Uterine Disorders COPY COPY Flashcards
The presence of endometrial glands and stroma outside the endometrial cavity and uterine musculature
Causes an inflammatory response
Usually located in the pelvis
Which condition?
endometriosis
_______ is a RF for epithelial ovarian CA.
Endometriosis is a RF for epithelial ovarian CA.
endometriosis pathophys
Retrograde menstruation
Retrograde flow of endometrial tissue through fallopian tubes and peritoneum
Nulliparity
Prolonged exposure to endogenous estrogen
Heavy menstrual bleeding
Obstruction of menstrual outflow
DES exposure in utero
Height greater than 68 inches
Lower BMI
High consumption of unsaturated fat
RF of what condition?
endometriosis
Premenstrual pelvic pain: Lesion growth stimulated by estrogen and progesterone. Lesions grow and are secretory but expansion is inhibited by surrounding fibrosis —> pressure and inflammation leads to pain
**PAIN SUBSIDES AFTER MENSES**
Infertility
Dysmenorrhea
Dyspareunia
Clinical px of what dz
endometriosis
what will be present on physical exam of endometriosis (3)
Tenderness / nodules at posterior cul-de-sac
Fixed or retroverted uterus (secondary to adhesions)
Endometriomas cause adnexal masses or tenderness

endometriosis dx
CA-125
Imaging
Laparoscopy:
- Erythematous, petechial lesions on peritoneal surface
- Surrounding peritoneum thickened and scarred
- MC site of dz: Ovaries can demonstrate lesions or endometriomas (“chocolate cysts”)
Adhesions
what is this showing
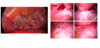
“chocolate cysts” on laporoscopy
what must you consider when thinking about how to tx endometriosis
Clinical presentation
Symptom severity
Extent and location of disease
Reproductive plans
Age
Medication side effects
Surgical complication rates
Cost
mild endometriosis tx
Expectant management
NSAIDS +/- OCPs
mod-severe endometriosis tx
main goal interrupt stimulation of endometrial tissue
Combo OCP’s
Progestins (PO, IM or IUD)
Gonadotropic-releasing hormone agonists (GnRH): Depot Lupro
What do the combination OCP’s do?
Continuous cycle fashion
Causes atrophy of endometrial tissue
40-50% pregnancy rate after discontinuation
↓ risk of ovarian cancer
What do the GnRH agonists do?
Suppression of estrogen and progesterone by down-regulation of pituitary gland
6 - 12 month therapy –> add Norethindrone acetate to prevent bone loss
Other endometriosis txq
Danazol (androgen)
Aromatase inhibitors
Laparoscopic excision
Hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy
Arise from smooth muscle cells within the uterine wall
Made up of collagen, smooth muscle, and elastin surrounded by a pseudocapsule
What dz?
uterine fibroid
uterine fibroids are 2-3x MC in which demographic & gender?
black women
seen earlier and grow faster
No evidence suggests estrogen causes myomas
Estrogen is implicated in growth
Myomas contain higher concentration of estrogen receptors than what is observed in the surrounding myometrium
May cause enlargement by increased production of extracellular matrix
Progesterone increases mitotic activity and possibly suppresses apoptosis within the tumor
Which dz pathophys?
uterine fibroids
uterine fibroids classification:
submucosal
subserosal
intramural
classified by anatomic location within the myometrium
Submucosal: Lie just beneath the endometrium
Subserosal: Lie just at the serosal surface of the uterus
Intramural: Lie within the uterine wall
What are these?

uterine fibroids
Abnormal uterine bleeding: increased surface area of endometrium leading to menorrhagia (+/- Fe anemia)
Pain: Degeneration, myometrial contractions, dyspareunia
Pelvic Pressure: Mass effect, compression of surrounding organs
Infertility: Submucosal fibroids impingement of intrauterine cavity
Spontaneous abortion
Clinical px of what?
uterine fibroids
physical exam of uterine fibroids
Bimanual exam reveals uterine abnormalities: Enlargement, Irregular shape, Masses
labs/imaging for uterine fibroids
Transvaginal US
Saline-infused sonohysertogram
Hysteroscopy
MRI
H&H
T/F: There is no standard of care for fibroid treatment in the United States.
True
Medical tx options for uterine fibroids (4)
COCs/progestin
GnRH analogs
Steroid therapies (androgens)
Tranexamic acid


