Surgical anatomy of the retroperitoneum, adrenal, kidney and ureters Flashcards
The dorsal lumbotomy incision to expose the kidney
Splits the lumbodorsal fascia without incising muscle,. This approach allows entrance to the retroperitoneum without violation of musculature

The lumbodorsal fascia originates from the
Lumbar vertebrae

The lumbodorsal fascia consists of how many layers
3- Posterior, middle and anterior
Posterior: covering for the sacrospinalis, latissimus dorsi origin
Middle: separates the anterior of of sacrospinalis from the posteror aspect of the quadratus lumborum,
Anterior: lumodorsal fascia probides the anterior covering to the quadratus lumborum muscle and forms the posterior margin of the retroperitoneum

All three layers of the lumbodorsal fascia join to form the a single thick aponeurosis lateral to the quadratus lumborum muscle before extending further anterolaterally, where they are contiguous with the aponeurosis of the ____________.
Transversus abdominis muscle

The psoas major joins the iliacus muscle, which originates ____, to become the _____ and insert on the _____ and _____ the thigh at the hip
- Inner aspect of the iliac wing of the pelvis
- iliopsoas
- lesser trochanter
- flex

What is the boundary of the retroperitoneum?
Posterior surface: lumbar vertebral bodies covered by shiny, longitudinal fibers of the anterior spinous ligament, these are flanked bilaterally by the psoas. Psoas is covered by the psoas sheath which are contiguous with the transversus abdominis muscle
LAterally: transversus abdominis
Superior: posterior insertion of the diaphragm along the lower ribs
Inferior: below the level of the iliac crest, iliopsoas forms the posterior confine

in a subcostal flank approach to the kidney, which of the ff may be incised to increase upward mobility of the 12th rib
the costovertebral ligament

What are the first abdominal branches of the aorta
the paired inferior phrenic arteries

which of the following arteries branches from the celiac trunk?
a. the left gastric
b. the right gastric
c. the pancreaticoduodenal
d. SMA
E. IMA
A. left gastric
The short celiac arterial trunk trifurcates into common hepatic, left gastric, and splenic branches

The renal arteries typically branch from the abdominal aorta at the level of the ____
2nd lumbar
the testicular arteries commonly originate from the
Abdominal aorta below the renal arteries

The inferior mesenteric artery can be sacrificed without complication
True, especially in individuals without atherosclerotic occlusive arterial disease
Which of the following drains directly to the IVC?
REnal veins, IMV,SMV,splenic veins
only renal vein, the rest drains into to the portal vein

the left gonadal vein usually enters the ____
inferior aspect of the left gonadal vein

left renal vein receives the ff
left adrenal, left lumbar, left gonadal

cysternal chyli is located
located at the 1st lumbar vertebra posterior to aorta
the right testis lymphatics drains into
interaortocaval region
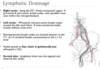
the lumbar sympathetic chains
- Run vertically in the retroperitoneum, ,medial to the psoas muscles
- contain numerous sympathetic ganglia
- Closely associated with the lumbar blood vessels
contain postganglionic sympathetic neurons supplying the lower ex
Disruption of which sympathetic nervous plexus on this anterior abdominal aorta during retrpoperioneal dissection will likely cause loss of seminal emission?
A. Celiac plexus
B. Renal plexus
C. Superior mesenteric plexus
D. Superior hypogastric plexus
E AOTA
D. superior hypogastric plexus
From book: At the lower extent of the abdominal aorta, much of the autonomic input to the pelvic urinary organs and genital tract travels through the superior hypogastric plexus. This plexus lies on the aorta anterior to its bifurcation and extends inferiorly on the anterior surface of the fifth lumbar vertebra. This plexus is contiguous bilaterally with inferior hypogastric plexuses, which extend into the pelvis. Disruption of the sympathetic nerve fibers that travel through these plexuses during retroperitoneal dissection can cause loss of seminal vesicle emission and/ or failure of bladder neck closure, resulting in retrograde ejaculation.
23
In the lateral abdominal wall, the iliohypogastric nerve will be found coursing in the plane:
a
deep to the transversalis fascia.
b
between the transversalis fascia and the transversus abdominis muscle.
c
between the transversus abdominis and internal oblique muscles.
d
between the internal oblique and external oblique muscles.
e
superficial to the external oblique muscle.
c. In between the transversus abdominis and internal oblique muscles.

