Vision loss - Gradual Flashcards
In general how does gradual types of vision loss generally occur ?
- Usually bilaterally
- Early with reduced visual acuity
- Late with reduced fields
What is the acronym for remembering the causes of gradual vision loss ?
- Cataract
- Age related macular degeneration (dry type)
- Refractive error
- Diabetic retinopathy (covered in other lecture)
- Inherited diseases e.g. retinitis pigmentosa
- Glaucoma
- Access (to eye clinic) Non-urgent
CARDIGAN
Describe the typical presentation of cataracts
- Blurred or cloudy vision
- Cloudiness of the lens
- Absent red reflexes
What are some of the causes of cataracts ?
- Age related
- Congenital – intrauterine infection e.g. Rubella, CMV, Toxoplasmosis (importance of checking red reflex in neonates)
- Traumatic
- Metabolic – diabetes
- Drug-induced (steroids)
What is the treatment of cataracts ?
- If symptomatic - then surgery (Phaco-emulsification with intra-ocular lens)
What is dry ARMD & what is it characterised by?
- Essentially ‘wear and tear’ of the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE)
- Characterised by deposition of drusen (hard or soft) and RPE hypo/hyperpigmentation
- Results in slow, progressive drop in central VA
What are the common signs/symptoms of Dry ARMD?
Symptoms:
- Gradual decline in vision
- Central vision missing
Signs:
- Drusen (the yellow patches)
- Atropic patches of retina
- Sometimes haemorrhage at macula

What is the treatment of Dry ARMD?
No cure so supportive with vision aids e.g. magnifiers
Define what is meant by refractive error ?
This is disorders to do with the size and shape of the eye preventing the eye from being able to focus clearly
What are the 4 main types of refractive error ?
- Myopia
- Hypermetropia
- Astigmatism
- Presbyopia
Define myopia
- This is short-sightedness
- The light focuses in front of the retina
Define hypermetropia
- This is long sightedness
- The light is focuses behind the retina
Define astigmatism
- This is where images are distorted longitudinally or vertically.
- This is caused if the cornea and lens does not have the same degree of curvature in the horizontal and vertical planes
Define presbyopia
- This is where with age the lens stiffness preventing it from quickly changing in shape going from far away objects to up-close ones
- Hence the need for reading glasses as you get older
- (this is normal age-related refractive error)
What is done to correct refractive errors ?
Corrective glasses given
Specifically what type of lens is used to correct myopias ?
Concave lens’s
Specifically what type of lens is used to correct hypermetropias?
Convex lens’s
Describe the overall idea of how gluacomas result in vision loss ?
- May be due to raised IOP but pathogenesis not fully understood
- But essentially there is damage to the optic nerve therefore vision loss
What are the 2 main classes of glucaoma’s?
Open and closed gluacomas
How do patients typically present with close-angle gluacomas ?
- Acutely
- Very painful red eye
- Visual loss
- Headache
- Nausea
- Vomiting
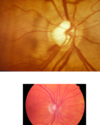
What are the signs/symptoms of open-angle gluacomas ?
Often symptomless
Signs:
- Increased cup to disc ratio (>0.7)
- Notching of optic cup
- Optic disc pallor - indicating optic atrophy
- Bayonetting of vessels - vessels have breaks as they disappear into the deep cup and re-appear at the base
- Peripheral vision loss & decreased VA
- +/- raised IOP
What is the first-line treatment of open angle gluacomas ?
1st line: (eye drops)
1st line = Topical ophthalmic prostaglandin analogues - e.g. lantanoprost, tovoprost (think oprost)
2nd line either:
- Topical ophthalmic beta-blockers - just think olol
- Topical ophthalmic carbonic anhydrase inhibitors - e.g. dorzolamide (think zolamide)
- Topical ophthalmic alpha-2 adrenergic agonists - e.g. apraclonidine (think onidine)
What is the treatment of acute close-angle glaucoma’s ?
- 1st line: carbonic anhydrase inhibitors and/or topical beta-blocker and/or topical alpha-2 agonist
- adjunct: topical ophthalmic cholinergic agonists - e.g. pilocarpine
- adjunct: hyperosmotic agents - e.g. glycerol
- plus: laser peripheral iridotomy after acute attack resolved


