The Cardiovascular System Flashcards
(151 cards)
WHEN DOES A MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION OCCUR?
When blood circulation to the muscle of the heart itself is blocked
WHAT IS DIFFUSION?
The net movement of solute down a concentration gradient, brought about by the innate, randomly-directed jumping around of the solute due to its thermal energy
FUNCTION OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
- Delivery of O2 and nutrients to each cell
- Removal of CO2 and waste products from each cell
- Communication between organs through transport of hormones and other extracellular mediator
- Temperature regulation
- Crucial hydrodynamic device in sexual reproduction!
WHAT THREE FACTORS DETERMINE BLOOD PRESSURE?
Blood pressure is determined by three main factors – cardiac output (pumping of the heart), the blood vessels or vasculature which not only carry the blood but are responsible for the resistance that creates the blood pressure and the various fluid compartments.
Cardiovascular circulation can be divided into the systemic and pulmonary (lung) circuits with the heart as the central pump

WHAT TWO CIRCUITS IS CARDIOVASCULAR CIRCULATION DIVIDED INTO?
Systemic and Pulmonary (lung)
WHAT IS THE COMPOSITION OF BLOOD?

BLOOD DISTRIBUTION AT REST
At rest….most blood is flowing through abdominal organs and _.
Majority of pumping is in parallel which means that all flow through organs is not linked. Some exceptions including intensines which run into liver….carry food. However if blood flow is occulled then reduction in blood to liver
Heart flow is quite small and any small change in flow and therefore oxygen can lead to reduce O2 and pain (called angina).
Kidneys
AT REST, WHERE DOES MOST BLOOD FLOW THROUGH?
Abdominal organs
Kidneys
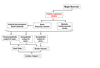
BLOOD VESSELS CONTAIN MULTIPLE CELL LAYERS THAT REGULATE THEIR FUNCTION
Lumen
Endothelial cells (Tunica Intima)
Smooth muscle cells (Tunica Media)
Connective Tissue (Tunica Adventita)
All blood vessels contain endothelial cells but vary in the _ of the smooth muscle and connective tissue.
Thickness
BLOOD VESSELS INVOLVED IN THE CIRCULATION

THICH LAYER OF ELASTIC SMOOTH MUSCLE ACTS AS A PRESSURE RESERVOIR

ARTERIOLES CONTAIN A THIN MUSCULAR WALL AND SMALL LUMEN
Contraction of the smooth muscle regulates the diameter of the lumen:
- Determine blood flow to organs
- Major determinant of mean arterial pressure
CAPILLARIES HAVE A SINGLE LAYER OF ENDOTHELIAL CELLS
Exchange of nutrients, oxygen and _ across the capillary wall but NOT proteins.
Intercellular clefts and fused vesicles channels assist the exchange.

Waste
WHAT SUBSTANCES ARE EXCHANGED ACROSS CAPILLARY WALLS?
Nutrients
Oxygen
Waste
THE SKELETAL MUSCLE PUMP
Return of venous blood to the heart is facilitated by valves and the skeletal muscle pump.
Veins run close to the _ muscle .
Skeletal
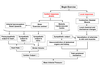
SUMMARY OF STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF BLOOD VESSELS

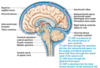
OVERALL STRUCTURE OF THE HEART

MAJOR BLOOD VESSELS TO THE HEART

INTERNAL STRUCTURE OF THE HEART
WHAT DO VALVES DO?
Prevent the backflow of blood (ensures that blood flows in one direction).
BLOOD FLOW

BLOOD SUPPLY TO THE HEART
- Heart is has an extensive network of blood vessels supplied with oxygenated blood via the coronary arteries.
- Coronary arteries branch off the _ (coming from left ventricle)
- Most deoxygenated blood drains back into the right atrium via a single vein (coronary sinus)

Aorta
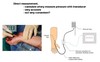
CORONARY ARTERIAL DISEASE CAN LEAD TO ISCHEMIA AND HEART ATTACKS
Coronary Arterial Disease
- insufficient blood flow (ischemia) is associated with chest pains (angina) often radiating down left arm
- severe blockage leads to damage (death) of the heart region and myocardial infarction or heart attack
- ventricular fibrillation and death (heart attack)
Causes of Coronary Arterial Disease
- Atherosclerosis (thickening of the coronary arteries)
- Blood clot (coronary thrombosis)
- Drugs
- Surgery