Third Party System [1854–1890s] II Flashcards
Review - Timeline: Troubled Times - The Tumultuous 1850s
1850: Henry Clay brokers ‘Compromise of 1850’. 1852: Harriet Beecher Stowe publishes ‘Uncle Toms Cabin’. 1854: Anti-Slavery Whigs, Democrats, and Free-Soilers form Republican Party; Congress passes Kansas-Nebraska Act. 1856: Preston Brooks canes Charles Sumner. 1857: Supreme Court hands down Dred Scott decision. 1858: Abraham Lincoln and Stephen Douglas debate in Illinois. 1859: John Brown raids Harpers Ferry. 1860: Lincoln elected president.
Timeline: The Civil War, 1860-1865
1860: South Carolina secedes from Union. 1861: Confederate forces fire on Fort Sumter; First Battle of Bull Run. 1862: Confederate forces retreat after Battle of Shiloh; General Robert E. Lee defends Richmond; Battle of Antietam. 1863: Abraham Lincoln signs Emancipation Proclamation; Racially motivated riots break out in New York; General Ulysses S. Grant leads Vicksburg Campaign; Battle of Gettysburg. 1864: General William Tecumseh Sherman invades the South; Atlanta falls to Sherman’s forces; Lincoln is reelected. 1865: Confederate general Robert E. Lee surrenders.

*The Origins and Outbreak of the Civil War*
The election of Abraham Lincoln to the presidency in 1860 proved to be a watershed event. While it did not cause the Civil War, it was the culmination of increasing tensions between the proslavery South and the antislavery North. Before Lincoln had even taken office, seven Deep South states had seceded from the Union to form the CSA, dedicated to maintaining racial slavery and white supremacy. Last-minute efforts to reach a compromise, such as the proposal by Senator Crittenden and the Corwin amendment, went nowhere. The time for compromise had come to an end. With the Confederate attack on Fort Sumter, the Civil War began.

*Early Mobilization and War*
Many in both the North and the South believed that a short, decisive confrontation in 1861 would settle the question of the Confederacy. These expectations did not match reality, however, and the war dragged on into a second year. Both sides mobilized, with advantages and disadvantages on each side that led to a rough equilibrium. The losses of battles at Manassas and Fredericksburg, Virginia, kept the North from achieving the speedy victory its generals had hoped for, but the Union did make gains and continued to press forward. While they could not capture the Southern capital of Richmond, they were victorious in the Battle of Shiloh and captured New Orleans and Memphis. Thus, the Confederates lost major ground on the western front.

List the parties involved in the presidential election of 1860.
The presidential election of 1860 was a four-way race between a split Democratic Party, the Republican Party, and the Constitutional Union Party. With just 40% of the popular vote and despite not even appearing on Southern ballots, Abraham Lincoln won the Electoral College and was elected president in November 1860.

Describe the circumstances under which Abraham Lincoln was elected president.
The U.S was polarized by geography after three decades of compromise. Southerners generally supported policies that supported agriculture and expanded slavery, while Northerners largely supported policies that supported business and contained slavery. The Lincoln-Douglas debates further divided the country. In a four way race, Lincoln won the Electoral College in the 1860 election with 40% of the popular vote and with 60% of American votes choosing anyone but Lincoln. The South did not accept the results.

Explain the effect that Lincoln’s election had on South Carolina.
A month after Lincolns electoral victory, South Carolina approved articles of secession, which claimed the Constitution protected slavery, the North’s refusal to assist in the return of fugitive slaves was a breach of their agreement (‘Compromise of 1850’), that Lincoln would not protect their rights once inaugurated, and cited the Declaration of Independence as support for their right to abolish a government that did not protect the rights of its people. In Congress, the ‘Crittenden Compromise’ was a last-minute effort to save the Union by restoring the Missouri Compromise, but Republicans refused to pass it.

Summarize why Southern states seceded from the Union and how the Confederacy was formed.
When South Carolina seceded, a few U.S. Army soldiers were trapped on an island fortress in Charleston Harbor. The state demanded that they evacuate and turn over the property. President Buchanan would not abandon Ft. Sumter, and when he tried to deliver supplies and reinforcements, the ship was fired upon and several more states seceded. In February 1861, they formed the ‘Confederate States of America’ with Jefferson Davis as their president. The Confederacy and other Southern states yet to secede took over more federal property located in their borders.

Civil War - Crisis At Fort Sumter
In late December 1860, a small number of U.S. soldiers were trapped in South Carolina after that state’s secession. In January 1861, rather than surrender Fort Sumter, President Buchanan sent a ship full of supplies and reinforcements. In response, the South Carolina militia fired on the ship, and six more states decided to secede in the face of what they felt was a blatant violation of state sovereignty. They formed the ‘Confederate States of America’ and began seizing U.S. military property and weapons as their own.
Civil War - The Fall of Fort Sumter and the Beginning of the Civil War
Soon after his inauguration in March 1861, President Lincoln also tried to resupply Fort Sumter, this time with food only. Rather than wait for the ship to arrive, South Carolina decided to attack the fort while it was most vulnerable. On April 14, 1861, Fort Sumter fell to the Confederacy. President Lincoln asked for troops to defend the remaining military posts in the South and retake those that had already been captured, prompting four more Southern states to secede. Lincoln then sent soldiers to prevent Maryland from seceding, which would have threatened the capitol. On the same day, April 19, Lincoln also began a naval blockade of the Confederacy. The Civil War had begun.

