Structure and Function of the Brain Flashcards
(89 cards)
What is the brain?
Part of the CNS within the skull cavity
What are the three main components of the brain?
- Forebrain (from prosencephalon)
- Midbrain (from mesencephalon)
- Hindbrain (from rhombencephalon)
What does the forebrain form?
- cerebral hemispheres and deep structures

What does the midbrain form?
Brainstem

What does the hindbrain form?
- brainstem, pons, medulla and cerebellum

Describe the inferior surface of the forebrain
ventral surface

Describe the anterior surface of the forebrain
dorsal surface

What is the ventral surface in the brainstem?
anterior surface
What is the dorsal surface in the brainstem?
posterior surface
Rostral =
- anything toward anterior pole of the forebrain
Caudal =
- anything toward the inferior pole of the spinal cord
Coronal section =
- cuts through the brain from superior to inferior

Horizontal/axial section =
- cuts through the brain parallel to the ground

Sagittal Section =
- cuts through the brain from anterior to posterior

Midsagittal section =
separates the two hemispheres
Gray matter =
- any collection of neuronal cell bodies
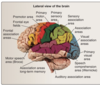
Describe the gray mater in the brain
Found in cortical layer (cortex) on the surface of the forebrain and cerebellum. Large surface area due to grooves (sulci) and ridges (gyri) developing overtime. Can also be found in deep structures of the forebrain, the basal ganglia, and structures of the limbic system

White matter =
consists of fibre tracts and is found deep to the cortical gray matter in the brain
Nucleus =
a collection of nerve cell bodies within the CNS
What is a collection of nerve cell bodies in the peripheral nervous system?
a ganglion
How are white and gray matter arranged in the spinal cord?
- gray matter is located centrally and surrounded by white matter

What is a tract/nerve?
a bundle of axons – mostly myelinated and appear white in colour
What comprises the forebrain?
- Telencephalon and diencephalon

Where is forebrain derived from?
- Derived from the most rostral parts of the developing neural tube