Neuroanatomy Revision Flashcards
(26 cards)
Describe the organisation of the gray matter in the spinal cord
H-shaped, contains neuron cell bodies within ‘horns’
What is contained within each of the horns of the gray matter of the spinal cord?
- Dorsal/posterior horns → cell bodies of interneurons
- Lateral horns → visceral (autonomic) motor cell bodies (T1-L2 segments)
- Ventral/anterior horns → somatic motor cell bodies
Draw a diagram showing the organisation of the spinal cord

Describe the organisation of white matter in the spinal cord
olumns containing a number of ascending and descending tracts (axons). All tracts are paired and most decussate
What are the three columns of the white matter of the spinal cord?
- Ventral (anterior) columns
- Lateral columns
- Dorsal (posterior) columns
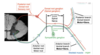
Draw a diagram showing how a spinal nerve functions
Describe C1 cervical nerve
passes above C1 vertebra
Motor only; no sensory fibres
Where does C8 spinal nerve pass?
Between C7 and T1
Where does the spinal cord end?
L1/2
Where are the cell bodies of the SNS distributed?
- Cell bodies in lateral horn of T1-L2 segments
- Postganglionic cell bodies lie in paravertebral sympathetic ganglia
- Ganglia interconnected by the sympathetic chain
Where are the cell bodies of the PSNS distributed?
Cell bodies in midbrain and S2-4 segments
where do sympathetic trunks extend between?
Each sympathetic trunk (chain) extends between the atlas and coccyx
What is Horner’s Syndrome?
Damage to the sympathetic nerves of the face
Mitosis (constriction), Ptosis and Anydrosis of the side of the face that is affected
What is the action of stimulants of the SNS?
- Increase BP
- Increase pulse rate
- Relax bronchioles
- Dilates pupils
- Relax uterine muscles
- Increase blood sugar
What is the action of stimulants of the PSNS?
- Decrease BP
- Decrease pulse rate
- Constricts bronchioles
- Constrict pupils
- Increase urinary contraction
- Increase peristalsis
- Increase muscle tone (indirect action)
What is the action of depressants of the SNS?
- Decrease PR
- Decrease BP
- Constrict bronchioles
What is the action of depressants of the PSNS?
- Increase PR
- Decrease mucous secretions
- Decrease GI motility
- Increase urinary retention
- Dilate pupils
What spinal cord segment is the knee reflex?
L3/4
What is the spinal cord segment of the ankle reflex?
S1
How is the L5 spinal cord segment tested?
Extension of big toe
Why is the great anterior medullary artery of Adamkiewz important? and where does it arise from?
- arises from the aorta in the lower thoracic or lumbar vertebral levels
- It may be the major source of blood to the lower two-thirds of the spinal cord
Where does the internal venous plexus lie and what are its properties?
- Lies in the epidural/extradural space (between the dura and vertebrae)
- Do not have valves and pressure gradients permit blood flow
- Communicates with cranial dural venous sinuses and pelvic veins → infection and metastasis spread

What are the characteristics of an UMN lesion?
- Hypertonia (spasticity)
- Hyperreflexia
- Abnormal reflex (positive Babinski sign unless younger than 6 months old)
What are the characteristics of a LMN lesion?
- Hypotonia/Flaccidity
- Hyporeflexia/areflexia
- Fasciculations
- Atrophy/wasting of muscles


