophilum is similar to RMSF except that _____. What is the vector? What kind of cells do they infect? Tx?
Presents with NO rash and leukopenia/thrombocytopenia
Vector = ticks
They infect monocytes and granulocytes
Tx: Tetracycline or chlorampheniol
What organism(s) cause Human Monocytic Ehrlichosis (HME)? Human Granulocytic Ehrlichosis (HE)?
HME: E. chaffeensis
HE: E. wingii/A. phagocytophilum
T/F: HME and HE always presents as a self limiting disease
FALSE
Depending on the severity (# of WBC infected), HME and HE can be fatal
Pasteurella multocida appears as a gram _____ _____
Gram negative rod
What are the two virulence factors of Pasteurella multocida?
1) Anti-phagocytic capsule
2) Endotoxin
How is Pasteurella multocida transmitted?
Through bites/scratches from cats or dogs (found in their oral cavity)
Pasteurella multocida causes _____ within 1-2 days after a bite. It presents as _____ in COPD patients.
Cellulitis 1-2 days after bite
Chronic lung infection in COPD patients

How is Pasteurella multocida diagnosed? Tx?
Diagnosis: Routine culture
Tx: Beta-lactams
The polypeptide capsule of Bacillus anthracis is made of _____ and provides the organism with protection from _____
Made of D-glutamic acid
Protects B. anthracis from phagocytosis
What virulence factor of B. anthracis is immunoprotective, is a component of the anthrax vaccine, and is a common binding subunit for other toxins?
Protective Angiten (PA)
B. anthracis Edema Toxin causes cell swelling and burst? How does it accomplish this?
Edema Toxin is an adenylate cyclase that increases cAMP
What virulence factor of B. anthracis cleaves MAP kinase? What does this induce in the host?
Lethal Toxin
Induces apoptosis and T cell proliferation
The virulence factors of B. anthracis are found _____ that are required for the organisms virulencs
Found on two plasmids. Both are required for virulence
T/F B. anthracis is an obligate aerobe
TRUE
_____ of B. anthracis represent the resting stage of the organism. They are very very resistant to disenfectants.
Spores








