T cell mediated immunity I Flashcards
Sphingosine 1 phosphate
A lipid molecule that acts like a chemokine attracting T cells ( both naive and effector) out of lymphoid organs. It binds to the S1PR1 receptor.
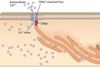
There is an S1P concentration maintained such that it is at high concertation in
lymph and blood, and low cocnetration within the extravascular tissue of SLOs.
If the naive T cells are not activated after a few hours, they will express S1PR1, and will be drawn out of the lymph node into lymphatics, and back into blood
ICOS‐L and ICOS are most important in. . .
T cell dependent B cell responses
Circulation of Naive and Effector T cells

B7 and CD28 family proteins

Antigen recognition with and without second signals

Downstream TCR signaling

TCR-mediated Ca2+ signaling

Inhibitors of calcineurin pathway
Cyclosporine and Tacrolimus
Cyclosporine binds to cyclophilin and tacrolimus binds to FKBP. Both complexes are inhibitors of calcineurin.
T cell defense against intracellular pathogens

The T Cell Receptor Complex

T cells are of particular importance for pathogens which. . .
. . .survive and replicate inside of host cells
How calcineurin mediates NFAT transcription
Calcineurin dephosphorylates cytosolic phospho‐NFAT, exposing a nuclear localization signal.
Summary of T cell migration events from infection to arrival of activated T cells on site

Calfineurin-NFAT pathway

Primary use of cyclosporine
Post-transplant operation to prevent graft rejection
Steps in T cell activation

Calcineurin
A cytosolic serine-threonine phosphatase activated by calmodulin, which is in turn activated by Ca2+
Mechanism of TCR signal transduction
Lck rests on CD4. When pMHCII is recognized by both CD4 and the TCR, induced proximity enables phosphorylation of the ITAMs on the TCR by Lck. The phosproylated CD3 and zeta chain ITAMs then recruit ZAP-70 via SH2 domains. ZAP-70 then autophosphorylates and activates its tyrosine kinase activity to further transduce and amplify the signal via phosphorylation of an adaptor which activates PLCγ1, PI3K, and GEFs by induced proximity and ZAP-70 phosphorylation.

IP3 receptor
Present on cytosolic side of ER. Binds to IP3 and triggers release of Ca2+ into cytosol.
What adhesion molecule contributes to naive T cell entry into lymph nodes, but not effector T cell entry into infected tissues?
L-selectin
PD1 inhibitory signaling

Antigen‐induced TCR signaling without B7‐induced CD28 signaling leads to. . .
No response, apoptosis, or anergy.
Role of CRAC and STIM1 in IP3→Ca2+ signaling