The cremaster muscle is innervated by the:
a
ilioinguinal nerve.
b
iliohypogastric nerve.
c
obturator nerve.
d
genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve.
D. genital branch

In the retroperitoneum, where can the genitofemoral nerve be found?
a
Posterior to the psoas muscle
b
On the anterior surface of the psoas muscle
c
Lateral to the psoas muscle
d
Medial to the psoas muscle
B. the genitofemoral branch lies directly atop and parallels the psoas on most of its retroperitoneal course
Autonomic system divided into sympathetic and parasympathetic fibers. The sympathetitic ganglion originates from ___ while the parasymphatetic originates from ____. The major autonomic plexuses are associated with the primary branches of the aorta namely: ___, ___, ___
sympathetic: thoracic and lumbar portions
PArasymphathetic: Cranial and sacral collumns
Major autonomic branches: Celiac, superior hypogastric, inferior hypogastric plexus
26
The descending duodenum:
a
lies within the retroperitoneum.
b
receives the common bile duct.
c
lies lateral to the head of the pancreas.
d
lies anterior to the right renal hilum.
e
does all of the above.
e. The second part of the duodenum descends vertically, directly anterior to the right renal hilum, and this is intimately related on its posterior aspect to the medial margin of the right kidney, right renal vessels, renal pelvis, UPJ, upper right ureter, the CBD also lies posterior and drains into this part
The posterior surface of the tail of the pancreas is closely associated with:
a
the splenic artery.
b
the splenic vein.
c
the upper pole of the left kidney.
d
the left adrenal gland.
e
all of the above.
e all of the above
In cases of renal ectopia, the ipsilateral adrenal gland is typically:
a
absent.
b
found in its normal anatomic position in the upper retroperitoneum.
c
found in association with the contralateral adrenal gland.
d
found closely applied to the superior pole of the ectopic kidney.
e
found closely associated with the ipsilateral renal artery.
B. found in its normal position in the upper retroperitoneum
30
Which of the following statements is NOT true?
a
The right renal vein is much shorter than the left renal vein.
b
The right adrenal vein is much shorter than the left adrenal vein.
c
The right kidney is typically located lower in the retroperitoneum than the left kidney.
d
The right adrenal gland is typically located lower in the retroperitoneum than the left adrenal gland.
e
Both c and d
d
s one proceeds outward from the adrenal medulla, the three separate functional layers of the adrenal cortex are, in correct order:
a
zona reticularis, zona fasciculata, and zona glomerulosa.
b
zona fasciculata, zona reticularis, and zona glomerulosa.
c
zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata, and zona reticularis.
d
zona glomerulosa, zona reticularis, and zona fasciculata.
e
zona reticularis, zona glomerulosa, and zona fasciculata.
a
Which of the following statements is (are) NOT true?
a
The adrenal medulla produces catecholamines in response to stimulation from the sympathetic nervous system.
b
The zona glomerulosa produces aldosterone in response to angiotensin II.
c
The zona reticularis of the adrenal cortex produces androgens in response to luteinizing hormone (LH).
d
The zona fasciculate of the adrenal cortex produces glucocorticoids in response to adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH).
e
Both b and c
C. it is regulated by ACTH not LH
The adrenal arteries are branches from:
a
the aorta.
b
the inferior phrenic arteries.
c
the renal arteries.
d
the celiac arterial trunk.
e
a, b, and c.
e

The kidney produces:
a
renin.
b
angiotensin.
c
erythropoietin.
d
both a and c.
e
a, b, and c.
D. Kidneys play a central role in the fluid electrolyte, and acid base balance in humans, but they have important endocrine functions known to include vit D met and the production of both renin and erythropoietin
The normal kidney in an avg sized adult man weighs
150 grams
Persistent fetal lobation identified in the kidney of an adult patient:
a
indicates the presence of a congenital renal disorder.
b
indicates childhood renal injury due to infection.
c
is observed only with long-standing obstructive uropathy.
d
is normal.
e
is never seen.
d
The upper pole of the kidney lies anterior to:
a
the 12th rib.
b
the diaphragm.
c
the pleura.
d
all of the above.
e
none of the above.
D
Which of the following statements regarding the typical anatomic positioning of the kidney is TRUE?
a
The lower pole of the kidney lies more anterior than the upper pole.
b
The lower pole of the kidney lies more lateral than the upper pole.
c
The medial aspect of the kidney lies more anterior than its lateral aspect.
d
The anterior renal calyces lie lateral to the posterior renal calyces.
e
All of the above.
e

During left radical nephrectomy performed via a transabdominal approach, excessive traction on which of the following structures might be expected to produce a significant injury to the spleen?
a
Left adrenal gland
b
Splenorenal ligament
c
Splenocolic ligament
d
Both b and c
e
a, b, and c
D
Gerota fascia envelops and contains:
a
the adrenal gland.
b
the kidney.
c
the ureter.
d
the gonadal vessels.
e
all of the above.
E
After blunt trauma to the right kidney, with a major laceration to the renal parenchyma and ongoing hemorrhage, the expanding hematoma contained within Gerota fascia will tend to extend:
a
across the midline into Gerota fascia surrounding the left (contralateral) kidney.
b
downward into the pelvis.
c
upward into the thorax.
d
anterolaterally, deep to the transversalis fascia.
e
anterolaterally, between the peritoneum and transversalis fascia.
b
After blunt trauma to the right kidney, with a major laceration to the renal parenchyma and ongoing hemorrhage, the expanding hematoma contained within Gerota fascia will tend to extend:
a
across the midline into Gerota fascia surrounding the left (contralateral) kidney.
b
downward into the pelvis.
c
upward into the thorax.
d
anterolaterally, deep to the transversalis fascia.
e
anterolaterally, between the peritoneum and transversalis fascia.
B.
The first branch segmental artery from the main renal artery is typically the:
a
apical anterior segmental artery.
b
lower anterior segmental artery.
c
posterior segmental artery.
d
upper anterior segmental artery.
e
middle anterior segmental artery.
C. posterior branch