Civil War - Effects of Fort Sumter
War was never actually declared because the Confederacy was never recognized as a nation by any sovereign states. Virginia split into what would become West Virginia and Virginia, with West Virginia joining the Union and Virginia joining the Confederacy. Lincoln suspended the writ of habeas corpus after a mob of 20,000 secessionists in Baltimore attempted to derail a train full of federal solders he sent to secure Maryland and Washington D.C. Lincoln commenced a naval blockade of southern ports, which ultimately extended from Virginia to Texas and was not effectively broken until the end of the Civil War. Initially, everyone predicted a short conflict, but ultimately the Civil War would be the bloodiest and most destructive war in American history.

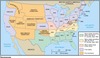
Civil War - Union states
California, Connecticut, Delaware, Illinois, Indiana, Indianapolis, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, Missouri, Nevada, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, Ohio, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont, West Virginia, and Wisconsin.

Civil War - Union states - Border states
Maryland, Missouri, Delaware, and Kentucky.

Civil War - Confederate states
South Carolina, Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, Texas, Virginia, Arkansas, Tennessee, and North Carolina.
Civil War - Explain the advantages and disadvantages of the North.
The North generally had the most nominal advantages. In regards to men and fighting age, the Union had the edge by about 2:1; however, Southern men were more willing to fight. In regards to industrial capacity, Northern factories made 97% of the nations firearms; however, the Confederacy immediately ramped up manufacturing and established foundries that used repurposed bronze. Southerners also utilized their hunting and horse riding culture to develop a formidable calvary that could outmaneuver the North’s cumbersome infantry. All of the U.S. Navy remained in federal hands and a blockade was instituted on the South shorty after the war started; however, the South could rely on their agriculture on the short term for food and found ways to evade the blockade. The North had more developed transportation systems than the South, but the South had intimate knowledge of their territory that put the North at a disadvantage when in the South.

Civil War - Explain the advantages and disadvantages of the South.

A majority of the nation’s experienced military leaders were Southerners, and seven of the nation’s eight military colleges were in Southern territory. They also controlled the Mississippi River Delta, and the Union devoted enormous resources to capturing it. This was critical not only for an effective blockade, but also to thwart the Confederacy’s plan to push west through New Mexico to the Pacific Ocean. The South fought a defensive war, while the North had to fight an offensive war, which meant the South didn’t need to win the war, but only needed to outlast the North’s will to fight.

Civil War - Explain the events that led to, and followed, the first Battle of Bull Run.
The First Battle of Bull Run was the first major battle of the Civil War. On July 21, 1861, the Union Army advanced, trailed by naive and excited picnickers from Washington D.C. who expected to see their soldiers call the Confederacy’s bluff and go home triumphant. Although the Union forces, led by General McDowell, outnumbered the Confederates, led by Stonewall Jackson, the experience of the Confederate soldiers proved the difference as the Confederates won the battle.

Civil War - Anaconda Plan
Designed by Union General Winfield Scott and implemented in 1862: (1) Blockade the South to cut off the export of cotton and the import of war supplies. (2) Seize the Mississippi River to keep the South from expanding west, and disable the movement of Confederate supplies. (3) Divide the South along the Tennessee River and march east through Georgia. (4) Capture Richmond, the Confederate capital.

Civil War - Explain the Confederacy’s goal in creating the ironclad CSS Virginia and the result of the ‘Battle of Hampton Roads’.
The Union blockade had effectively reduced cotton exports to the South by 95% in 1861. Southern forces decided to challenge the Union’s naval superiority by converting the USS Merrimack into an ironclad and renaming it the CSS Virginia. At the ‘Battle of Hampton Roads’ on March 8-9th, 1862, the CSS Virginia faced off against a technologically superior USS Monitor and was forced to retreat.
Civil War - Describe the Battle of Shiloh.
Part of the Anaconda Plan’s strategy of dividing the South along the Tennessee River, also known as the Battle of Pittsburg Landing, the Battle of Shiloh took place from April 6 to April 7, 1862, and was one of the major early engagements of the American Civil War (1861-65). The battle began when the Confederates launched a surprise attack on Union forces under General Ulysses S. Grant (1822-85) in southwestern Tennessee. After initial successes, the Confederates were unable to hold their positions and were forced back, resulting in a Union victory. Both sides suffered heavy losses, with more than 23,000 total casualties, and the level of violence shocked North and South alike.

Civil War - The fall of New Orleans.
The Anaconda Plan also involved controlling the Mississippi River, not only to keep the Confederacy from moving west to the Pacific, but also to allow the Union to transport troops and supplies into the South. To do this, they had to capture New Orleans. New Orleans was captured on April 25, 1862 and remained under martial law for the rest of the war.

Civil War - Describe the Battle of Antietam and its effects.
The Battle of Antietam, on September 17, 1862, was a setback for both sides. The bloodiest single day in American history ended in a draw, convincing France and England to distance themselves from the conflict and prompting Abraham Lincoln to issue the Emancipation Proclamation.

*The Changing Nature of the War*
The year 1863 proved decisive in the Civil War for two major reasons. First, the Union transformed the purpose of the struggle from restoring the Union to ending slavery. While Lincoln’s Emancipation Proclamation actually succeeded in freeing few slaves, it made freedom for African Americans a cause of the Union. Second, the tide increasingly turned against the Confederacy. The success of the Vicksburg Campaign had given the Union control of the Mississippi River, and Lee’s defeat at Gettysburg had ended the attempted Confederate invasion of the North.

Civil War - Understand what the Emancipation Proclamation did and did not do.
Following the Battle of Antietam, Lincoln issued an ultimatum to the Confederacy: Stop the rebellion or lose your slaves. They chose the latter. And on January 1, 1863, the Emancipation Proclamation went into effect, setting free millions of humans in the southern part of the United States. Lincoln believed the Constitution clearly empowered the nation’s leaders to defend and preserve the Union, and he felt that setting the South’s slaves free would help accomplish that goal.


















