W2: S10 - Pharynx Flashcards
What are the three parts of the pharynx?
- Nasopharynx
- Oropharynx
- Laryngopharynx

What forms the roof oof the nasopharynx?
Nasopharyngeal tonsils
In relation to the larynx, where does the laryngopharynx lie?
Posteriosuperior

During swallowing, what prevents a bolus from entering the nasopharynx?
Soft palate muscles

During swallowing, what prevents the bolus from entering the larynx?
Epiglottis

How many layers does the pharynx have?
3
What are the 3 layers of the pharynx?
- Outer muscular layer
- Middle fibrous layer
- Inner mucous membrane
How can the outer muscular layer of the pharynx be further divided?
- Outer circular layer
- Inner longitudinal layer
What muscles form the outer circular layer?
Pharyngeal constrictor muscles

What muscles form the inner longitudinal layer?
- Stylopharyngeus
- Salpingopharyngeus
- Palatopharyngeus
What muscle is shown here?

Stylopharyngeus
What muscle is shown here?

Salpingopharyngeus
What muscle is shown here?

Palatopharyngeus
What’s the role of the fibrous pharyngeal layer?
Connects with deep fascia
Fills in gap between muscles
Where does the pharynx recieve innervation from?
The pharyngeal plexus

What 2 cranial nerves form the pharyngeal plexus?
Vagus
Glossopharyngeal
Which of the cranial nerves provides sensory innervation to the pharynx?
Glossopharyngeal
Which nerve of the pharnygeal plexus provides most of the motor innervation?
Vagus
What is the role of the pharyngeal constrictors during swallowing?
Peristalsis
What is the action of the longitudinal muscles during swallowing?
Shorten and widen the pharnyx
What is Waldeyer’s ring?
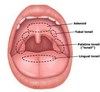
A collection of lymphoid tissue that protects the entrance to the oropharynx (also known as the pharyngeal lymphoid ring)
What is the purpose of Waldeyer’s ring?
First line of defence


