Week 2 tute - autoimmune and inflammation Flashcards
what is type I hypersensitivity also called?
immediate hypersensitivity
what is type I hypersensitivity mediated by?
IgE antibodies attached to mast cells or basophils
how long after exposure does type I hypersensitivity occur?
within 30 minutes of exposure
describe the steps of type I hypersensitivity
- Sensitisation: TH2 releases interleukins in the prescence of Ag to cause B cells to make a new kind of Ab (IgE) for that Ag. New Abs bind to FcERI on mast cells (or basophils)
- Activation: next time IgE encounters Ag, Ag induces crosslinking of IgE on mast cell/basophil. Degranulation of mast/basophils releases vasoactive mediators
- Effector step: Pharmacological effect (vasodilation, oedema, brochoconstriction) and chemotaxis resulting in further inflammation (mainly from eosinophils)

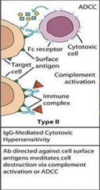
what is type II also known as?
Cytolytic or Cytotoxic
which antibodies is type II hypersensitivity mediated by?
IgG or IgM antibodies binding to antigens on cell surfaces
describe the steps of type II sensitivity
- IgG or IgM antibodies binding to antigens on cell surfaces
- activating the complement cascade
- cell destruction
which immunoglobulin/antigen complexes is type III hypersensitivity mediated by?
Ag-IgM or Ag-IgG complexes
how long after exposure does type III hypersensitivity occur?
within hours of challenge with antigen
describe the steps of type III hypersensitivity
- antigen binds to immunoglobulin
- Ag-IgM or Ag-IgG complexes activate complement
- granulocytes (e.g. neutrophils) are attracted to the site of activation
- damage is caused by the release of lytic enzymes.

what is type IV hypersensitivity also known as?
delayed-type hypersensitivity
which cell is type IV (Delayed-type hypersensitivity) mediated by?
Th1 cells
which 2 cells are involved in type IV (Delayed-type hypersensitivity)?
cytotoxic T cells (CD8+) and Th1 cells (CD4+)
which antibodies are involved in type IV hypersensitivity?
there is no antibody involvement in type IV, you muggle
describe the steps of type IV hypersensitivity
- antigen causes Th1 cells to release cytokines
- accumulation & activation of macrophages and activation of cytotoxic T cells which mediate local damage

