Tapeworms of Ruminants Flashcards
What are some generic features of cestodes/tapeworms?
Adult worms are segmented
Indirect life cycles
Adult parasite in difinitive host, generally considered less pathogenic
Stage in the intermediate host is referred to as the metacestode, can be considered pathogenic
Describe the outside structure of an adult tapeworm?
Scolex at top of head- sometimes with suckers- and attaches to host
Extends into a neck and then segments
Newly produced segments- proglotids- near head
All the segments together form the Strobila

Describe the inside strucutre of an adult tapeworm’s proglottid
Testes lined up around the outside
Dark structure at bottom of segment- vitelline gland- produces egg shell
Viteline gland connected to ovary and uterus which extends through middle
Connected to genital pore

How do tapeworms ingest food?
The tegument- body wall- allows passage of food
No gut
What is the order and families of the relevant tapeworms?
Order: Cyclophillidae
Families:
Taeniidae
Dilepididae
Anoplocephalidae
Describe the general life cycle of a tapeworm
Adult tapeworm always found in difinitive host, metacestode found in intermediate host
Adults found in SI
Proglottids break off
Eggs/proglottids shed in faeces
Eggs immediatley infective
Eggs eaten by intermediate host
Metacestode develops in intermediate host
Metacestode eaten by difinitive host
What are the 4 different types of metacestode?
Cysticercus
Coenurus
Hyatid
Cysticercoid
What kind of metacestode is this and why?

Cysticercus- one single invaginated scolex
What type of metacestode is this and why?

Coenurus- several invaginated scolex
What type of metacestode is this and why?
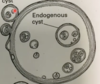
Hyatid- endogenous and exogenous cysts containing several scolex
What type of metacestode is this and why?

Cysticercoid- exvaginated scolex, not fluid filled- solid structure
Very small
What are the 4 tapeworms which are metacestodes in sheep and dogs are the definitive host?
Taenia ovis
T.hydatigena
T.multiceps
Echinococcus granulosus
Where are the metacestode of taenia ocivs found in sheep?
Cysticercus in muscles
Where is the metacestode of Taenai hydatigena found in sheep?
Cysticercus in peritoneum
Where are the metacestode of taenia multiceps found in sheep?
Coenurus in brain
Where is the metacestode of echinococcus granulosus found in sheep?
Hydatid cyst in liver or lung
What parasite causes sheep measles?
Taenia ovis- cysticercus in muscles
What is the problem and solution for ‘sheep measles’?
Affects value of carcase
Major economic losses in Australia and New Zealand
Vaccine produced- recombinant oncosphere antigen. Highly effective, no commercial take up
New Zealand- education and regular worming of dogs
Canada- Liver condemnations have increased a lot
What is the problem of Taenia hydatigena in sheep?
Cysticercus migrates through the sheep
Forms mature cysticercus in the peritoneum
Liver condemnation
What are the complications of taenia multiceps and why?
Neurological complications
Space occupying lesion from cyst in the brain of the sheep- (coenrus)
What is the problem with Echinocococcus granulosus
Hyatid cyst in liver and lungs- no pathogenic significance for sheep and cattle
Serious Human pathogen
How can tapeworms (metacestode) of sheep be controled?
Praziquantel treatment of dogs to remove adult tapeworm (dictated by PPP, every 6 weeks)
Break the life cycle through controlling access to intermediate host/metacestode stage
Can’t treat metacestode
What tapeworms have humans as their definitive host?
Taenia saginata- beef tapeworm
Taenia solium- pork tapeworm
How does taenia saginata affect the UK?
Rare
Adult in SI of humans
Metacestode in muscle of cattle- cysticercus
No disease in cattle
Mild disease in humans- hunger pains, aesthetically unpleasant




