Week 2 lec - immunology fundamentals Flashcards
where are T cells matured?
the thymus
where do B cells mature?
In the bone marrow
osteoclasts, Kuppfer cells (liver) and microglial cells are all types of ________
macrophages
after maturation, where do B and T cells move to?
various lymphoid tissues
viruses, bacteria, helminths and mites are all types of _____ ___-_____
pathogenic micro-organisms
bacterial toxins are a product of a ____ ___-______
pathogenic micro-organism
____ proteins may neutralise viruses and bacterial toxins
plasma proteins
the process of ingestion and killing of pathogens by leukocytes is known as _____
phagocytosis
humoral immunity involves c_____ + a______
complement and antibodies
infected cells are contained by g_____
granulomas
the ____ immune response has a rapid onset (hours to days) whereas the ____ immune response has a slow onset (days to weeks)
choose from: adaptive, innate
the innate immune response has a rapid onset (hours to days) whereas the adaptive immune response has a slow onset (days to weeks)
Humoral immune response is:
- Innate and adaptive immune responses mediated by soluble (cell-free) proteins in plasma, interstitial fluids and mucosal secretions
- Innate and adaptive immune responses mediated by cells of the immune system -Particularly effective against intra-cellular pathogens
pick 1
- Innate and adaptive immune responses mediated by soluble (cell-free) proteins in plasma, interstitial fluids and mucosal secretions
Cellular immune response is:
- Innate and adaptive immune responses mediated by soluble (cell-free) proteins in plasma, interstitial fluids and mucosal secretions
- Innate and adaptive immune responses mediated by cells of the immune system -Particularly effective against intra-cellular pathogens
- Innate and adaptive immune responses mediated by cells of the immune system -Particularly effective against intra-cellular pathogens
Give one example of how the complement system exerts an antimicrobial effect
Could have chosen any of the following:
- forms a membrane attack complex (MAC) to lyse bacteria
- opsonisation of pathogens
- triggers release of histamine from mast cells
- enhances clearance of Ab-Ag complexes

which Ig is a primary B cell receptor?
IgD (also IgM but it has more functions than that)
which Ig has roles as primary B cell receptor, plus roles in agglutination, complement activation and opsonophagocytosis?
IgM
which Igs function as broad complement and cell activators?
IgG1 and IgG3
Which Igs are mucosal antibodies?
IgA1 and 2
which Ig activates mast cells and eosinophils?
IgE
which Ig is involved in opsonophagocytosis of complex antigens?
IgG2
which Ig is passed from mother to baby via the placenta?
IgG
which Ig is passed from mother to baby via titty juice?
IgA
give 3 functional effects of antibodies to pathogenic microbes
Could have chosen from any of the following:
- Neutralisation of bacterial toxins and viruses
- Opsonisation (for phagocytosis by neutrophils, macrophages/monocytes, dendritic cells)
- Activation of the complement pathway
- Activation of NK cells Antibody-dependant cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC)
- Activation of basophils/mast cells
- Activation of eosinophils
name a toxin-producing bacteria and the disease it causes

what are the steps of phagocytosis?
- chemotaxis and adherence of microbe to phagocyte
- ingestion
- formation of phagosome
- formation of phagolysosome (fusion of phagosome and lysosome)
- digestion
- formation of residual body containing undigested material
- discharge of waste

name a cell surface molecule that can activate phagocytosis
FcR (there are many others but this is the only one we have learnt about)
which cells carry out phagocytosis of opsonised antigens?
neutrophils, macrophages/monocytes, dendritic cells (conventional or plasmacytoid)
Functional phagocytotic effect of activating neutrophils?
intracellular killing (bacteria and fungi)
Functional phagocytotic effect of activating monocytes/macrophages?
antigen processing and presentation to B and T lymphocytes as well as intracellular killing of bacteria, mycobacteria and fungi
Functional phagocytotic effect of activating conventional dendritic cells?
antigen processing and presentation to B and T lymphocytes
Functional phagocytotic effect of activating plasmacytoid dendritic cells?
production of type 1 interferons
what does ADCC mean?
Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity
what cells perform Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC)?
NK cells
which antibody activates eosinophils to destroy helminth parasites?
IgE
give one effect of mast cells activation
HOLY SHIT THERE ARE SO MANY

what type of mycobacterium is phagocytosed by macrophages but evades killing?
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
what type of cells respond to antigen presentation by MHC class I?
CD8+ T cells
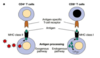
MHC class I presents antigens via the E_______ pathway
endogenous
what type of cells recognise antigens displayed on MHC class II?
CD4+ T cells
MHC class II presents antigens via the E______ pathway
exogenous
no idea what we’re supposed to learn from this image, but it seems important

what do CD4 cells release when presented with antigen on MHC class II?
cytokine IFN-y

what do CD8 cells release when presented with antigen on MHC class I?
3 cytolytic things - granzymes, perforin and fas ligand
2 cytokines - IFN-y and TNF-a

Induced Treg cells
- what cytokines cause a naive CD4 T cells to mature into this?
- what cytokines do these cells produce/release and what is its effect?
- IL-2 and TGF-beta
- IL-10 - regulation, suppression of inflammatory response

Th17 cell
- what cytokines cause naive CD4 T cells to mature into this?
- what cytokines do these cells produce/release and what is its effect?
- IL-6 and TGF-beta
- IL-17A, IL-17F and IL-22 - inflammation
Th2 cells
- what cytokines cause naive CD4 T cells to mature into this?
- what cytokines do these cells produce/release and what is its effect?
- IL-4
- IL-4, IL-5, IL-13 - allergic and helminth responses

Tfh cells
- what cytokines cause naive CD4 T cells to mature into this?
- what cytokines do these cells produce/release and what is its effect?
- IL-6 and IL-21
- IL-4 and IL-21 - germinal centre help
Th1 cells
- what cytokines cause naive CD4 T cells to mature into this?
- what cytokines do these cells produce/release and what is its effect?
- IL-12, IFNy
- IFNy, TNF - macrophage activation, inflammation

Cytolytic CD4 T cell
- what cytokines cause naive CD4 T cells to mature into this?
- what cytokines do these cells produce/release and what is its effect?
- IL-2
- granzyme B, perforin, Fas ligand (FASL) - kills infected cells
what is a granuloma and what infection would you most commonly find one in?
a bunch of leukocytes and necrotic cells at the site of infection, commonly seen in TB

what do T follicular helper (Tfh) cells do?
provide help for B cells in germinal centres

give one mechanism used by T-reg cells

what type of T cell helps CD8 cells in their response?
CD4

what does class I HLA do?
present peptides ( ie fragments of virus) to CD8
where in the body are naive T cells presented with antigens?
lymph nodes
what is the name of the process where lymphocytes with an affinity for self-antigens are deleted? where does this happen?
central tolerance, in the bone marrow or thymus
where does peripheral tolerance occur?
lymphoid organs (lymph nodes and spleen)


