Viral Infections Flashcards
DNA virus in the herpesvirus family; HHV-1 (oral) and HHV-2 (genital)
herpes simplex virus
children, sometimes adults; diffuse painful shallow ulcers; fever malaise; lymphadenopathy; one episode- 10 to 14 days; virus remains dormant in sensory or autonomic ganglia
primary herpetic gingivostomatitis
punched out areas at gingival margins

primary herpetic gingivostomatitis

primary herpetic gingivostomatitis
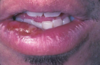
primary herpetic gingivostomatitis
reactivation of virus; asymptomatic shedding vs. symptomatic; can be stimulated by UV light, trauma, stress
recurrent herpes labialis

recurrent herpes labialis
perioral skin or vermilion; prodromal itching or tingling; cluster of vesicles; heal with crusting- 7 to 10 days
recurrent herpes labialis

recurrent herpes labialis
recurrence on thumbs or fingers; less common with universal use of gloves
herpetic whitlow

herpetic whitlow
relatively uncommon; usually few symptoms; cluster of shallow ulcer- intact vesicles rare; mucosa bound to periosteum (Hard palate and attached gingiva); heal within one week
recurrent intraoral herpes

recurrent intraoral herpes
reactivation of virus; any oral mucosal surface; large shallow ulcers; scalloped, elevated borders; antiviral meds indicated; may co-infect with CMV
Herpes in the Immunocompromised host

hepes in the immunocompromised pt
acantholysis and ulceration of the epithelium; epithelial cells at margin of ulcer show ballooning degeneration and multiple anglulated nuclei; Tzanck cells- Acantholytic epithelial cells; mixed inflammatory infiltrate
herpesvirus infection
ballooning degeneration

herpesvirus infection
Primary herpes treatment: antiviral meds if recongnized early (1st _ hrs)
72
primary varicella-zoster infection; upon resolution, the virus will remain dormant in sensory nerve ganglia; reactivation- shingles
chicken pox
fever, malaise, rhinitis; cutaneous lesions-pruritic vesicles (dew drops on rose petals); patients are contagious until all lesions crusted
varicella

varicella
varicella: few, diffuse, 1-2 mm oral ulcers; typically affect the _ and _
palate and buccal mucosa
varicella treatment: typically symptomatic in children; antiviral meds are helpful if administered within the first _ hrs of the exantham
24
reactivation of VZV; typically occurs in elderly; single recurrence only; associated with immunosuppression, trauma like dental treatment
Herpes zoster (shingles)

































