Cranial Nerves - Parasympathetic Function Flashcards
(13 cards)
What is Horner’s syndrome?
- Ptosis (drooping) of the upper eyelid
- Pupillary constriction (miosis)
- Anhydrosis (lack of sweating)
- Flushing of the face
**unopposed PSNS activity due to damage to the sympathetic chain on that side of the face
What is the nucleus of the oculomotor nerve? And where is it located?
- Autonomic nucleus (Edinger-Westphall)
- In midbrain
Where do the afferents of the oculomotor nerve run?
- Afferents from cortex and pretectal nucleus, bilaterally
- Interpeduncular fossa
- Between superior cerebellar and posterior cerebral arteries
- On the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus o Through superior orbital fissure
- Enters orbit
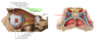
What does the superior ramus of the oculomotor nerve contain?
contains motor fibres to levator palpebra superoioris as well as sympathetic fibres from superior cervical ganglion to the same muscle
What do short ciliary nerves run along side? What do they enter? And what do they supply?
- alongside long ciliary nerves and ciliary artery
- Enter the eyeball
- Supply ciliary muscle and sphincter pupilla

What are the main aspects involved in the light reflex?
- Optic Nerve
- Optic tract
- Pretectal area: Pretectal nucleus
- Edinger-Westphal BILATERALLY (posterior commissure)
- Oculomotor nerve
- Ciliary ganglion
- Short ciliary nerves
- Pupillary constrictor

What occurs when there is injury to the oculomotor nerve?
- No parasympathetic input for pupil constriction –> Dilated pupil
- Loss of motor innervation to levator palpebrae superioris –> Ptosis
- Loss of motor innervation to extraocular muscles except superior oblique and lateral rectus the eye –> turns downwards and outwards

What is the PSNS aspect of the facial nerve?
- Superior salivatory nucleus
What is the course of the facial nerve?
- In pons
- Exits brainstem at pontocerebellar angle
- Enters internal acoustic meatus
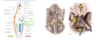
Describe the supply of the lacrimal gland by the facial nerve
- Parasympathetics are found in N. intermedius
- Through facial canal
- Greater petrosal nerve
- Joins deep petrosal in foramen lacerum
- Nerve of pterygoid canal
- Through pterygoid canal
- Synapse at pterygopalatine ganglion
- Zygomatic nerve of maxillary division (V2)
- Lacrimal branch of ophthalmic division (V1) –> Lacrimal gland

Describe the PSNS innervation of the salivry glands by the facial nerve
- Lingual nerve carries parasympathetic secretomotor supply to the submandibular and sublingual glands
- Synapse at submandibular ganglion

What is the PSNS nucleus of the glossopharyngeal nerve?
Inferior salivatory nucleus

Overview of the PSNS, secretomotor supply to the salivary glands



