Cranial Nerves - Sensorimotor Function Flashcards
(90 cards)
How many cranial nerves are there and where do they arise from?
12 pairs of cranial nerves arise from the cerebrum or brain stem
How is the nuclei of the cranial nerves laid out?
Their nuclei are essentially laid out from medial to lateral in the brainstem and sequentially, longitudinally in the midbrain, pons and medulla
What are the motor modalities of the cranial nerves?
somatic efferent, special visceral efferent to muscles derived from brachial arch, general visceral efferent (parasympathetic)
What are the sensory modalities of the cranial nerves?
somatic efferent, special visceral afferent (smell and taste), general visceral afferent, special somatic afferent (sight, hearing and balance)
What do the cranial nerves pass through?
foramina on cranial bones
What is the function of the cranial nerves? And what nerve is the exception to this?
With the exception of vagus, all cranial nerves innervate structures of the head and neck


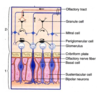
What area is referred to as the olfactory region?
The upper third of the nasal cavity (superior nasal concha, roof od the nasal cavity and nasal septum)
Where do the olfactory nerves pass through? And what is it anchored by?
Olfactory nerves pass through the cribriform plate, where they are anchored by dura mater and synapse at the olfactory bulb
What do axons of the neurons in the olfactory bulb form?
olfactory tract
Where does the olfactory tract project to?
Projects to the olfactory cortex FIRST and then to the limbic system, hypothalamus and reticular formation for visceral and behavioural responses to odours
What is Anosmia? And what is likely to cause this clinical condition?
- Olfactory neuropathy caused by upper respiratory tract infections (loss of sense of smell)
- Trauma, causing the brain and olfactory bulb to move may tear the olfactory nerves
- Fractures of the cribriform plate may cause CSF rhinorrhoea (blood stained CSF leaking from the nose)
What is unqiue about the basal cells of the olfactory region?
- Basal cells can differentiate to bipolar (olfactory neurons)
- Regeneration in adult humans
What is unique about the special sense olfaction?
Only sense that travels to the cortical field prior to thalamus
What is the largest cranial nerve and what are its main divisions?
- The largest cranial nerve = Trigeminal Nerve
- Has three divisions: V1, V2 and V3
- V1 and V2 are afferent only
- V3 is both afferent and efferent
What is the function of the trigeminal nerve?
Supplies general, conscious sensation to much of the face, head and associated orbital, nasal and oral cavities
How many nuclei does the trigeminal nerve have?
- Has 4 nuclei (and 2 roots)
- Sensory roots: to mesencephalic nucleus, principle (pontine) nucleus, spinal nucleus
- Motor root: from motor nucleus

Where do the sensory and motor roots of the trigeminal nerve emerge?
the mid-pons and run towards the trigeminal ganglion
What emerges from the trigeminal ganglion?
- Three divisions of the trigeminal nerve
- V1 = opthalmic division
- V2 = maxillary division
- V3 = mandibular division

What is the course of CN V1
lateral wall of the cavernous sinus –> superior orbital fissure –> orbit
What is the course of CN V2
Lateral wall of cavernous sinus –> foramen rotundum –>
pterygopalatine fossa
What is the course of CN V3
foramen ovale –> infratemporal fossa
Describe the opthalmic nerve
- Sensory division only
- Picks up sympathetic fibres from the carotid plexus
- Gives off meningeal branch near trigeminal ganglion that supplies dura

What are the three branches of the opthalmic nerve?
o Lacrimal
o Frontal
o Nasocillary


























