T cell and B cell Cross-Talk Flashcards
When a naive B cell recognizes its monovalent antigen, it loses expression of ____ and upregulates ____.
When a naive B cell recognizes its monovalent antigen, it loses expression of CXCR5 and upregulates CCR7 and MHCII.
This targets it to merge with the T cell zone and to display its antigen on pMHCII.
Germinal centers include. . .
T follicular helper cells, activated B cells, and follicular dendritic cells
BCR signaling
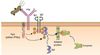
CR2
A complex of 3 proteins (including CD19 and CD81) on the B cell membrane. Detects C3d, which acts as a second signal for B cell activation.
Unconjugated toxin vaccine

If a T cell sees its antigen being presented by a B cell, both it and the B cell will lose expression of ____ and gain expression of ____.
If a T cell sees its antigen being presented by a B cell, both it and the B cell will lose expression of CCR7 and gain expression of CXCR5.
This brings the B cell and T cell back to the follicular zone to form a germinal center, leaving behind an extrafollicular focus made up of short-lived plasma cells.
What ultimately controls which heavy chain isotype a class-switching B cell will switch to?
- Whether or not it has switched before (which regions are left?)
- Which S region AID introduces a uracil into
B cell selection within the germinal center

Part of the reason that secondary responses result in greater antibody production is because ___ is more readily obtained.
Part of the reason that secondary responses result in greater antibody production is because Helper T Cell help is more readily obtained.
At the end of a secondary antigen challenge, there are more ___ and ___ than at the end of the primary challenge.
At the end of a secondary antigen challenge, there are more antigen-specific plasma cells and memory B cells than at the end of the primary challenge.
Extrafollicular focus
Created when a T cell recognizes its antigen on an antigen-loaded B cell in the T cell zone of an SLO.
Represents a proliferation of short-lived plasma cells stimulated by the T cell before it and the B cell progeny exit to form a germinal center in the follicular zone.
What does CD40L/CD40 + cytokine induced signaling do to the B cells?

Only ____ respond in a primary antibody response.
Only Naive B cells respond in a primary antibody response.
mIg
Monomeric transmembrane form of IgM present in naive B cells. May also be IgD.
Phases of B cell response

Commencement of T cell / B cell interaction

BCR structure

B cell second signals

Isotype class switching in a B cell

Important outcomes of germinal center action
- Heavy-chain class switching
- Affinity maturation
- Long lived plasma cells
- Memory B cells
Characteristics of primary and secondary antibody response

Unconjugated polysaccharide vaccines

S and C sites in Ig locus
S = switch site, the regions at which the germline may recombine in order to switch constant regions.
C = constant site, the coding region for the constant chains of antibodies. Each has an associated S site just 5’ of it.
Common conjugate vaccines