how long after exposure does type IV reaction occur?
days-weeks after challenge with antigen
What % of the western world suffers from allergies?
20%
What is atopy?
A predisposition toward developing IgE mediated hypersensitivity allergic reactions.
IgE is important for the sensitisation stage of type I hypersensitivity, how is IgE produced and what cytokines are involved? Where is it localised?
Sensitization:
- Ag presenting cell (dendrocyte or macrphage) presents Ag to naive T-helper in lymph nodes
- Naive T-helper binds to Ag and costimulating factor of Ag presenting cell, in the prescnece of cytokines IL-4, IL-5 and IL-10 is “primed” and becomes a TH2 cell
- TH2 releases their own IL-4 and IL-13 causing B cell to undergo Ab class switching - B cell switches from producing IgM to IgE Abs. TH2 also releases IL-5 to stimulate eosinophil maturation/activation
- IgE Abs bind to FcERI in mast cells, once mast cell is loaded with Abs it can crosslink with Ag upon next exposure and degranulate
How does IgE contribute to the activation stage of type I hypersensitivity?
Post sensitisation (eg months later) IgE binds to FcERI on mast cells (and occasionally basophils). On exposure to the specific Ag that the IgE Abs have been sensitised to, Ag binding causes cross linking, resulting in degranulation and the release of histamine and other inflammatory mediators to the local tissues
Name the inflammatory mediators released by mast cells and what are the effects of these reagents?
Histamine, cytokines and chemokines are released from granules, leukotrienes, protoglandins and PAF are synthesised in plamsa membrane.
- Histamine: binds to H1 receptors cells causing vascular permeability and oedema of edothelial cells and smooth muscle contractions causing bronchoconstriction in the lungs. Binds to H2 receptors causing mucus secretion from respiratory mucosa & release of stomach acid from gut mucosa.
- Cytokines and chemokines: IL-3, IL-4, IL-5, IL-8, IL-9, TNF-α and GM-CSF recruit inflammatory cells - neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils, macrophages and lymphocytes.
- Leukotrienes and prostaglandins (very potent): contraction of bronchial and tracheal smooth muscle, increases vascular permeability and mucus secretion. Contributes to prolonged bronchospasm and mucus build-up in asthma.
- Platelet activating factor (PAF): causes platelets to aggregate and release their mediators, including histamine.
What are the differences between the early and late stages of an allergic response? What cell types & cytokines are involved in the late stage?
Early phase: happens within minutes, caused by direct effects on blood vessels and smooth muscle by mediators such as histamine (IgE/mast cell mediation)
Late Phase: happens 6-10 hours after initial allergic reaction and can last for days. Caused by influx of inflammatory eosinophils, neutrophils, basophils, macrophages and TH2 cells attracted by the cytokines and chemokines secreted by mast cells.
- Eosinophils make the biggest appearance. They are attracted to IL-4 and chemokines secreted by mast cells and casued to differentiate and grow by IL-3, IL-5 (main player) & GM-CSF secreted by TH2. Eosinophils express FcεRII for IgE and Fc receptors that bind IgG, which, when bound to the antigen cause degranualation and released inflammatory mediators (e.g. leukotrienes, major basic protein, eosinophilic cationic protein, eosinophilic peroxidase and platelet activating factor) causing extensive tissue damage (particularly to respiratory epithelium in asthma).
- Neutrophils also contribute to the late phase. They migrate in response to IL-8 (neut. chemotatic factor) from mast cells. Their surface IgG Fc receptors bind antibody coated antigen causing cell activation, phagocytosis of antibody-antigen complexes and the release of leukotrienes & lysosomal enzymes that cause tissue damage.
- Th2 lymphocytes release cytokines that cause a second wave of muscle contraction and sustained edema.
How do mast cells contribute to an allergic reaction?
- IgE binds to mast cells
- Ag binds to IgE causing crosslinking
- Degranulation of mast cells releases:
- Histamine causes vasodilation/oedema and bronchoconstriction.
- Leukotrienes and prostaglandins cause bronchoconstriction and muscous production.
- Platelet activating factor causes platelets to aggregate and release histamine.
- Interleukins recruit other WBCs.
Name some diseases associated with type I hypersensitivity.
- asthma
- anaphylaxis
- acute urticaria (hives)
- seasonal rhinoconjunctivitis (hayfever)
- food allergy
Explain what happens in anaphylaxis.
- Allergen cross links with IgE which is bound to FcεRI on mast cell
- Mast cell activation and degranulation releasing histamine, cytokines and chemokines and synthesis and release of prostaglandins, leukotrienes, and platelet-activating factor from the plasma membrane
- Recruitment of TH2 lymphocytes, eosinophils, and basophils.
- Histamine causes vasodilation/oedema and bronchoconstriction.
- Leukotrienes and prostaglandins cause bronchoconstriction and muscous production (trachea and GIT).
- Platelet activating factor causes platelets to aggregate and release histamine.
- Interleukins recruit other WBCs.

Allergy has a key role in the majority of asthma cases, but non-allergic asthma is also a possibility, explain.
Non-allergic asthma (not IgE-mediated) associated with exposure to air pollution, cigarette smoke, diesel particles, cold air, exercise and infection. Irritant acts on lung epithelium triggering release of IL- 33. This binds to ST2 receptors on ILC2 (type 2 innate lymphoid cells) to activate them to release IL-5, IL-13 and other type 2 cytokines resulting in inflammation plus eosinophil recruitment/degranulation.

what type of hypersensitivity is this?

Type I hypersensitivity
Match the immunoglobulin class to its main function:
A. IgD
B. IgE
C. IgM
i. agglutination, complement activation, primary B cell receptor and opsonophagocytosis
ii. activation of mast cells and eosinophils
iii. primary B cell receptor
A. IgD = iii. primary B cell receptor
B. IgE = ii. activation of mast cells and eosinophils
C. IgM = i. agglutination, complement activation, primary B cell receptor and opsonophagocytosis
IgE is important for the sensitisation stage of type I hypersensitivity, how is IgE produced and what cytokines are involved? Where is it localised?
- Naive T cell is presented with Ag and becomes primed, under the influence of IL-4, IL-5 and IL-10 it becomes a Th2 cell
- Th2 releases IL-4, IL-5 and IL-13 causing B cells to become plasma cells, stop producing IgM and start producing IgE specific to Ag
- IgE binds to fuckery on mast cell surface, reintroduction of Ag causes crosslinking and degranulation of mast
- Occurs mostly in mucosal and epithelial tissues, in the vicinity of small blood vessels and in the subendothelial connective tissues as this is where mast cells live. Basophils also act like mast cells and can bind to Ab in the blood.


