STROKES Flashcards
label angiogram


Stroke
The damaging or killing of brain cells starved of oxygen as a result of the blood supply to part of the brain being cut off
TIA (Transient Ischaemic Attack)
A stroke that recovers within 24 hours from the onset of symptoms
Stroke Syndrome
Constellation of signs and symptoms produced due to occlusion or damage of an artery supplying part of the brain
2 main types of stroke? how do u know what type it is?
u wont know, cuz they present the same way!
until u get a CT scan

if young patients had a stroke, what things would u take into acount?
- Vasculitis
- Sickle cell anaemia
- Cocaine (coke stroke)
where has blood clot come from?

circle of willis
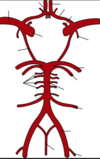

where do vertaberal arteries branch off?
describe course
vertebral arteries arise from the subclavian A., one on each side of the body, then enter deep to the transverse process at the level of the 6th cervical vertebrae
(skips 7th!)
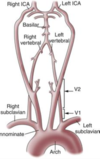
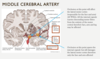
- Anterior circulation come from___________arteries
- Posterior circulation comes from__________arteries
anything off the carotid artery is part of the ANTERIOR circulation!

when assessing STROKE SYNDROMES …
• 4 QUESTIONS:
– 1. What artery has been affected?
– 2. What area of the brain does it supply?
– 3. What does this part of the brain do?
– 4. How will the patient present if these areas are damaged?
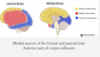
anterior cerebral artery
What area of the brain does it supply?
What does this part of the brain do?
How will the patient present?

Initially flaccid paralysis, then over time, once that loss of descending inhibition takes over>> u get spasticity and UMN signs!
Spasticity is a condition in which certain muscles are continuously contracted.

what area of brain has a role in Role in voluntary control of micturition? which A. supplies it?
PARACENTRAL LOBULES
area in medial cortex!
one of the higher cortical centers that allows u to suppress micturition

explain split-brain syndrome

Alien-hand syndrome
The feeling that one’s hand is possessed by a force outside of one’s control.
The syndrome typically arises after trauma to the brain, after brain surgery or after a stroke or an infection of the brain.
A person with the alien hand syndrome can feel sensation in the affected hand but thinks that the hand is not part of their body and that they have no control over its movement, that it belongs to an alien.