4
During pyeloplasty, the posterior segmental renal artery is inadvertently divided. This will produce:
a
no effect on the kidney.
b
ischemic loss of a large posterior segment of the renal parenchyma.
c
ischemic loss of a small posterior segment of the renal parenchyma.
d
ischemic loss of a segment of upper pole renal parenchyma.
e
ischemic loss of a segment of lower pole renal parenchyma.
b

The sequential branches of the renal artery are, in order, the:
a
segmental, interlobar, arcuate, interlobular, and afferent arteriole.
b
segmental, interlobular, arcuate, interlobar, and afferent arteriole.
c
segmental, subsegmental, interlobar, interlobular, arcuate, and afferent arteriole.
d
segmental, arcuate, interlobar, interlobular, and afferent arteriole.
e
segmental, interlobar, interlobular, arcuate, and afferent arterio
a

48
The most common renal vascular anomaly is a:
a
supernumerary left renal artery.
b
supernumerary right renal artery.
c
supernumerary left renal vein coursing anterior to the aorta.
d
supernumerary left renal vein coursing posterior to the aorta.
e
supernumerary right renal vein.
A
After involvement of lymph nodes directly at the renal hilum, the primary lymph node drainage site for the left kidney is:
a
the left lateral para-aortic lymph nodes.
b
the interaortocaval lymph nodes.
c
the right paracaval lymph nodes.
d
the left retrocrural lymph nodes.
e
all of the above.
A-
In a typical human kidney, there are approximately how many renal papillae and corresponding minor calyces?
a
3 to 5
b
7 to 9
c
11 to 12
d
14 to 15
e
17 to 18
B
51
A compound renal papilla and calyx:
a
is protective against ascending infection.
b
is least common at the upper pole of the kidney.
c
is a rare finding.
d
is commonly associated with formation of kidney stones.
e
is none of the above.
E.

The ureteral smooth muscle consists of:
a
a single layer of longitudinally oriented muscle bundles.
b
a single layer of circular and obliquely oriented muscle bundles.
c
a single layer of randomly oriented muscle bundles.
d
two layers—an inner layer of longitudinal muscle and an outer layer of circular and oblique muscle.
e
two layers—an inner layer of circular and oblique muscle and an outer layer of longitudinal muscle.
d
The ureter receives its blood supply from the:
a
renal artery.
b
aorta.
c
common iliac artery.
d
gonadal artery.
e
all of the above.
e

An invasive transitional cell carcinoma is diagnosed in the left proximal ureter, at the level of the third lumbar vertebral body. The primary site of potential nodal metastases from this lesion will be the:
a
left para-aortic lymph nodes.
b
interaortocaval lymph nodes.
c
left common iliac lymph nodes.
d
lymph nodes at the left renal hilum.
e
left external iliac lymph nodes.
a
During surgical dissection, the ureter can be identified as it enters the pelvis:
a
at the aortic bifurcation.
b
crossing the superior border of the sacrum.
c
crossing the common iliac artery at the branching of the internal iliac artery.
d
crossing the uterine artery.
e
at the internal inguinal ring.
c
A young man with right-sided abdominal pain is diagnosed with right hydroureteronephrosis by renal ultrasonography. Which of the following inflammatory processes might impinge on the right ureter and cause obstruction?
a
Acute appendicitis
b
Crohn ileitis
c
Perforated cecal carcinoma
d
All of the above
d
Narrowing of the ureteral luminal caliber naturally occurs at:
a
the ureteropelvic junction.
b
the crossing of the iliac vessels.
c
the ureterovesical junction.
d
all of the above.
e
none of the above.
D

Sympathetic nerve input to the kidney typically travels through:
a
the celiac plexus.
b
the superior mesenteric plexus.
c
the superior hypogastric plexus.
d
the inferior hypogastric plexus.
e
none of the above.
a- the kidneys receive preganglionic sympathetic input from the eight thoracic through the first lumbar segements. Postganglionic fibers arise from the celiac and aorticorenal ganglia
Ureteral peristalsis requires:
a
intact sympathetic input.
b
intact parasympathetic input.
c
both sympathetic and parasympathetic input.
d
intact spinal cord.
e
intrinsic smooth muscle pacemakers in the renal collecting system.
e


