Tissues, Organs, Cell Migration Flashcards
(36 cards)
Primary and Secondary Lymphoid Organs
Primary: Bone marrow and thymus
Secondary: Spleen (blood), lymph nodes (specific tissues), and mucosal associated lymphoid tissues (mucosal surfaces)
B cell development

T cell development

Thymus layout
The Pro-T cells reside in the cortex (on the periphery)
After they begin to express TCRs, they move into the medulla (the center)

Hassal’s corpuscles
Reside within the medulla of the thymus. Eosinophilic-staining, concentric layers of epithelial cells. This is where AIRE is expressed and T-cell seletion takes place.
Rag enzymes
“Recombinase activating genes”
Mediate VDJ recombination.
Order of magnitude of possible human VDJs within a given genome
~109
This does not account for facilitated mutagenesis.
T/B-cell selection

pre-antigen receptors have. . .
only a single chain.
Lymph node structure

Lymphadenopathy
Lymphadenopathy most frequently occurs when an immune response is taking place in a node that drains a site of infection. This is because lymphocytes proliferate and more lymph drains into the node.
Another clinically important cause of lymphadenopathy is cancer of lymphocytes (lymphoma) or cancer from other tissue that has spread (metastasized) via lymph to the node.
Lymph node histology

Germinal Center
Contain activated B cells, plus other cells types.
Germinal centers form during an active B cell immune response to protein antigens. In order for germinal centers to form, antigen‐ activated B cells also must get signals from helper T cells.
If a pathologist sees germinal centers in a lymph node biopsy, she/he would inform the clinical team that this is a “reactive” node.

High endothelial venules
Present only in secondary lymphoid organs, named for the characteristically tall appearance of their endothelial cells.
These HEV, located in the T cells zone, are the sites where naïve T and B cells leave the circulation and enter the lymph node tissue. There are adhesion molecules on naïve lymphocytes that bind to adhesion molecules on the HEV which mediate the lymphocyte migration out of these HEV. Naive lymphocytes will not migrate out of the post‐capillary vessels in most other tissues, which are not HEVs.
How do the B cells get to the follicles, while the T cells stay in the T cell zone?
Chemokines!

Spleen
The red pulp is composed vascular channels called sinusoids, connected directly downstream to branches of the splenic artery. The sinusoids are lined by macrophages.

Structure of splenic white pulp
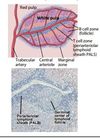
Marginal zone
Located in the margins of the white and red pulp of the spleen.
The B cells in the marginal zone (marginal zone B cells, MZB) are different from those in the follicles (follicular B cells); MZBs do not interact so much with T cells, and the antibodies they produce are less diverse than those produced by B cells in the germinal centers.
Mucosal associated lymphoid tissues
Organized, but not encapsulated, collections of lymphocytes, antigen presenting cells and supporting vascular and conduit structures similar to those found in lymph nodes.
They have T and B cell zones like regular lymph nodes, but have overall a higher B to T cell ratio.
Unlike lymph nodes, they are not downstream of lymphatics and do not have feeding vascular sinusoids.
Examples: Tosils, aneloids, Peyer’s patches, lymphoid aggregates in SI/colon/bronchial mucosa.
Peyer’s Patches
The PP in the yellow box is interfacing with the epihelia with the aid of dendritic cells and M cells.

How antigens reach Peyer’s patches from the lumen

M cells
Take up antigens, even whole microbes, at the lumenal surface, place them into membrane bound vesicles, and transport them (transcytose) to the ablumenal surface, at the edge of the PP, where they are handed over to antigen presenting cells that can display the antigens to lymphocytes.
Mesenteric lymph nodes
Located in the connective tissue sheets that are attached to the bowel wall. Supplied with lymph draining from the vacsulation of the lamina propria, as opposed to peyer’s patches with interact with the lumenal compartment.
May also serve as a site of initiation of adaptive response for mucosal challenges, as lamina propria dendritic cells may migrate to a peyer’s patch or a mesenteric lymph node.
Lymphocytes that are activated and differentiate into effector cells in MALT structures . . .
express combinations of adhesion molecules and chemokine receptors that allow them to preferentially home back to the subepithelial tissues of the same mucosa





