T cell mediated immunity II Flashcards
(36 cards)
After an infection is resolved, __% of CTLs undergo apoptosis.
After an infection is resolved, ~90%% of CTLs undergo apoptosis.
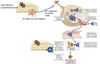
How Th1 cells activate macrophages
IFN-γ production
CD40L
Both promote classical activation
IL‐5
A potent eosinophil growth factor and activator
ILCs vs T cells
ILCs have no antigen receptor, but have analogous effector functions to TH1, 2, and 17.
NK cells are also ILCs, and are the functional equivalents of CTLs.
T cell memory can last for up to ____ years.
T cell memory can last for up to 75 years.
Th1, Th2, Th17, and Tfh

Perforin molecules that diffuse away are inhibited by ___.
Perforin molecules that diffuse away are inhibited by plasma lipids.
Pathogen types and associated TH subsets
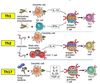
Classical vs Alternative macrophage activation

_____ are required for ILC development from a common precursor
IL‐15 or IL‐7 are required for ILC development from a common precursor
CTL granule contents

At peak after EBV, CMV, HIV infection, ____ % of all T cells in the blood may be specific for just one single viral peptide‐ MHC antigen
At peak after EBV, CMV, HIV infection, 25‐ 50 % of all T cells in the blood may be specific for just one single viral peptide‐ MHC antigen
CTL-Target Cell Interaction
Bystander cells (e.g. antigen presenting cells) may be protected from CTL-mediated death by expressing _____
Bystander cells (e.g. antigen presenting cells) may be protected from CTL-mediated death by expressing specific and irreversible granzyme inhibitors (serpins).
Helper T cell Differentiation

TH2 functions

Development of ILCs

Clonal expansion of T cells

The major benefit of CD4 help to CD8 cells is enhanced _____.
The major benefit of CD4 help to CD8 cells is enhanced generation of memory CD8 T cells.
All TH subsets
1, 2, 3, 9, 17, 22, follicular helper, regulatory
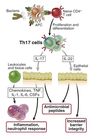
IL‐22
Enhances epithelial barrier function by promoting epithelial cell growth (to repair breaches) and reinforcing tight junctions.
Also increases defensin production.
JAK STAT Signaling

Classical Macrophage Activation

“licensing” of the DC
T cell activation by a DC recpirocally activates the costimulatory activity of the DC, as it has been “liscensed” as a dangerous antigen-carrying DC. This makes subsequent CD4 or CD8 T cell activation easier.