Papilloedema Flashcards
(11 cards)
Define the slight difference between optic disc swelling in general and papilloedema ?
- Swollen disc means disc swelling secondary to ANY cause
- Papilloedema refers to swollen optic discs due to raised ICP
What should be suspected in all patients with bilateral optic disc swelling until proven otherwise ?
- Raised ICP due to a space occupying lesion (SOL)
- This is a med emergency
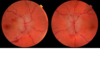
How does the optic discs become swollen due to raised ICP?
- Raised ICP is transmitted onto the Subarachnoid space (SAS) around optic nerve (ON)
- This causes interruption of axoplasmic flow and venous congestion= swollen discs
What are the 3 components which together make up ICP
- Brain (80%)
- Blood (10%)
- CSF (10%)
What can happen if there is raised ICP ?
- The brain can be squeezed out of the foramen magnum as rest of the skull is solid and doesn’t vary in size
- This can then result in death
How does malignant hypertension result in disc swelling/rasied ICP?
- Failure of autoregulation of blood supply to the brain
- Resulting in ischaemia and swelling
What are the causes of raised ICP in-relation to CSF?
- Obstruction to CSF circulation
- Overproduction of CSF
- Inadequate absorption
What investigations should be done to find the cause of raised ICP ?
- Ophthalmoscope to first off see the disc swelling
- Scan of the head
- Check BP
- And lumbar puncture to check CSF
What are the potential complications of chronic disc swelling ?
Loss of visual function occurs and blindness may result.
What are the causes of papilloedema ?
- space-occupying lesion: neoplastic, vascular
- malignant hypertension
- idiopathic intracranial hypertension
- hydrocephalus
- hypercapnia
What are the features of papilloedema seen on fundoscopy ?
- venous engorgement: usually the first sign
- loss of venous pulsation: although many normal patients do not have normal pulsation
- blurring of the optic disc margin
- elevation of optic disc
- loss of the optic cup
- Paton’s lines: concentric/radial retinal lines cascading from the optic disc



