Bacterial Infections Flashcards
Superficial skin infection; most common in children with poor hygeine, crowed living conditions, hot and humid climates
impetigo
which microbes caused impetigo?
Streptococcus pyogenes, Staphylococcus aureus
Clinical presentation of _?: arises in areas of trauma, vesicles or bullae that rupture, leaving an amber or honey colored crust, pruritis and lymphadenopathy may be present
impetigo
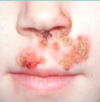
impetigo
Patients with streptococcal tonsillitis and pharyngitis (strep throat) are at risk for _ or _ and _
scarlet fever, post-infectious rheumatic fever and glomerulonephritis
What condition/s commonly caused by A beta-hemolytic streptococci; also adenoviruses, enteroviruses, Epstein-Barr virus
streptococcal tonsillitis and pharyngitis (strep throat)
Clinical presentation of _: sore throat, dysphagia, redness, tonsillar hyperplasia, exudate, fever, cervial lymphadenopathy
streptococcal tonsillitis

streptococcal tonsillitis
Appropriate therapy of streptococcal tonsillitis within _ days will prevent the development of rheumatic fever
9
calcified structures that develop within tonsillar crypts; originate from a nidus of cellular and food debris, bacterial colonies
tonsillolithiasis

tonsillolithiasis

tonsillolithiasis
Which spirochete causes syphilis?
Treponema pallidum
Spread by intimate sexual contact, transplacental transmission, contaminated blood exposure; 3 stages (primary, secondary, tertiary); congenital
syphilis
Latent phase (1-30 yrs) of syphilis occurs between _ and _ phases
secondary and tertiary
Which phase of syphilis?: relatively painless ulceration- chancre, 2-3 weeks after exposure, most are genital (5% are oral), resolves in 3-8 weeks
primary
which phase of syphilis?

primary
which phase of syphilis?: erythematous maculopapular cutaneous eruption, mucous patches of oral mucosa, fever, malaise, headache, musculoskeletal pain
secondary
Associated with secondary phase of syphilis

condylomata lata
Widespread disease seen in secondary syphilis in the immunocompromised; prodrome of fever, headache, myalgia, necrotic ulcerations of the skin and oral cavity, malaise, pain, arthralgia
lues maligna
which phase of syphilis?: gumma formation, leutic glossitis, may affect any tissue, palatal perforation, aneurysm of the ascending aorta, neurosyphilis (psychosis, dementia, death)
tertiary
associated with tertiary syphilis

leutic glossitis
Hutchinson’s triad, saddle-nose deformity, saber shins
congenital syphilis
Hutchinson’s triad?
incisors and molars malformed, interstitial keratitis, eighth nerve deafness








