Unit 4 Dermatology Images Flashcards
(52 cards)
1
Q
- absence of melanocytes
- causes depigmentation

A
Vitiligo
2
Q
- associated with defects in collagen support structure of dermis

A
Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome
3
Q
- location: flexor surfaces in adults
- etiology: filaggrin mutation
- associated with asthma and allergic rhinitis
- staph aureus is suggested to exacerbate this disorder
- in children, is on cheecks and extensor surfaces
- eczema is type of atopic dermatitis

A
Atopic Dermatitis
4
Q
- type of atopic dermatitis

A
Eczema
5
Q
- etiology: common irritants
- caused by perfume, soap, etc

A
Irritant Contact Dermatitis
6
Q
- etiology: common allergens
- delayed type hypersensitiviey reaction (type 4)
- diagnosis confirmed with patch testing
- skin biopsy would reveal spongiotic dermatitis
- caused by poison ivy

A
Allergic Contact Dermatitis
7
Q
- location: lower legs
- etiology: lower extremity edema

A
Stasis Dermatitis
8
Q

A
Lichen Simplex Chronicus
9
Q
- same as nummular eczema
- round, annular, scaly plaques
- due to dry skin
- overuse of soap can make this worse

A
Numular Dermatitis
10
Q
- location: scalp
- etiology: malassezia furfur
- also known as cradle cap
- infection of sebaceous glands
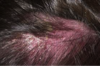
A
Seborrheic Dermatitis
11
Q
- location: extensor surfaces
- may include arthritis
- may be associated with increased cardiovascular risk

A
Chronic Plaque Psoriasis
12
Q

A
Guttate Psoriasis
- associated with strep
13
Q
- skin cancer
- most common
- pearly
- common on nose
- common PATCH1 mutation: most BCC have loss of PATCH1 that normally block SMOOTHENED gene
- tx: mohs surgery, vismoedgib (blocks smoothend gene)

A
Basal Cell
14
Q
- second most common skin cancer
- occurs more common in immunosupporessed pts
- keratoacanthoma is a type of this cancer
- center crater
- develop rapidly
- on sunexposed skin, HPV, thermal injury
- actinic keratosis is premalignant skin lesion
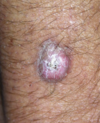
A
Squamous Cell
15
Q
- skin cancer
- common mutation: BRAF
- tx: vemurafinib
- breslow thickness: measurement of depth of tumor
- clark level: layers of skin affected
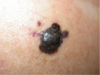
A
Melanoma
16
Q
- often associated with immunodeficiency

A
Kaposi Sarcome
17
Q
- can be treated with beta blockers
- most common benign soft tissue tumor of infants
- GLUT1 positive

A
Infantile Hemangioma
18
Q
- most common benign vascular tumor in adults

A
Cherry Angioma
19
Q
- associated with high levels of GLUT-1 expression (a placenta associated marker)
- also called strawberry hemangioma
- often develops rapidly in first 3 months of life
- involution (decrease) common into adulthood (50% by 5, 70% by 7, 90% by 9)

A
Infantile Hemangioma
20
Q
- associated with glaucoma and seizures
- assocaited with sturge weber in infants with port wine stain in trigemminal nerve

A
Port Wine Stain
21
Q
- linear plaque on the face or scalp
- yellow-orange
- associated with allopecia
- assocated with mutations in HRAS and KRAS

A
Nevus Sebaceus
22
Q
- most commonly on face>trunk>extremity
- beign tumor of oil gland

A
Sebaceus Hyperplasia
23
Q

A
Acrochordon
24
Q
- benign tumor of adipose tissue
- often soft, movable, painless

A
Lipoma
25
* from fibroblast
* firm papule
* most common on legs
* dimple sign is characteristic (Fitzpatrick sign)

Dermatofibroma
26
* scar gowth above and beyond original border
* composed of type 3 or type 1 collagen
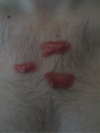
Keloid Scar
27
* sudden appearance associated with adenocarcinoma of the stomach
* barnicles of life
* appear dark in people with dark complexion- Morgan Freeman

Seborrheic Karatosis
28
* head and neck most common
* similar in color to shade of skin

Intradermal Nevus
29
* flat macules
* palms and soles most common

Junctional Nevus
30
* trunk and proximal extremities
* color brown to black

Compound Nevus
31
* more common in asians and causcasians

Blue Nevus
32
* low risk of progressing to malignant melanoma

Congenital Nevi
33
* usually apparent by 20 years

Dysplastic Nevus
34
* biggest risk factor for melanoma
* familial atypical moles and melanoma
* criteria:
* The occurrence of malignant melanoma in 1 or more first- or second-degree relatives
* The presence of numerous (often \>50) melanocytic nevi, some of which are clinically atypical
* Many of the associated nevi showing certain histologic features
* CDK2NA mapped to 9p21
* CDK4 mapped to 12q14
* CMM1 mapped to 1p

FAMMM Syndrome
35
* six or more cafe au lait spots
* two or more neurofibromas
* axillary or inguinal freckling (Crowe's sign)
* first degree relative with disorder
* optic glioma (iris freckles)
* autosomal dominant
* Defect in neurofibromin gene, a tumor suppressor, on chromosome 17 for NF-1

Neurofibromatosis
36
* multiple lesions associated with neurofibromatosis

Cafe au Lait Patch
37
* melassezia furfur is causative agent
* diagnos with KOH

Tinea Versicolor
38
* acquired disease involving antibodies to cell-to-cell adhesion molecules in the stratum spinosum (keratinocytes)
* attacks desmosomes
Permphigus Vulgaris
39
* vitamin cross links tropocollagen together
* this disease is characterized by lack of vitamin C
* SS: keratotic plugging of hairs, corkscrew hairs, hemorrhagic gingivitis
Scurvy
40
* type 2 antibody mediated
* detachment between dermis and epidermis- hemidesomsomes

Bullous Pemphigoid
41
42
* do not debride
* tx with steroids and immunosuppression

Pyoderma Gangrenosum
43
* associated with hepatitis
Lichen Planus
44
* with internal malignancies, pts tend to have weight loss- most common is stomach cancer
* thickening of the skin
* common causes: obesity, diabetes

Acanthosis Nigricans
45
* filagrin mutation

Icthyosis Vulgaris
46
* honey colored
* associated with bacteria like strep and staph
* can be bullus (staph) or non-bullus (strep/staph)

Impetigo
47
* begins 7-14 days after taking new medication
* located over trunk and extremities
Drug Eruption
48
* inital presentation is chancre
* secondary skin lesions form 4-10 weeks after onset of chancre
* sometimes presents with lymphadenopathy
* moth-eaten alopecia

Syphilis
49
* can also have black dot appearance
* casued by fungus
* test is KOH, dermatophyte test medium (changes colors)
* other types:
* tinia faciei- face
* tinia barbae- beard area
* tinia corpus- body
* tinia pedis- feet
* tinia manum- one hand two feet syndrome

Tinia Capitis
50
fungus under nails
Onychomycosis
51
* infestation
* burrows and genital nodules
* use mineral oil wet prep for diagnosis

Scabies
52
* fungus

Oral Candidiasis (Thrush)


